Related Research Articles
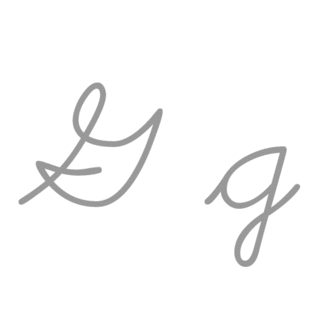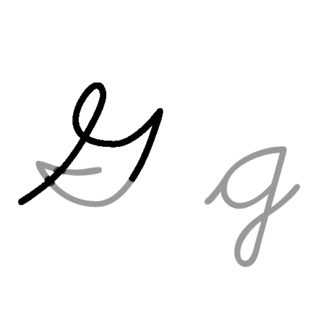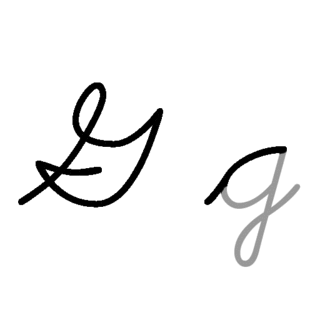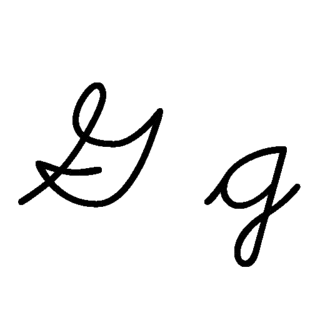
G or g is the seventh letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

Christopher George Latore Wallace, better known by his stage names the Notorious B.I.G., Biggie Smalls, or simply Biggie, was an American rapper and songwriter. Rooted in the New York rap scene and gangsta rap traditions, he is considered one of the greatest rappers of all time. The Notorious B.I.G. became known for his distinctive laidback lyrical delivery, offsetting the lyrics' often grim content and his own intimidating appearance. His music was often semi-autobiographical, telling of hardship and criminality, but also of debauchery and celebration.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one.
Correbidia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by George Hampson in 1898.
Hyperbaniana is a monotypic moth genus of the family Erebidae. Its only species, Hyperbaniana costinotata, is found in Sulawesi. Both the genus and species were first described by George Hampson in 1926.

Pangrapta is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1818.

Rivula is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae described by Achille Guenée in 1845.

Tamba is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. It was erected by Francis Walker in 1869.
Triommatodes is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was described by Warren in 1889.

Cyclophora is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae. Many species are referred to as mochas in reference to their colouration, primarily in Europe.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide by 2025, according to the GSM Association. Like its predecessors, 5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell are connected to the Internet and telephone network by radio waves through a local antenna in the cell. The main advantage of the new networks is that they will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s). Due to the increased bandwidth, it is expected the networks will not exclusively serve cellphones like existing cellular networks, but also be used as general internet service providers for laptops and desktop computers, competing with existing ISPs such as cable internet, and also will make possible new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas. 4G cellphones are not able to use the new networks, which require 5G enabled wireless devices.
Correbidia terminalis is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found from Mexico through Central America and Cuba and Puerto Rico to South America.
Cyclophora costinotata is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in Colombia.
Correbidia calopteridia is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1878. It is found in Pará, Brazil.
Correbidia notata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1878. It is found in the Amazon region.
Correbidia striata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Herbert Druce in 1884. It is found in Panama.
Correbidia assimilis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912. It is found in Venezuela and possibly Central America.
Correbidia joinvillea is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1921. It is found in Brazil.
Correbidia simonsi is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912.
The Euchromiina are a subtribe of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876. Many species in the subtribe are mimics of wasps.
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Correbidia costinotata". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum . Retrieved May 1, 2018.
| This Arctiinae-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |