
The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth longest river and the third longest in Asia. Its estimated length is 4,909 km (3,050 mi), and it drains an area of 795,000 km2 (307,000 sq mi), discharging 475 km3 (114 cu mi) of water annually. From the Tibetan Plateau the river runs through China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam. The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids and waterfalls in the Mekong make navigation difficult. Even so, the river is a major trade route between western China and Southeast Asia.
The Greater Mekong Sub-region Academic and Research Network (GMSARN) is a network of academic and research institutions in a Greater Mekong sub-region.

The Khmer National Armed Forces were the official armed defense forces of the Khmer Republic, a short-lived state that existed from 1970 to 1975, known today as Cambodia. The FANK was the successor of the Royal Khmer Armed Forces (FARK) which had been responsible for the defense of the previous Kingdom of Cambodia since its independence in 1953 from France.

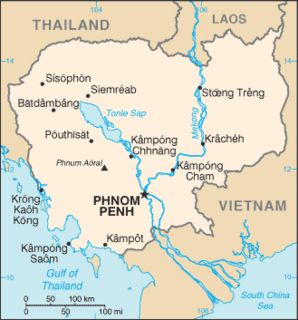
The largest of the ethnic groups in Cambodia are the Khmer, who comprise approximately 90% of the total population and primarily inhabit the lowland Mekong subregion and the central plains. The Khmer historically have lived near the lower Mekong River in a contiguous arc that runs from the southern Khorat Plateau where modern-day Thailand, Laos and Cambodia meet in the northeast, stretching southwest through the lands surrounding Tonle Sap lake to the Cardamom Mountains, then continues back southeast to the mouth of the Mekong River in southeastern Vietnam.
The Sihanouk Trail was a logistical supply system in Cambodia used by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and its Viet Cong (VC) guerillas during the Vietnam War (1960–1975). Between 1966 and 1970, this system operated in the same manner and served the same purposes as the much better known Ho Chi Minh Trail which ran through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos. The name is of American derivation, since the North Vietnamese considered the system integral to the supply route mentioned above. U.S. attempts to interdict this system began in 1969.
Operation Freedom Deal was a United States Seventh Air Force interdiction and close air support campaign waged in Cambodia between 19 May 1970 and 15 August 1973, as an expansion of the Vietnam War, as well as the Cambodian Civil War. Launched by Richard Nixon as a follow-up to the earlier ground invasion during the Cambodian Campaign, the initial targets of the operation were the base areas and border sanctuaries of the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and the Viet Cong (VC).
The East–West Economic corridor is an economic development program initiated in order to promote development and integration of 5 Southeast Asian countries, namely: Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and Vietnam. The concept was agreed upon in 1998 at the Ministerial Conference of the Greater Mekong Subregion, organized in Manila, the Philippines. This corridor became operational on December 12, 2006.

The Bassac River is a distributary of the Tonlé Sap and Mekong River. The river starts in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, and flows southerly, crossing the border into Vietnam near Châu Đốc. The name Bassac comes from the Khmer prefix “pa” added to sak (សក្តិ), a Khmer word borrowed from the Sanskrit “sakti” (शक्ति).

The Mekong–Ganga Cooperation (MGC) was established on November 10, 2000, at Vientiane, Laos at the First MGC Ministerial Meeting. It comprises six member countries, namely India, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. The four areas of cooperation are tourism, culture, education, and transportation. The organization takes its name from the Ganga and the Mekong, two large rivers in the region.

Cambodia has 612 km (380 mi) of 1,000 mm metre gauge rail network, consisting of two lines: one from the capital Phnom Penh to Sihanoukville, and another from Phnom Penh to Poipet on the Thai border. The lines were originally constructed during the time when the country was part of French Indochina, but due to neglect and damage from civil war during the latter half of the 20th century, the railways were in a dilapidated state and all services had been suspended by 2009. Through rehabilitation efforts by the Government of Cambodia, with funding from the Asian Development Bank, Australian Agency for International Development (AusAID) and Australian company Toll Holdings, freight and limited passenger service returned between Phnom Penh and Sihanoukville by 2016, and passenger service between Phnom Penh and Poipet was fully restored in 2019.

The Stung Treng Dam is a proposed hydroelectric dam on the Mekong River in Stung Treng Province, Cambodia. It would be located on the mainstream of the Lower Mekong River. The project is controversial for several reasons, including its possible impact on the fisheries, as well as other ecological and environmental factors.
The Xayaburi Dam is a run-of-river hydroelectric dam on the Lower Mekong River, approximately 30 kilometres (19 mi) east of Sainyabuli (Xayaburi) town in northern Laos. Commercial operation of the dam started in October 2019. The main purpose of the dam is to produce hydroelectric power, 95% of which is to be purchased by the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT). The project is surrounded in controversy due to complaints from downstream riparians and environmentalists. Preliminary construction began in early-2012, but work on the dam itself was suspended shortly thereafter due to complaints from Cambodia and Vietnam downstream. After making modifications to the dam's design, Laos started construction with a ceremony on 7 November 2012. The Xayaburi Dam is the first of the 11 dams planned on the lower Mekong.
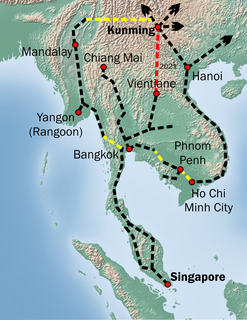
The Kunming–Singapore railway, increasingly called the Pan–Asia railway Network is a network of railways that connects China, Singapore and all the countries of mainland Southeast Asia. The concept originated with British and French imperialists, who sought to link the railways they had built in southwest China, Indochina and Malaya, but international conflicts in the 20th century kept regional railways fragmented. The idea was formally revived in October 2006 when 18 Asian and Eurasian countries signed the Trans-Asian railway Network Agreement, which incorporated the Kunming–Singapore railway into the Trans-Asian railway network.
This page describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Laos.
The 2015 Mekong Club Championship was the 2nd season of the Mekong Club Championship. Five teams entered as respective domestic league winners from Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam. The championship is sponsored by Toyota.
The 2016 Mekong Club Championship is the 3rd season of the Mekong Club Championship. The championship is sponsored by Toyota and will be played between October 2016 and January 2017 featuring teams from Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam.

Lanmei Airlines (Cambodia) Co., Ltd is a hybrid airline registered in Cambodia.
The 2017 Mekong Club Championship was the 4th season of the Mekong Club Championship. The championship was sponsored by Toyota and was played between December 2017 and January 2018 featuring teams from Cambodia, Laos, Thailand and Vietnam. This edition, the champions of 2017 Myanmar National League was absent from the tournament.

A small tree with tortuous twigs, Dillenia pentagyna is a member of the family Dilleniaceae, and is found from Sulawesi to South-Central China to India and Sri Lanka. Material from the tree has some minor uses.
Hydnocarpus saigonensis is a tree in the Achariaceae family. It is endemic to the Mekong basin of Cambodia and southern Vietnam.











