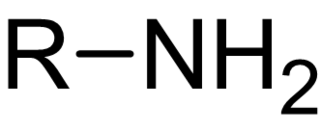
In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Formally, amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.

In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom bonded to two organyl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It is a tertiary amine, featuring a dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans.

In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon.

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
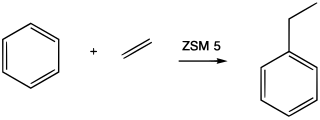
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.

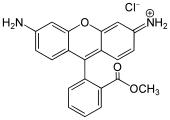
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are rhodamine 6G, rhodamine 123, and rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing.

Triphenylmethane or triphenyl methane (sometimes also known as Tritan), is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display fluorescence. A trityl group in organic chemistry is a triphenylmethyl group Ph3C, e.g. triphenylmethyl chloride (trityl chloride) and the triphenylmethyl radical (trityl radical).
Fuchsine (sometimes spelled fuchsin) or rosaniline hydrochloride is a magenta dye with chemical formula C20H19N3·HCl. There are other similar chemical formulations of products sold as fuchsine, and several dozen other synonyms of this molecule.
In organic chemistry, the Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl functional group by formaldehyde and a primary or secondary amine or ammonia. The final product is a β-amino-carbonyl compound also known as a Mannich base. Reactions between aldimines and α-methylene carbonyls are also considered Mannich reactions because these imines form between amines and aldehydes. The reaction is named after Carl Mannich.
IARC group 3 substances, chemical mixtures and exposure circumstances are those that can not be classified in regard to their carcinogenicity to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used most commonly for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which the level of evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans and inadequate or limited in experimental animals. Exceptionally, agents (mixtures) for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans, but sufficient in experimental animals may be placed in this category when there is strong evidence that the mechanism of carcinogenicity in experimental animals does not operate in humans. Agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances that do not fall into any other group are also placed in this category.
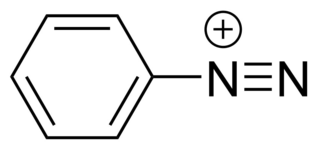
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols, where the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring in phenol is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.

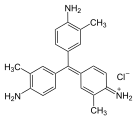
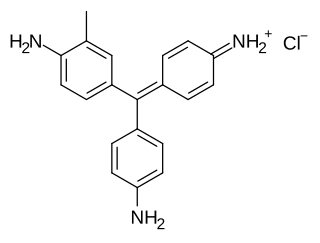
Pararosaniline, Basic Red 9, or C.I. 42500 is an organic compound with the formula [(H2NC6H4)3C]Cl. It is a magenta solid with a variety of uses as a dye. It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine. (The others are rosaniline, new fuchsine and magenta II.) It is structurally related to other triarylmethane dyes called methyl violets including crystal violet, which feature methyl groups on nitrogen.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.
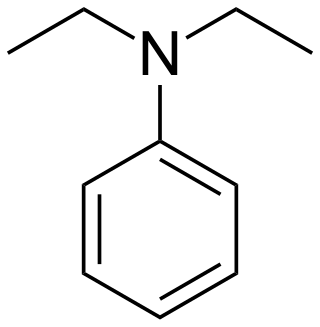
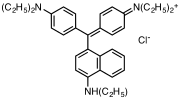
Diethylaniline is the organic compound with the molecular formula (C2H5)2NC6H5. It is a colorless liquid but commercial samples are often yellow. It is a precursor to several dyes and other commercial products.
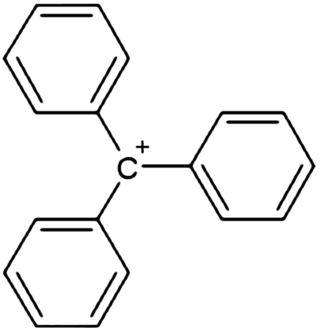
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an ion with formula [C19H15]+ or (C6H5)3C+, consisting of a carbon atom with a positive charge connected to three phenyl groups. It is a charged version of the triphenylmethyl radical (C6H5)3C•. The name is often abbreviated to triphenylmethyl or trityl in salts, although these names also denote the chemical group in compounds like triphenylmethyl chloride that do not contain the cation.

Methyl violet 6B is a violet triarylmethane dye from the group of cationic dyes and an essential component of C.I. Basic Violet 1. The compound is sometimes equated with methyl violet in the literature.