Bile, or gall, is a yellow-green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, produced continuously by the liver, and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After a human eats, this stored bile is discharged into the first section of the small intestine.

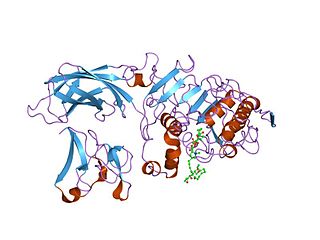
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-soluble enzyme that hydrolyzes triglycerides in lipoproteins, such as those found in chylomicrons and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), into two free fatty acids and one monoacylglycerol molecule:

Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.

Perilipin, also known as lipid droplet-associated protein, perilipin 1, or PLIN, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the PLIN gene. The perilipins are a family of proteins that associate with the surface of lipid droplets. Phosphorylation of perilipin is essential for the mobilization of fats in adipose tissue.

Hormone-sensitive lipase (EC 3.1.1.79, HSL), also previously known as cholesteryl ester hydrolase (CEH), sometimes referred to as triacylglycerol lipase, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the LIPE gene, and catalyzes the following reaction:

Hepatic lipase (HL), also called hepatic triglyceride lipase (HTGL) or LIPC (for "lipase, hepatic"), is a form of lipase, catalyzing the hydrolysis of triacylglyceride. Hepatic lipase is coded by chromosome 15 and its gene is also often referred to as HTGL or LIPC. Hepatic lipase is expressed mainly in liver cells, known as hepatocytes, and endothelial cells of the liver. The hepatic lipase can either remain attached to the liver or can unbind from the liver endothelial cells and is free to enter the body's circulation system. When bound on the endothelial cells of the liver, it is often found bound to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG), keeping HL inactive and unable to bind to HDL (high-density lipoprotein) or IDL (intermediate-density lipoprotein). When it is free in the bloodstream, however, it is found associated with HDL to maintain it inactive. This is because the triacylglycerides in HDL serve as a substrate, but the lipoprotein contains proteins around the triacylglycerides that can prevent the triacylglycerides from being broken down by HL.

Gastric lipase, also known as LIPF, is an enzymatic protein that, in humans, is encoded by the LIPF gene.

Bile salt-dependent lipase, also known as carboxyl ester lipase is an enzyme produced by the adult pancreas and aids in the digestion of fats. Bile salt-stimulated lipase is an equivalent enzyme found within breast milk. BSDL has been found in the pancreatic secretions of all species in which it has been looked for. BSSL, originally discovered in the milk of humans and various other primates, has since been found in the milk of many animals including dogs, cats, rats, and rabbits.

Non-specific lipid-transfer protein also known as sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2) or propanoyl-CoA C-acyltransferase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCP2 gene.
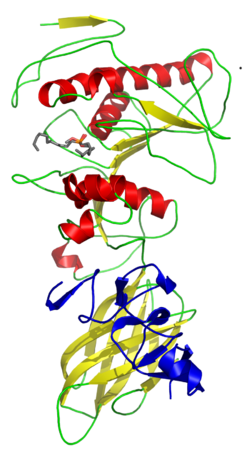
In molecular biology the PLAT domain is a protein domain that is found in a variety of membrane or lipid associated proteins. It is called the PLAT domain or LH2 domain. The known structure of pancreatic lipase shows this domain binds to procolipase Pfam PF01114, which mediates membrane association.

Phospholipase A2, group 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLA2G1B gene.
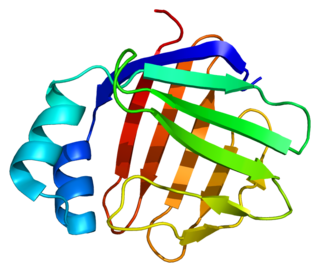
Fatty acid binding protein 6, ileal (gastrotropin), also known as FABP6, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FABP6 gene.

Adipose triglyceride lipase, also known as patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 2 and ATGL, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PNPLA2 gene. ATGL catalyses the first reaction of lipolysis, where triacylglycerols are hydrolysed to diacylglycerols.

Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP2 gene.

Triglyceride lipases are a family of lipolytic enzymes that hydrolyse ester linkages of triglycerides. Lipases are widely distributed in animals, plants and prokaryotes.

Phospholemman (PLM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXYD1 gene.

Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 7 also known as alkaline sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (Alk-SMase) or intestinal alkaline sphingomyelinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENPP7 gene.

CYP8B1 also known as sterol 12-alpha-hydroxylase is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CYP8B1 gene.

In biochemistry, lipase refers to a class of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms.

ANGPTL8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C19orf80 gene.