In system administration, orchestration is the automated configuring, coordinating, and managing of computer systems and software.
Information technology management or IT management is the discipline whereby all of the information technology resources of a firm are managed in accordance with its needs and priorities. Managing the responsibility within a company entails many of the basic management functions, like budgeting, staffing, change management, and organizing and controlling, along with other aspects that are unique to technology, like software design, network planning, tech support etc.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users.
Dynamic Infrastructure is an information technology concept related to the design of data centers, whereby the underlying hardware and software can respond dynamically and more efficiently to changing levels of demand. In other words, data center assets such as storage and processing power can be provisioned to meet surges in user's needs. The concept has also been referred to as Infrastructure 2.0 and Next Generation Data Center.

Fabric computing or unified computing involves constructing a computing fabric consisting of interconnected nodes that look like a weave or a fabric when seen collectively from a distance.
HP Cloud Service Automation is cloud management software from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) that is used by companies and government agencies to automate the management of cloud-based IT-as-a-service, from order, to provision, and retirement. HP Cloud Service Automation orchestrates the provisioning and deployment of complex IT services such as of databases, middleware, and packaged applications. The software speeds deployment of application-based services across hybrid cloud delivery platforms and traditional IT environments.
HP Business Service Automation was a collection of software products for data center automation from the HP Software Division of Hewlett-Packard Company. The products could help Information Technology departments create a common, enterprise-wide view of each business service; enable the automation of change and compliance across all devices that make up a business service; connect IT processes and coordinate teams via common workflows; and integrate with monitoring and ticketing tools to form a complete, integrated business service management solution. HP now provides many of these capabilities as part of HP Business Service Management software and solutions.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Networking is the networking products division of Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE). HPE Networking and its predecessor entities have a long history of developing and selling networking products. Today, it offers campus and small business networking products through its wholly owned company Aruba Networks which was acquired in 2015. Prior to this, HP Networking was the entity within HP offering networking products.
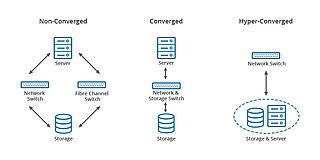
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.
HP ConvergedSystem is a portfolio of system-based products from Hewlett-Packard (HP) that integrates preconfigured IT components into systems for virtualization, cloud computing, big data, collaboration, converged management, and client virtualization. Composed of servers, storage, networking, and integrated software and services, the systems are designed to address the cost and complexity of data center operations and maintenance by pulling the IT components together into a single resource pool so they are easier to manage and faster to deploy. Where previously it would take three to six months from the time of order to get a system up and running, it now reportedly takes as few as 20 days with the HP ConvergedSystem.
HP CloudSystem is a cloud infrastructure from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) that combines storage, servers, networking and software.

Virtual Computing Environment Company (VCE) was a division of EMC Corporation that manufactured converged infrastructure appliances for enterprise environments. Founded in 2009 under the name Acadia, it was originally a joint venture between EMC and Cisco Systems, with additional investments by Intel and EMC subsidiary VMware. EMC acquired a 90% controlling stake in VCE from Cisco in October 2014, giving it majority ownership. VCE ended in 2016 after an internal division realignment, followed by the sale of EMC to Dell.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.

HP Cloud was a set of cloud computing services available from Hewlett-Packard that offered public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, managed private cloud and other cloud services. It was the combination of the previous HP Converged Cloud business unit and HP Cloud Services, an OpenStack-based public cloud. It was marketed to enterprise organizations to combine public cloud services with internal IT resources to create hybrid clouds, or a mix of private and public cloud environments, from around 2011 until 2016.
Software-defined data center is a marketing term that extends virtualization concepts such as abstraction, pooling, and automation to all data center resources and services to achieve IT as a service (ITaaS). In a software-defined data center, "all elements of the infrastructure — networking, storage, CPU and security – are virtualized and delivered as a service."
Cloud management is the management of cloud computing products and services.

Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined IT infrastructure that virtualizes all of the elements of conventional "hardware-defined" systems. HCI includes, at a minimum, virtualized computing, software-defined storage, and virtualized networking. HCI typically runs on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers.

SAP Converged Cloud is a private managed cloud developed and marketed by SAP.
Composable disaggregated infrastructure (CDI), sometimes stylized as composable/disaggregated infrastructure, is a technology that allows enterprise data center operators to achieve the cost and availability benefits of cloud computing using on-premises networking equipment. It is considered a class of converged infrastructure, and uses management software to combine compute, storage and network elements. It is similar to public cloud, except the equipment sits on premises in an enterprise data center.
A secure access service edge (SASE) is technology used to deliver wide area network (WAN) and security controls as a cloud computing service directly to the source of connection rather than a data center. It uses cloud and edge computing technologies to reduce the latency that results from backhauling all WAN traffic over long distances to one or a few corporate data centers, due to the increased movement off-premises of dispersed users and their applications. This also helps organizations support dispersed users and their devices with digital transformation and application modernization initiatives.






