Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve goals and meet success criteria at a specified time. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.
Project management software (PMS) has the capacity to help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management, time management and documentation or administration systems. Today, numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software solutions exist, and are finding applications in almost every type of business.

A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development is a process of writing and maintaining the source code, but in a broader sense, it includes all that is involved between the conception of the desired software through to the final manifestation of the software, sometimes in a planned and structured process. Therefore, software development may include research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities that result in software products.
The Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) is a procedural software cost estimation model developed by Barry W. Boehm. The model parameters are derived from fitting a regression formula using data from historical projects.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the software development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life-cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The systems development life cycle concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from inception, through engineering design and manufacture, to service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprise.
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed project or system. A feasibility study aims to objectively and rationally uncover the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture, opportunities and threats present in the natural environment, the resources required to carry through, and ultimately the prospects for success. In its simplest terms, the two criteria to judge feasibility are cost required and value to be attained.
Cost estimation in software engineering is typically concerned with the financial spend on the effort to develop and test the software, this can also include requirements review, maintenance, training, managing and buying extra equipment, servers and software. Many methods have been developed for estimating software costs for a given project.
Query optimization is a feature of many relational database management systems and other databases such as graph databases. The query optimizer attempts to determine the most efficient way to execute a given query by considering the possible query plans.
The function point is a "unit of measurement" to express the amount of business functionality an information system provides to a user. Function points are used to compute a functional size measurement (FSM) of software. The cost of a single unit is calculated from past projects.
A cost estimate is the approximation of the cost of a program, project, or operation. The cost estimate is the product of the cost estimating process. The cost estimate has a single total value and may have identifiable component values.
In project management, the Cone of Uncertainty describes the evolution of the amount of best case uncertainty during a project. At the beginning of a project, comparatively little is known about the product or work results, and so estimates are subject to large uncertainty. As more research and development is done, more information is learned about the project, and the uncertainty then tends to decrease, reaching 0% when all residual risk has been terminated or transferred. This usually happens by the end of the project i.e. by transferring the responsibilities to a separate maintenance group.
Cost engineering is "the engineering practice devoted to the management of project cost, involving such activities as estimating, cost control, cost forecasting, investment appraisal and risk analysis." "Cost Engineers budget, plan and monitor investment projects. They seek the optimum balance between cost, quality and time requirements."
In software development, effort estimation is the process of predicting the most realistic amount of effort required to develop or maintain software based on incomplete, uncertain and noisy input. Effort estimates may be used as input to project plans, iteration plans, budgets, investment analyses, pricing processes and bidding rounds.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
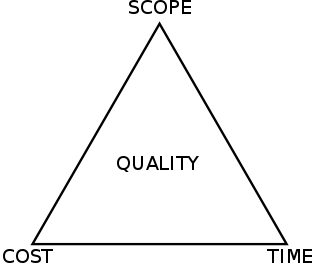
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
Daniel D. Galorath is the President and CEO of Galorath Incorporated and the chief architect of SEER-SEM, an algorithmic project management software application. He is a recognized expert in the fields of software estimation and sizing and the author of Software Sizing, Estimation, and Risk Management.
PRICE Systems was founded in 1975 as a business within the RCA Corporation. It is generally acknowledged as the earliest developer of parametric cost estimation software.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:


