Related Research Articles

The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old, it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints.
The cloudinids, an early metazoan family containing the genera Acuticocloudina, Cloudina and Conotubus, lived in the late Ediacaran period and became extinct at the base of the Cambrian. They formed millimetre-scale conical fossils consisting of calcareous cones nested within one another; the appearance of the organism itself remains unknown. The name Cloudina honors the 20th-century geologist and paleontologist Preston Cloud.

Rodinia was a Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.1–0.9 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. Valentine & Moores 1970 were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by McMenamin & McMenamin 1990 who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent.

An exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton (endoskeleton) of, for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of animals with exoskeletons include insects such as grasshoppers and cockroaches, and crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters, as well as the shells of certain sponges and the various groups of shelled molluscs, including those of snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus. Some animals, such as the tortoise, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton.

Dickinsonia is an extinct genus of fossils of the Ediacaran biota. The individual Dickinsonia typically resembles a bilaterally symmetrical ribbed oval. Its affinities are presently unknown; its mode of growth is consistent with a bilaterian affinity, though some have suggested that it belongs to the fungi, or even an "extinct kingdom". The discovery of cholesterol molecules in fossils of Dickinsonia lends support to the idea that Dickinsonia was an animal.

Charles Doolittle Walcott was an American paleontologist, administrator of the Smithsonian Institution from 1907 to 1927, and geologist. He is famous for his discovery in 1909 of well-preserved fossils, including some of the oldest soft-part imprints, in the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada.

Foraminifera are members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment, while a smaller variety float in the water column at various depths. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA.

Biomineralization, or biomineralisation is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often to harden or stiffen existing tissues. Such tissues are called mineralized tissues. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon; all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that are able to form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds. Organisms have been producing mineralised skeletons for the past 550 million years. Ca carbonates and Ca phosphates are usually crystalline, but silica organisms (sponges, diatoms...) are always non crystalline minerals. Other examples include copper, iron and gold deposits involving bacteria. Biologically-formed minerals often have special uses such as magnetic sensors in magnetotactic bacteria (Fe3O4), gravity sensing devices (CaCO3, CaSO4, BaSO4) and iron storage and mobilization (Fe2O3•H2O in the protein ferritin).
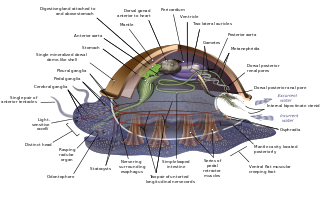
The evolution of the molluscs is the way in which the Mollusca, one of the largest groups of invertebrate animals, evolved. This phylum includes gastropods, bivalves, scaphopods, cephalopods, and several other groups. The fossil record of mollusks is relatively complete, and they are well represented in most fossil-bearing marine strata. Very early organisms which have dubiously been compared to molluscs include Kimberella and Odontogriphus.
Namacalathus is a problematic metazoan fossil occurring in the latest Ediacaran. The first, and only described species, N. hermanastes, was first described in 2000 from the Nama Group of central and southern Namibia.

Andrew Herbert Knoll is the Fisher Professor of Natural History and a Professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Harvard University. Born in West Reading, Pennsylvania in 1951,Andrew Knoll graduated from Lehigh University with a bachelor of arts in 1973 and received his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1977 for a dissertation entitled "Studies in Archean and Early Proterozoic Paleontology." Knoll taught at Oberlin College for five years before returning to Harvard as a professor in 1982. At Harvard, he serves in the departments of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology and Earth and Planetary Sciences.
Namapoikia rietoogensis is among the earliest known animals to produce a calcareous skeleton. Known from the Ediacaran period, before the Cambrian explosion of calcifying animals, the long-lived organism grew up to a metre in diameter and resembles a colonial sponge. It was an encruster, filling vertical fissures in the reefs in which it originally grew.

The Ediacaranbiota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period. These were composed of enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms.
Mark A. S. McMenamin is an American paleontologist and professor of geology at Mount Holyoke College. He has contributed to the study of the Cambrian explosion and the Ediacaran biota.

A calcite sea is one in which low-magnesium calcite is the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate. An aragonite sea is the alternate seawater chemistry in which aragonite and high-magnesium calcite are the primary inorganic carbonate precipitates. The Early Paleozoic and the Middle to Late Mesozoic oceans were predominantly calcite seas, whereas the Middle Paleozoic through the Early Mesozoic and the Cenozoic are characterized by aragonite seas ).

An aragonite sea contains aragonite and high-magnesium calcite as the primary inorganic calcium carbonate precipitates. The chemical conditions of the seawater must be notably high in magnesium content relative to calcium for an aragonite sea to form. This is in contrast to a calcite sea in which seawater low in magnesium content relative to calcium favors the formation of low-magnesium calcite as the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate.
The small shelly fauna, small shelly fossils (SSF), or early skeletal fossils (ESF) are mineralized fossils, many only a few millimetres long, with a nearly continuous record from the latest stages of the Ediacaran to the end of the Early Cambrian Period. They are very diverse, and there is no formal definition of "small shelly fauna" or "small shelly fossils". Almost all are from earlier rocks than more familiar fossils such as trilobites. Since most SSFs were preserved by being covered quickly with phosphate and this method of preservation is mainly limited to the Late Ediacaran and Early Cambrian periods, the animals that made them may actually have arisen earlier and persisted after this time span.
The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.
The fossils of the Burgess Shale, like the Burgess Shale itself, formed around 505 million years ago in the Mid Cambrian period. They were discovered in Canada in 1886, and Charles Doolittle Walcott collected over 60,000 specimens in a series of field trips up from 1909 to 1924. After a period of neglect from the 1930s to the early 1960s, new excavations and re-examinations of Walcott's collection continue to discover new species, and statistical analysis suggests discoveries will continue for the foreseeable future. Stephen Jay Gould's book Wonderful Life describes the history of discovery up to the early 1980s, although his analysis of the implications for evolution has been contested.
The Walcott–Rust quarry, in Herkimer County, New York, is an excellent example of an obrution Lagerstätte. Unique preservation of trilobite appendages resulted from early consolidation (cementation) of the surrounding rock, followed by spar filling of the interior cavity within the appendages. The presence of so many well preserved trilobites in one location alone qualifies the beds as an exceptional trilobite site, but the beds are further distinguished as the source of the first trilobites for which appendages were definitively described.
References
- ↑ Porter, S. M. (Jun 2007). "Seawater chemistry and early carbonate biomineralization". Science. 316 (5829): 1302. Bibcode:2007Sci...316.1302P. doi:10.1126/science.1137284. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17540895.
- ↑ Walcott, C. D. (1889). "Stratigraphic position of the Olenellus fauna in North America and Europe". American Journal of Science . 37 (223): 388–9. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-38.223.29.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek E. G.; Crowther, Peter R. (2008). Palaeobiology II. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780470999288.
- ↑ McMenamin, M.A.; McMenamin, D.L. (1990). The Emergence of Animals . Columbia University Press. pp. 52–53. ISBN 0-231-06647-3.
| This article related to the Cambrian period is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |