
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) deals with a system of procurement, operations management, logistics and marketing channels, through which raw materials can be developed into finished products and delivered to their end customers. A more narrow definition of supply chain management is the "design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronising supply with demand and measuring performance globally". This can include the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, finished goods, and end to end order fulfilment from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Interconnected, interrelated or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain.
Institute for Supply Management (ISM) is the oldest, and the largest, supply management association in the world. Founded in 1915, the U.S.-based not-for-profit educational association serves professionals and organizations with a keen interest in supply management, providing them education, training, qualifications, publications, information, and research.

A supply chain, sometimes expressed as a "supply-chain", is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers. Meanwhile, supply chain management deals with the flow of goods within the supply chain in the most efficient manner.
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as government procurement or public procurement.

A purchase order, often abbreviated to PO, is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services required. It is used to control the purchasing of products and services from external suppliers. Purchase orders can be an essential part of enterprise resource planning system orders.
Purchasing is the procurement process a business or organization uses to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations.
E-procurement is the business-to-business or business-to-consumer or business-to-government purchase and sale of supplies, work, and services through the Internet as well as other information and networking systems, such as electronic data interchange and enterprise resource planning systems.
Strategic sourcing is the process of developing channels of supply at the lowest total cost, not just the lowest purchase price. It expands upon traditional organisational purchasing activities to embrace all activities within the procurement cycle, from specification to receipt, payment for goods and services to sourcing production lines where the labor market would increase firms' ROI. Strategic sourcing processes aim for continuous improvement and re-evaluation of the purchasing activities of an organisation.
Supplier relationship management (SRM) is the systematic, enterprise-wide assessment of suppliers' strengths, performance and capabilities with respect to overall business strategy, determination of what activities to engage in with different suppliers, and planning and execution of all interactions with suppliers, in a coordinated fashion across the relationship life cycle, to maximize the value realized through those interactions. The focus of supplier relationship management is the development of two-way, mutually beneficial relationships with strategic supply partners to deliver greater levels of innovation and competitive advantage than could be achieved by operating independently or through a traditional, transactional purchasing arrangement. Underpinning disciplines which support effective SRM include supplier information management, compliance, risk management and performance management.
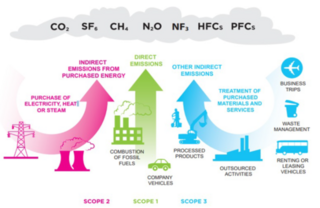
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.
Procurement software refers to a range of business software designed to streamline and automate purchasing processes for businesses and organizations. By managing information flows and transactions between procuring entities, suppliers, and partners, procurement software aims to cut costs, improve efficiency, and boost organizational performance.
Industrial market segmentation is a scheme for categorizing industrial and business customers to guide strategic and tactical decision-making. Government agencies and industry associations use standardized segmentation schemes for statistical surveys. Most businesses create their own segmentation scheme to meet their particular needs. Industrial market segmentation is important in sales and marketing.
Sustainable procurement or green procurement is a process whereby organizations meet their needs for goods, services, works and utilities in a way that achieves value for money on a life-cycle basis while addressing equity principles for sustainable development, therefore benefiting societies and the environment across time and geographies. Procurement is often conducted via a tendering or competitive bidding process. The process is used to ensure the buyer receives goods, services or works for the best possible price, when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Procurement is considered sustainable when organizations broadens this framework by meeting their needs for goods, services, works, and utilities in a way that achieves value for money and promotes positive outcomes not only for the organization itself but for the economy, environment, and society.
Global sourcing is the practice of sourcing from the global market for goods and services across geopolitical boundaries. Global sourcing often aims to exploit global efficiencies in the delivery of a product or service. These efficiencies include low cost skilled labor, low cost raw material, extreme international competition, new technology and other economic factors like tax breaks and low trade tariffs. Common examples of globally sourced products or services include labor-intensive manufactured products produced using low-cost Chinese labor, call centers staffed with low-cost English speaking workers in the Philippines, India and Pakistan, and IT work performed by low-cost programmers in India, Pakistan and Eastern Europe. While these are examples of low-cost country sourcing, global sourcing is not limited to low-cost countries.
Forward Commitment Procurement (FCP) is a procurement model designed to be used to deliver cost-effective environmental products and services to the public sector and help to create the market conditions in which the environmental goods and services sector can thrive.
Supply-chain sustainability is the management of environmental, social and economic impacts and the encouragement of good governance practices, throughout the lifecycles of goods and services. There is a growing need for integrating sustainable choices into supply-chain management. An increasing concern for sustainability is transforming how companies approach business. Whether motivated by their customers, corporate values or business opportunity, traditional priorities such as quality, efficiency and cost regularly compete for attention with concerns such as working conditions and environmental impact. A sustainable supply chain seizes value chain opportunities and offers significant competitive advantages for early adopters and process innovators.
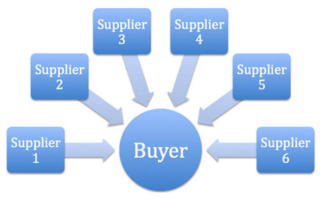
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.

An invitation to tender is a formal, structured procedure for generating competing offers from different potential suppliers or contractors looking to obtain an award of business activity in works, supply, or service contracts, often from companies who have been previously assessed for suitability by means of a supplier questionnaire (SQ) or pre-qualification questionnaire (PQQ).
Category management is an approach to the organisation of purchasing within a business organisation, also often referred to as procurement. Applying category management to purchasing activity benefits organisations by providing an approach to reduce the cost of buying goods and services, reduce risk in the supply chain, increase overall value from the supply base and gain access to more innovation from suppliers. It is a strategic approach which focuses on the vast majority of organisational spend. If applied effectively throughout an entire organisation, the results can be significantly greater than traditional transactional based purchasing negotiations, however the discipline of category management is sorely misunderstood.
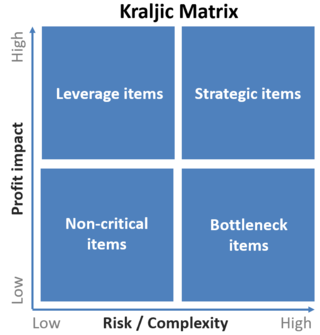
In supply chain management, the Kraljic matrix is a method used to segment the purchases or suppliers of a company by dividing them into four classes, based on the complexity of the supply market and the importance of the purchases or suppliers. This subdivision allows the company to define the optimal purchasing strategies for each of the four types of purchases or suppliers.






