
Algae are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.

The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta, are a clade of algae.
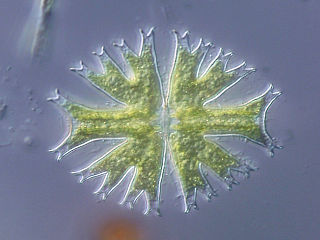
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids, are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional.

The green algae are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.

The International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants". It was formerly called the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN); the name was changed at the International Botanical Congress in Melbourne in July 2011 as part of the Melbourne Code which replaced the Vienna Code of 2005.

Ornamental grasses are grasses grown as ornamental plants. Ornamental grasses are popular in many colder hardiness zones for their resilience to cold temperatures and aesthetic value throughout fall and winter seasons.

Tridacna is a genus of large saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the subfamily Tridacninae, the giant clams. Many Tridacna species are threatened. They have heavy shells, fluted with 4 to 6 folds. The mantle is often brightly coloured. They inhabit shallow waters of coral reefs in warm seas of the Indo-Pacific region. These clams are popular in marine aquaria, and in some areas, such as the Philippines, members of the genus are farmed for the marine aquarium trade. They live in symbiosis with photosynthetic algae (zooxanthellae). Some species are eaten by humans.

William Henry Harvey, FRS FLS was an Irish botanist and phycologist who specialised in algae.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species, and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.

Vanvoorstia bennettiana was an extinct red algae from Australia. It is named after naturalist George Bennett.
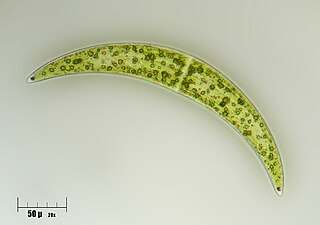
The Closteriaceae are one of four families of Charophyte green algae in the order Desmidiales (desmids). It contains two genera, Closterium and Spinoclosterium.
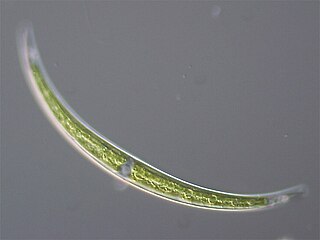
Closterium is a genus of desmid, a group of charophyte green algae. It is placed in the family Closteriaceae. Species of Closterium are a common component of freshwater microalgae flora worldwide.

Cosmarium is a genus of freshwater organisms belonging to the Charophyta, a division of green algae from which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged.
Spinoclosterium is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Closteriaceae. It is rare, but widely distributed in freshwater regions throughout the world.

The green ormer is a northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean species of sea snail, a coastal marine gastropod mollusc in the family Haliotidae, the abalones or ormer snails.

Zygnematophyceae is a class of green algae in the paraphylum streptophyte algae, also referred to as Charophyta, consisting of more than 4000 described species. The Zygnematophyceae are the sister clade of the Embryophyta.

George Henry Kendrick Thwaites was an English botanist and entomologist.

Paspalum setaceum is a species of grass known by several common names, including thin paspalum. It is native to the Americas, where it can be found in the eastern and central United States, Ontario in Canada, Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. It can be found in other areas of the world as an introduced, and often invasive, species, including many Pacific Islands. It is a weed of lawns and turf.
C. ehrenbergii may refer to:

Trichostema setaceum is an herbaceous flowering plant. Commonly referred to as narrowleaf bluecurls, it is in the Lamiaceae. It grows in sandy soil, sandhills, and rocky uplands.
















