
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size, and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix.

Agarose is a heteropolysaccharide, generally extracted from certain red algae. It is a linear polymer made up of the repeating unit of agarobiose, which is a disaccharide made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Agarose is one of the two principal components of agar, and is purified from agar by removing agar's other component, agaropectin.

Gel electrophoresis is an electrophoresis method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules and their fragments, based on their size and charge through a supportive medium. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.

Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation, and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species.

Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids is an analytical technique to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules are placed on a gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the positively charged anode. The molecules separate as they travel through the gel based on the each molecule's size and shape. Longer molecules move more slowly because the gel resists their movement more forcefully than it resists shorter molecules. After some time, the electricity is turned off and the positions of the different molecules are analyzed.

Ethidium bromide is an intercalating agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag in molecular biology laboratories for techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis. It is commonly abbreviated as EtBr, which is also an abbreviation for bromoethane. To avoid confusion, some laboratories have used the abbreviation EthBr for this salt. When exposed to ultraviolet light, it will fluoresce with an orange colour, intensifying almost 20-fold after binding to DNA. Under the name homidium, it has been commonly used since the 1950s in veterinary medicine to treat trypanosomiasis in cattle. The high incidence of antimicrobial resistance makes this treatment impractical in some areas, where the related isometamidium chloride is used instead. Despite its reputation as a mutagen, tests have shown it to have low mutagenicity without metabolic activation.

Protein electrophoresis is a method for analysing the proteins in a fluid or an extract. The electrophoresis may be performed with a small volume of sample in a number of alternative ways with or without a supporting medium, namely agarose or polyacrylamide. Variants of gel electrophoresis include SDS-PAGE, free-flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis, affinity electrophoresis, immunoelectrophoresis, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. Each variant has many subtypes with individual advantages and limitations. Gel electrophoresis is often performed in combination with electroblotting or immunoblotting to give additional information about a specific protein.
Coomassie brilliant blue is the name of two similar triphenylmethane dyes that were developed for use in the textile industry but are now commonly used for staining proteins in analytical biochemistry. Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 differs from Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 by the addition of two methyl groups. The name "Coomassie" is a registered trademark of Imperial Chemical Industries.

Bromophenol blue, albutest is used as a pH indicator, an electrophoretic color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid.
A restriction digest is a procedure used in molecular biology to prepare DNA for analysis or other processing. It is sometimes termed DNA fragmentation, though this term is used for other procedures as well. In a restriction digest, DNA molecules are cleaved at specific restriction sites of 4-12 nucleotides in length by use of restriction enzymes which recognize these sequences.
Xylene cyanol can be used as an electrophoretic color marker, or tracking dye, to monitor the process of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Bromophenol blue and orange G can also be used for this purpose.

Immunoelectrophoresis is a general name for a number of biochemical methods for separation and characterization of proteins based on electrophoresis and reaction with antibodies. All variants of immunoelectrophoresis require immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, reacting with the proteins to be separated or characterized. The methods were developed and used extensively during the second half of the 20th century. In somewhat chronological order: Immunoelectrophoretic analysis, crossed immunoelectrophoresis, rocket-immunoelectrophoresis, fused rocket immunoelectrophoresis ad modum Svendsen and Harboe, affinity immunoelectrophoresis ad modum Bøg-Hansen.

Orange G also called C.I. 16230, Acid Orange 10, or orange gelb is a synthetic azo dye used in histology in many staining formulations. It usually comes as a disodium salt. It has the appearance of orange crystals or powder.
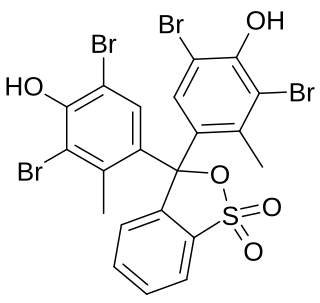
Bromocresol green (BCG) is a dye of the triphenylmethane family. It belongs to a class of dyes called sulfonephthaleins. It is used as a pH indicator in applications such as growth mediums for microorganisms and titrations. In clinical practise, it is commonly used as a diagnostic technique. The most common use of bromocresol green is to measure serum albumin concentration within mammalian blood samples in possible cases of kidney failure and liver disease. In chemistry, bromocresol green is used in Thin-layer chromatography staining solutions to visualize acidic compounds.

A molecular-weight size marker, also referred to as a protein ladder, DNA ladder, or RNA ladder, is a set of standards that are used to identify the approximate size of a molecule run on a gel during electrophoresis, using the principle that molecular weight is inversely proportional to migration rate through a gel matrix. Therefore, when used in gel electrophoresis, markers effectively provide a logarithmic scale by which to estimate the size of the other fragments.

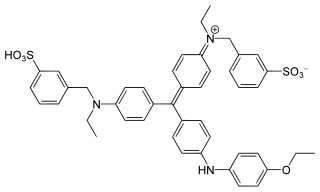
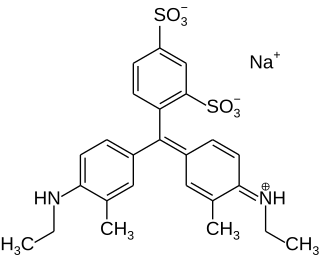
An electrophoretic color marker is a chemical used to monitor the progress of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) since DNA, RNA, and most proteins are colourless. The color markers are made up of a mixture of dyes that migrate through the gel matrix alongside the sample of interest. They are typically designed to have different mobilities from the sample components and to generate colored bands that can be used to assess the migration and separation of sample components.

Affinity electrophoresis is a general name for many analytical methods used in biochemistry and biotechnology. Both qualitative and quantitative information may be obtained through affinity electrophoresis. Cross electrophoresis, the first affinity electrophoresis method, was created by Nakamura et al. Enzyme-substrate complexes have been detected using cross electrophoresis. The methods include the so-called electrophoretic mobility shift assay, charge shift electrophoresis and affinity capillary electrophoresis. The methods are based on changes in the electrophoretic pattern of molecules through biospecific interaction or complex formation. The interaction or binding of a molecule, charged or uncharged, will normally change the electrophoretic properties of a molecule. Membrane proteins may be identified by a shift in mobility induced by a charged detergent. Nucleic acids or nucleic acid fragments may be characterized by their affinity to other molecules. The methods have been used for estimation of binding constants, as for instance in lectin affinity electrophoresis or characterization of molecules with specific features like glycan content or ligand binding. For enzymes and other ligand-binding proteins, one-dimensional electrophoresis similar to counter electrophoresis or to "rocket immunoelectrophoresis", affinity electrophoresis may be used as an alternative quantification of the protein. Some of the methods are similar to affinity chromatography by use of immobilized ligands.

GelRed is an intercalating nucleic acid stain used in molecular genetics for agarose gel DNA electrophoresis. GelRed structurally consists of two ethidium subunits that are bridged by a linear oxygenated spacer.

GelGreen is an intercalating nucleic acid stain used in molecular genetics for agarose gel DNA electrophoresis. GelGreen consists of two acridine orange subunits that are bridged by a linear oxygenated spacer.

Stains-all is a carbocyanine dye, which stains anionic proteins, nucleic acids, anionic polysaccharides and other anionic molecules.



















