
The Rio Grande in the United States or the Río Bravo in Mexico, also known as P’osoge in Tewa and Tó Ba’áadi in Navajo, is one of the principal rivers in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is 1,896 miles (3,051 km), making it the 4th longest river in the United States and in North America by main stem. It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of 182,200 square miles (472,000 km2); however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to 336,000 square miles (870,000 km2).

The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that temporarily defused tensions between slave and free states in the years leading up to the American Civil War. Designed by Whig senator Henry Clay and Democratic senator Stephen A. Douglas, with the support of President Millard Fillmore, the compromise centered on how to handle slavery in recently acquired territories from the Mexican–American War (1846–48).
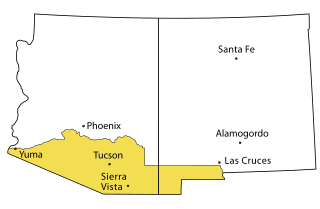
The Gadsden Purchase is a 29,640-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the U.S. wanted to build a transcontinental railroad along a deep southern route, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.

The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo officially ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). It was signed on 2 February 1848 in the town of Guadalupe Hidalgo.

The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by metropolitan area are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson. Before 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854.

The Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty, was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined the boundary between the U.S. and Mexico. It settled a standing border dispute between the two countries and was considered a triumph of American diplomacy. It came during the successful Spanish American wars of independence against Spain.

James Gadsden was an American diplomat, soldier and businessman after whom the Gadsden Purchase is named, pertaining to land which the United States bought from Mexico, and which became the southern portions of Arizona and New Mexico. James Gadsden served as Adjutant General of the U.S. Army from August 13, 1821 – March 22, 1822. Between 1853 and 1856, he served as U.S. Minister to Mexico. He was known commonly as General Gadsden, although he never had a rank above colonel.

The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of Nuevo México becoming part of the American frontier after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. It existed with varying boundaries until the territory was admitted to the Union as the U.S. state of New Mexico in 1912. This jurisdiction was an organized, incorporated territory of the US for nearly 62 years, the longest period of any territory in the contiguous United States.

The Mexican Cession is the region in the modern-day western United States that Mexico previously controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, though the Texas annexation resolution two years earlier had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new state of Texas. At roughly 529,000 square miles (1,370,000 km2), not including any Texas lands, the Mexican Cession was the third-largest acquisition of territory in U.S. history, surpassed only by the 827,000-square-mile (2,140,000 km2) Louisiana Purchase and the 586,000-square-mile (1,520,000 km2) Alaska Purchase.

Arizona Territory, colloquially referred to as Confederate Arizona, was an organized incorporated territory of the Confederate States of America that existed from August 1, 1861, to May 26, 1865, when the Confederate States Army Trans-Mississippi Department, commanded by General Edmund Kirby Smith, surrendered at Shreveport, Louisiana. However, after the Battle of Glorieta Pass, the Confederates had to retreat from the territory, and by July 1862, effective Confederate control of the territory had ended. Delegates to the secession convention had voted in March 1861 to secede from the New Mexico Territory and the Union, and seek to join the Confederacy. It consisted of the portion of the New Mexico Territory south of the 34th parallel, including parts of the modern states of New Mexico and Arizona. The capital was Mesilla, along the southern border. The breakaway region overlapped Arizona Territory, established by the Union government in February 1863.
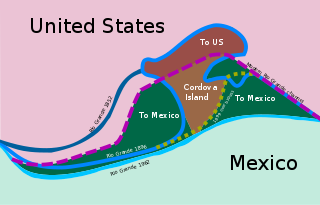
The Chamizal dispute was a border conflict over around 600 acres on the Mexico–United States border between El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua. It was caused by a shift in the Rio Grande, as a survey presented in 1852 marked differences between the bed of the Rio Grande and the present channel of the river. Tensions over the territory during the historic Taft–Díaz summit almost resulted in the attempted assassination of both presidents on October 16, 1909.

The International Boundary and Water Commission is an international body created by the United States and Mexico in 1889 to apply the rules for determining the location of their international boundary when meandering rivers transferred tracts of land from one bank to the other, as established under the Convention of November 12, 1884.
The Rio Grande has changed course several times in recorded history, leading to a number of border disputes and uncertainties, both international and between individual U.S. states:

The Mexico–United States border is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. The Mexico–U.S. border is the most frequently crossed border in the world with approximately 350 million documented crossings annually. Illegal crossing of the border to enter the United States has been a top issue in the States and is causing a border crisis. It is one of two international borders that the United States has, the other being the Canada–United States border to the north. It is the tenth-longest border between two countries in the world.
New Mexico v. Texas, 275 U.S. 279 (1927), was a United States Supreme Court case that determined the boundary between Texas and New Mexico in the vicinity of El Paso, Texas.
Andrew Belcher Gray was an American surveyor.
The area currently occupied by the U.S. State of New Mexico has undergone numerous changes in occupancy and territorial claims and designations. This geographic chronology traces the territorial evolution of New Mexico.
Founded as El Paso del Norte by Spanish Franciscan friars at an important mountain pass, the area became a small agricultural producer though most settlement was south of the river where modern Mexico lies. The city was considered part of New Mexico under Spanish Conquerors and was tied economically to Santa Fe, New Mexico and the Chihuahuan mining districts of San Felipe El Real and San José del Parral.
In 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed to the United States of America, becoming the 28th U.S. state. Border disputes between the new state and Mexico, which had never recognized Texas independence and still considered the area a renegade Mexican state, led to the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). When the war concluded, Mexico relinquished its claim on Texas, as well as other regions in what is now the southwestern United States. Texas' annexation as a state that tolerated slavery had caused tension in the United States among slave states and those that did not allow slavery. The tension was partially defused with the Compromise of 1850, in which Texas ceded some of its territory to the federal government to become non-slave-owning areas but gained El Paso.













