
Chad is one of the 47 landlocked countries in the world and is located in North Central Africa, measuring 1,284,000 square kilometers (495,755 sq mi), nearly twice the size of France and slightly more than three times the size of California. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometer in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. (Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti) desert region, which itself is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is the largest country of sub-Saharan Africa, occupying some 2,344,858 square kilometres (905,355 sq mi). Most of the country lies within the vast hollow of the Congo River basin. The vast, low-lying central area is a plateau-shaped basin sloping toward the west, covered by tropical rainforest and criss-crossed by rivers. The forest center is surrounded by mountainous terraces in the west, plateaus merging into savannas in the south and southwest. Dense grasslands extend beyond the Congo River in the north. High mountains of the Ruwenzori Range are found on the eastern borders with Rwanda and Uganda.

The Republic of Equatorial Guinea is located in west central Africa. Bioko Island lies about 40 kilometers (24.9 mi) from Cameroon. Annobón Island lies about 595 kilometres (370 mi) southwest of Bioko Island. The larger continental region of Río Muni lies between Cameroon and Gabon on the mainland; it includes the islands of Corisco, Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, and adjacent islets. The total land area is 28,051 km2 (10,831 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 303,509 km2 (117,185 sq mi).
Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea.

Nigeria is a country in West Africa, it shares land borders with the Republic of Benin to the west, Chad and Cameroon to the east, and Niger to the north. Its coast lies on the Gulf of Guinea in the south and it borders Lake Chad to the northeast. Notable geographical features in Nigeria include the Adamawa Plateau, Mambilla Plateau, Jos Plateau, Obudu Plateau, the Niger River, Benue River, and Niger Delta.

Sri Lanka, formerly called Ceylon, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean, southeast of the Indian subcontinent, in a strategic location near major sea lanes. The nation has a total area of 65,610 square kilometres (25,330 sq mi), with 64,630 square kilometres (24,950 sq mi) of land and 980 square kilometres (380 sq mi) of water. Its coastline is 1,340 kilometres (830 mi) long. The main island of Sri Lanka has an area of 65,268 km2; it is the twenty-fifth largest island in the world by area. Dozens of offshore islands account for the remaining 342 km2 area. The largest offshore island, Mannar Island, is linked to Adam's Bridge, a land connection to the Indian mainland, which is now mostly submerged with only a chain of limestone shoals remaining above sea level. According to temple records, this natural causeway was formerly whole, but was breached by a violent storm in 1480. The formation is also known as Rama's Bridge, as according to Hindu mythology, it was constructed during the rule of Lord Rama.

Thailand is in the middle of mainland Southeast Asia. It has a total size of 513,120 km2 (198,120 sq mi) which is the 50th largest in the world. The land border is 4,863 km (3,022 mi) long with Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos and Malaysia. The nation's axial position influenced many aspects of Thailand's society and culture. It controls the only land route from Asia to Malaysia and Singapore. It has an exclusive economic zone of 299,397 km2 (115,598 sq mi).

Zimbabwe is a landlocked country in southern Africa lying north of the Tropic of Capricorn. During summer, the whole country experiences warm temperatures as a result of the sun being directly overhead. It straddles an extensive high inland plateau that drops northwards to the Zambezi valley where the border with Zambia is and similarly drops southwards to the Limpopo valley and the border with South Africa. The country has borders with Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 km and almost meets Namibia at its westernmost point. The highest point is at 2 592m

Libreville is the capital and largest city of Gabon. Occupying 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi) in the northwestern province of Estuaire, Libreville is a port on the Komo River, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.

South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).
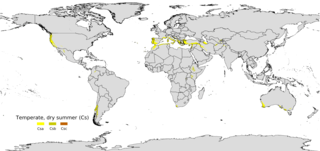
A Mediterranean climate, also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen as Cs, is a climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes, characterized by warm to hot, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the majority of Mediterranean-climate regions and countries, but remain highly dependent on proximity to the ocean, altitude and geographical location.

Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the coolest month, and feature hot temperatures all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates.

The South Region is located in the southwestern and south-central portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the East Region, to the north by the Centre Region, to the northwest by the Littoral Region, to the west by the Gulf of Guinea, and to the south by the countries of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Congo. The South occupies 47,720 km2 of territory, making it the fourth largest region in the nation. The major ethnic groups are the various Beti-Pahuin peoples, such as the Ewondo, Fang, and Bulu.
The Adamawa Region is a constituent region of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Centre and East regions to the south, the Northwest and West regions to the southwest, Nigeria to the west, the Central African Republic (CAR) to the east, and the North Region to the north.

The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The temperate counterpart to the tropical dry season is summer or winter.

The wet season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least a month. The term green season is also sometimes used as a euphemism by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the tropics and subtropics.

Trinidad, Kimsantin officially La Santísima Trinidad, is a city in Bolivia, capital of the department of Beni. The population is 130,000. While historically a peripheral city in Bolivia, Trinidad is today an important center for the Bolivian Bovine industry and has enjoyed a modest economic boom in recent years and enjoys an HDI index of above 0.700.

Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories Aw and As. The driest month has less than 60 mm (2.4 in) of precipitation and also less than mm of precipitation.
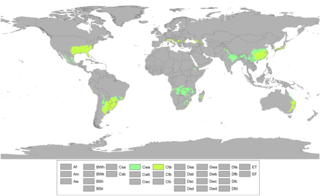
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.
Climate change in Guam encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. territory of Guam.






















