
The sap beetles, also known as Nitidulidae, are a family of beetles.
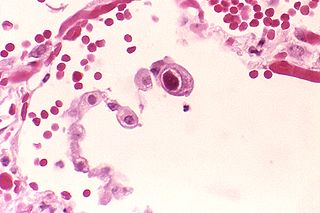
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia, and congenital CMV in infants can lead to deafness and ambulatory problems.

Stag beetles are a family of about 1,200 species of beetles in the family Lucanidae, currently classified in four subfamilies. Some species grow to over 12 centimetres, but most to about 5 cm (2 in).

The Rutaceae is a family, commonly known as the rue or citrus family, of flowering plants, usually placed in the order Sapindales.

Plovers are members of a widely distributed group of wading birds of family Charadriidae. The term "plover" applies to all the members of the family, though only about half of them include it in their name.

The Curculionidae are a family of weevils, commonly called snout beetles or true weevils. They are one of the largest animal families with 6,800 genera and 83,000 species described worldwide. They are the sister group to the family Brentidae.

The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, but the precise taxonomy and systematics are likely to change with ongoing research.

The Acalyphoideae are a subfamily within the family Euphorbiaceae with 116 genera in 20 tribes.

Noctuoidea is the superfamily of noctuid or "owlet" moths, and has more than 70,000 described species, the largest number of any Lepidopteran superfamily. Its classification has not yet reached a satisfactory or stable state. Since the end of the 20th century, increasing availability of molecular phylogenetic data for this hugely successful radiation has led to several competing proposals for a taxonomic arrangement that correctly represents the relationships between the major lineages.

Littorinimorpha is a large order of snails, gastropods, consisting primarily of sea snails, but also including some freshwater snails and land snails.

Asparagaceae, known as the asparagus family, is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family name is based on the edible garden asparagus, Asparagus officinalis. This family includes both common garden plants as well as common houseplants. The garden plants include asparagus, yucca, bluebell, and hosta, and the houseplants include snake plant, corn cane, spider plant, and plumosus fern.

Myobatrachidae, commonly known as Australian ground frogs or Australian water frogs, is a family of frogs found in Australia and New Guinea. Members of this family vary greatly in size, from species less than 1.5 cm (0.59 in) long, to the second-largest frog in Australia, the giant barred frog, at 12 cm (4.7 in) in length. The entire family is either terrestrial or aquatic frogs, with no arboreal species.

Ennominae is the largest subfamily of the geometer moth family (Geometridae), with some 9,700 described species in 1,100 genera. Most species are fairly small, though some grow to be considerably large. This subfamily has a global distribution. It includes some species that are notorious defoliating pests. The subfamily was first described by Philogène Auguste Joseph Duponchel in 1845.
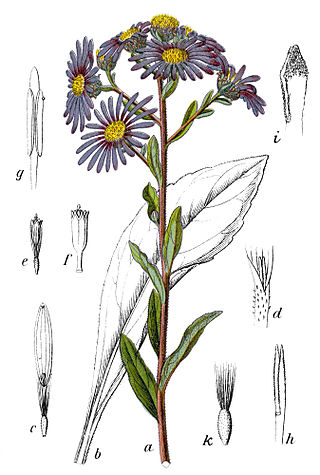
Asteroideae is a subfamily of the plant family Asteraceae. It contains about 70% of the species of the family. It consists of several tribes, including Astereae, Calenduleae, Eupatorieae, Gnaphalieae, Heliantheae, Senecioneae and Tageteae. Asteroideae contains plants found all over the world, many of which are shrubby. There are about 1,135 genera and 17,200 species within this subfamily; the largest genera by number of species are Helichrysum (500–600) and Artemisia (550).

Enidae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks.

Littorinoidea are a superfamily of both sea snails and land snails which have a gill and an operculum, terrestrial and marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Littorinimorpha.

Olivoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of minute to medium-large predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the order Neogastropoda.

The Erebidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family is among the largest families of moths by species count and contains a wide variety of well-known macromoth groups. The family includes the underwings (Catocala); litter moths (Herminiinae); tiger, lichen, and wasp moths (Arctiinae); tussock moths (Lymantriinae), including the arctic woolly bear moth ; fruit-piercing moths ; micronoctuoid moths (Micronoctuini); snout moths (Hypeninae); and zales, though many of these common names can also refer to moths outside the Erebidae. Some of the erebid moths are called owlets.

Pelodryadinae, also known as Australian treefrogs, is a subfamily of frogs found in the region of Australia and New Guinea, and have also been introduced to New Caledonia, Guam, New Zealand, and Vanuatu.
Liopteridae is a family of wood-boring parasitoid wasps. They occur worldwide with concentrations in the African Tropics. These insects have a petiolate abdomen. There are 10 genera and more than 140 species known.



















