Related Research Articles

Chamaecyparis, common names cypress or false cypress, is a genus of conifers in the cypress family Cupressaceae, native to eastern Asia and to the western and eastern margins of the United States. The name is derived from the Greek khamai (χαμαί), meaning "on the earth", and kuparissos (κυπάρισσος) for "cypress".

Chamaecyparis obtusa is a species of cypress native to central Japan in East Asia, and widely cultivated in the temperate northern hemisphere for its high-quality timber and ornamental qualities, with many cultivars commercially available.

Banksia obtusa, commonly known as shining honeypot, is a species of shrub that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has underground stems, linear pinnatifid leaves with triangular lobes on each side, cream-coloured to yellow flowers in heads of up to seventy, surrounded by dark reddish bracts and egg-shaped follicles.
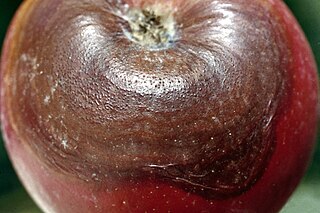
Botryosphaeria obtusa is a plant pathogen that causes frogeye leaf spot, black rot and cankers on many plant species. On the leaf it is referred to as frogeye leaf spot; this phase typically affects tree and shrubs. In fruit such as the apple, cranberry and quince, it is referred to as black rot, and in twigs and trunks it causes cankers.

The broad-tailed paradise whydah is a species of bird in the family Viduidae. It is found in woodland and acacia savanna habitat in Sub-Saharan Africa from Angola to Uganda, Tanzania and Mozambique. A brood parasite, it has a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed it as being of least concern.
Shorea obtusa, the Siamese sal, is a species of hardwood tree in the family Dipterocarpaceae, native to Southeast Asia.

Plumeria obtusa, the Singapore graveyard flower, is a species of the genus Plumeria (Apocynaceae). It is native to the Neotropics, but widely cultivated for its ornamental and fragrant flowers around the world, where suitably warm climate exists.

Chamaecyparis taiwanensis is a species of cypress, native to the mountains of Taiwan, where it grows at altitudes of 1300–2800 m.

Neverita is a genus of medium-sized to large sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Polinicinae of the family Naticidae, the moon snails

Azenia obtusa, the obtuse yellow moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1854. It is found in North America from southern Ontario and New York to Florida and west to Texas and Missouri.

Pelosia obtusa, the small dotted footman, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1847. It is found from central Europe through Asia to the Pacific Ocean.

Colobotheini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.

Colobothea is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.

Oreta obtusa is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India, China, Myanmar and Indonesia.
Colobothea olivencia is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bates in 1865. It is known from Brazil.
Colobothea unilineata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bates in 1872. It is known from Nicaragua and Panama.
Colobothea amoena is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Gahan in 1889. It is known from Brazil.
Colobothea andina is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Monné in 1993. It is known from Peru.
Colobothea cincticornis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Schaller in 1783.
Colobothea subcincta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Laporte in 1840. It is known from Brazil.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Colobothea obtusa. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.