
Quorn is a small town and railhead in the Flinders Ranges in the north of South Australia, 39 kilometres (24 mi) northeast of Port Augusta.

Pichi Richi Railway is a 39 kilometres narrow-gauge heritage railway in the southern Flinders Ranges of South Australia between Quorn and Port Augusta. For much of its length the line lies in the picturesque Pichi Richi Pass, where the line was completed in 1879 as work proceeded north to build a railway to the "Red Centre" of Australia – the Central Australia Railway.
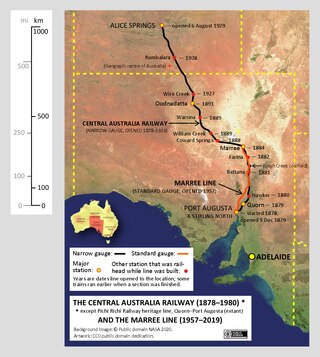
The former Central Australia Railway, which was built between 1878 and 1929 and closed in 1980, was a 1241 km (771 mi) 1067 mm narrow gauge railway between Port Augusta and Alice Springs. A standard gauge line duplicated the southern section from Port Augusta to Maree in 1957 on a new nearby alignment. The entire Central Australia Railway was superseded in 1980 after the standard gauge Tarcoola–Alice Springs Railway was opened, using a new route up to 200 km to the west. A small southern section of the original line between Port Augusta and Quorn has been preserved as the Pichi Richi Tourist Railway.

South Australian Railways (SAR) was the statutory corporation through which the Government of South Australia built and operated railways in South Australia from 1854 until March 1978, when its non-urban railways were incorporated into Australian National, and its Adelaide urban lines were transferred to the State Transport Authority.

The Steamtown Peterborough Railway Preservation Society Inc. was a not-for-profit incorporated society that operated a heritage steam railway from Peterborough, South Australia, north along a section of the Peterborough to Quorn railway line, between 1977 and 2002. The society based its operations on the former South Australian Railways roundhouse at Peterborough and purpose-built sheds and yard at Peterborough West.
Railmotor is a term used in the United Kingdom and elsewhere for a railway lightweight railcar, usually consisting of a railway carriage with a steam traction unit, or a diesel or petrol engine, integrated into it.

The Commonwealth Railways NC class consisted of two diesel-hydraulic locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Granville, New South Wales in 1956. The Lakewood Firewood Company, Kalgoorlie was the first owner; the Commonwealth Railways purchased them in 1965. They ceased revenue service in the early 1980s.

The Commonwealth Railways NSU class was a class of diesel-electric locomotives built in 1954 and 1955 by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company, England, for the Commonwealth Railways to be deployed on the narrow-gauge Central Australia Railway and North Australia Railway.

The NT class were a class of diesel-electric locomotives built between 1965 and 1968 by Tulloch Limited, Rhodes for the Commonwealth Railways. They saw service on the Central Australia Railway and North Australia Railway, and on the Port Lincoln Division of Australian National.

The Commonwealth Railways NM class locomotive was a class of 4-8-0 locomotives of the Commonwealth Railways, Australia. The class operated on 1,067 mm narrow gauge lines in South Australia and the Northern Territory.

The South Australian Railways T class was a class of 4-8-0 steam locomotives operated by the South Australian Railways. Several were sold to the Tasmanian Government Railways; some others operated on the Commonwealth Railways.

The Fyansford Cement Works Railway was an industrial railway near Geelong, Australia, built by the Australian Portland Cement Company to carry limestone from its quarry to its cement works at Fyansford.

The South Australian Railways W and Wx class was a class of 2-6-0 steam locomotives operated by the South Australian Railways. Some were used by the Commonwealth Railways in the Northern Territory and by contractors.

Port Augusta railway station is a rail station located on the Adelaide-Port Augusta railway line in Port Augusta, South Australia.

Quorn railway station was located on the Central Australia Railway, and also the Peterborough-Quorn railway line serving the South Australian town of Quorn.

The NDH class railcars are a class of self propelled diesel-hydraulic railcars designed by Commonwealth Engineering and built by the Gloucester Railway Carriage & Wagon Company in England for the Commonwealth Railways, Australia in 1954. They were known as Gloucester railcars.

The eight members of the South Australian Railways U class were the first narrow-gauge 1067 mm locomotives on the South Australian Railways and the first of many steam locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock and Company for the railway. They entered service in 1876: four on the Port Wakefield to Hoyleton line and four on the Port Pirie to Crystal Brook line. Subsequently they operated on the Port Wakefield, Port Pirie and Port Augusta lines.

The South Australian Railways O Class (2nd) locomotive was a 4-4-0WT built by Robert Stephenson and Company in 1868 for the Launceston and Western Railway Company. It entered service with the South Australian Railways in 1912 and was cut up in 1930.

The South Australian Railways K class (narrow gauge) comprised a single locomotive. The design, by South Australian Railways Locomotive Engineer William Thow, was very similar to that of the broad-gauge K class, but it was smaller and lighter. It was allocated number 52 within the sequence allocated to the larger locomotives.





















