
The clarinet is a type of single-reed woodwind instrument. Like many wind instruments, clarinets are made in several different sizes, each having its own range of pitches. All have a nearly-cylindrical bore and a flared bell, and utilize a mouthpiece with a single reed. A person who plays a clarinet is called a clarinetist.

The recorder is a family of woodwind musical instruments in the group known as internal duct flutes: flutes with a whistle mouthpiece, also known as fipple flutes. A recorder can be distinguished from other duct flutes by the presence of a thumb-hole for the upper hand and seven finger-holes: three for the upper hand and four for the lower. It is the most prominent duct flute in the western classical tradition.

Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the more general category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and reed instruments. The main distinction between these instruments and other wind instruments is the way in which they produce sound. All woodwinds produce sound by splitting the air blown into them on a sharp edge, such as a reed or a fipple. Despite the name, a woodwind may be made of any material, not just wood. Common examples include brass, silver, cane, as well as other metals such as gold and platinum. The saxophone, for example, though made of brass, is considered a woodwind because it requires a reed to produce sound. Occasionally, woodwinds are made of earthen materials, especially ocarinas.

A clef is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces.
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian, historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In 4-part voice leading alto is the second highest part, sung in choruses by either low women's or high men's voices. In vocal classification these are usually called contralto and male alto or countertenor.

A concert band, variously also called a wind ensemble, symphonic band, wind symphony, wind orchestra, wind band, symphonic winds, symphony band, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind, brass, and percussion families of instruments, and occasionally including the harp and the double bass or bass guitar. On rare occasions, additional non-traditional instruments may be added to such ensembles such as piano, synthesizer, or electric guitar.
Contrabass refers to several musical instruments of very low pitch—generally one octave below bass register instruments. While the term most commonly refers to the double bass, many other instruments in the contrabass register exist.
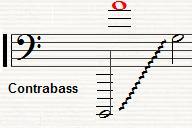
The contrabass clarinet and contra-alto clarinet are the two largest members of the clarinet family that are in common usage. Modern contrabass clarinets are pitched in B♭, sounding two octaves lower than the common B♭ soprano clarinet and one octave lower than the B♭ bass clarinet. Some contrabass clarinet models have a range extending down to low (written) E♭, while others can play down to low D or further to low C. This range, C(3) – E(6), sounds B♭(0) – D(4), see the table on the right. Some early instruments were pitched in C; Arnold Schoenberg's Fünf Orchesterstücke specifies a contrabass clarinet in A, but there is no evidence of such an instrument ever having existed.

The contra-alto clarinet or E♭ contrabass clarinet is a large clarinet pitched a perfect fifth below the B♭ bass clarinet. Contra-alto clarinets are a transposing instrument in E♭ sounding an octave and a major sixth below its written pitch. As it is pitched between the bass clarinet and the B♭ contrabass clarinet, the contra-alto clarinet is the great bass member of the clarinet family.

The alto flute is an instrument in the Western concert flute family, the second-highest member below the standard C flute after the uncommon flûte d'amour. It is the third most common member of its family after the standard C flute and the piccolo. It is characterized by its rich, mellow tone in the lower portion of its range. It is a transposing instrument in G, and uses the same fingerings as the C flute.
The bass flute is a member of the flute family. It is in the key of C, pitched one octave below the concert flute. Despite its name, its playing range makes it the tenor member of the flute family. Because of the length of its tube, it is usually made with a J-shaped head joint, which brings the embouchure hole within reach of the player. It is usually only used in flute choirs, as it is easily drowned out by other instruments of comparable register, such as the clarinet.

The Western concert flute is a family of transverse (side-blown) woodwind instruments made of metal or wood. It is the most common variant of the flute. A musician who plays the flute is called a flautist, flutist, or simply a flute player.
The alto clarinet is a woodwind instrument of the clarinet family. It is a transposing instrument pitched in the key of E♭, though instruments in F have been made. In size it lies between the soprano clarinet and the bass clarinet. It bears a greater resemblance to the bass clarinet in that it typically has a straight body, but a curved neck and bell made of metal. All-metal alto clarinets also exist. In appearance it strongly resembles the basset horn, but usually differs in three respects: it is pitched a whole step lower, it lacks an extended lower range, and it has a wider bore than many basset horns.

The contrabass flute is one of the rarer members of the flute family. Typically seen in flute ensembles, it is sometimes also used in solo and chamber music situations. Its range is similar to that of the regular concert flute, except that it is pitched two octaves lower; the lowest performable note is two octaves below middle C. Many contrabass flutes in C are also equipped with a low B, Contrabass flutes are only available from select flute makers.

The subcontrabass flute is one of the largest instruments in the flute family, measuring over 15 feet (4.6 m) long. The instrument can be made in the key of G, pitched a fourth below the contrabass flute in C and two octaves below the alto flute in G; which is sometimes also called double contra-alto flute, or in C, which will sound three octaves lower than the C flute.
The flûte d'amour is an uncommon member of the Western concert flute family, pitched in A♭, A, or B♭ and is intermediate in size between the modern C concert flute and the alto flute in G. It is the alto member of the flute family. It is also sometimes called a tenor flute.

The clarinet family is a musical instrument family including the well-known B♭ clarinet, the bass clarinet, the slightly less familiar E♭ and A clarinets and other clarinets.
A flute choir is an instrumental chamber ensemble consisting of range extensions of the flute family. Although a flute quartet can, in some cases depending on instrumentation, be considered a flute choir, most flute choirs extend the melodic range of the group in either direction with the addition of "melody" flutes. Most flute ensembles of five or more people can be considered a flute choir, although this is not a fixed number.
The western concert flute family has a wide range of instruments.

The tenor recorder is a member of the recorder family. It has the same form as a soprano recorder and an alto recorder, but it produces a lower sound than either; a still lower sound is produced by the bass recorder and great bass recorder.












