
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.

N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It is a tertiary amine, featuring a dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.

Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are rhodamine 6G, rhodamine 123, and rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing.
Fuchsine (sometimes spelled fuchsin) or rosaniline hydrochloride is a magenta dye with chemical formula C20H19N3·HCl. There are other similar chemical formulations of products sold as fuchsine, and several dozen other synonyms of this molecule.

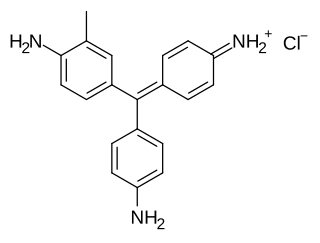
New fuchsine is an organic compound with the formula [(H2N(CH3)C6H3)3C]Cl. It is a green-colored solid that is used as a dye of the triarylmethane class. It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine, and one of the two that are available as single dyes. The other is pararosaniline. It is prepared by condensation of ortho-toluidine with formaldehyde. This process initially gives the benzhydrol 4,4'-bis(dimethylamino)benzhydrol, which is further condensed to give the leuco (colorless) tertiary alcohol [(H2N(CH3)C6H3)3COH, which is oxidized in acid to give the dye.
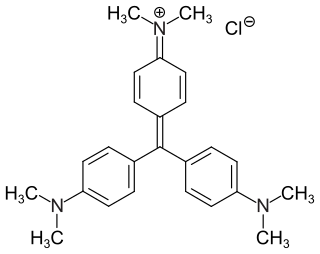
Crystal violet or gentian violet, also known as methyl violet 10B or hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride, is a triarylmethane dye used as a histological stain and in Gram's method of classifying bacteria. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antifungal, and anthelmintic (vermicide) properties and was formerly important as a topical antiseptic. The medical use of the dye has been largely superseded by more modern drugs, although it is still listed by the World Health Organization.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.
There are three isomers of toluidine, which are organic compounds discovered and named by James Sheridan Muspratt and August Wilhelm von Hofmann in 1845. These isomers are o-toluidine, m-toluidine, and p-toluidine, with the prefixed letter abbreviating, respectively, ortho; meta; and para. All three are aryl amines whose chemical structures are similar to aniline except that a methyl group is substituted onto the benzene ring. The difference between these three isomers is the position where the methyl group (–CH3) is bonded to the ring relative to the amino functional group (–NH2); see illustration of the chemical structures below.

Patent Blue V, also called Food Blue 5, Sulphan Blue, Acid Blue 3, L-Blau 3, C-Blau 20, Patentblau V, Sky Blue, or C.I. 42051, is a sky blue synthetic triphenylmethane dye used as a food coloring. As a food additive, it has E number E131. It is a sodium or calcium salt of [4-(α- -5-hydroxy- 2,4-disulfophenylmethylidene)-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene] diethylammonium hydroxide inner salt.

Eosin Y, also called C.I. 45380 or C.I. Acid Red 87, is a member of the triarylmethane dyes. It is produced from fluorescein by bromination.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.

The dithionite is the oxyanion with the formula [S2O4]2−. It is commonly encountered as the salt sodium dithionite. For historical reasons, it is sometimes called hydrosulfite, but it contains no hydrogen and is not a sulfite. The dianion has a steric number of 4 and trigonal pyramidal geometry.
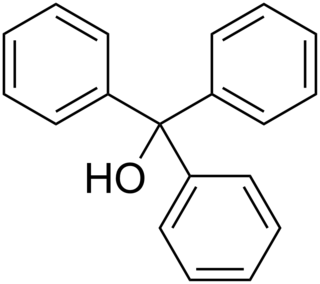
Triphenylmethanol is an organic compound. It is a white crystalline solid that is insoluble in water and petroleum ether, but well soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene. In strongly acidic solutions, it produces an intensely yellow color, due to the formation of a stable "trityl" carbocation. Many derivatives of triphenylmethanol are important dyes.

Victoria blue BO, also known as C.I. Basic Blue 7 and C.I. 42595, is a chloride salt of a dye with the chemical formula [C33H40N3]Cl. It has the appearance of a reddish blue powder. Victoria Blue BO base, also known as Solvent Blue 5 and C.I. 42595:1, is the hydroxide derivative of the same cation. Its chemical formula is [C33H40N3]OH. Victoria blues are members of the triarylmethane dyes, but unlike most such dyes, the Victoria blues have a naphthylamine group.
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.

Brilliant green is one of the triarylmethane dyes. It is closely related to malachite green.
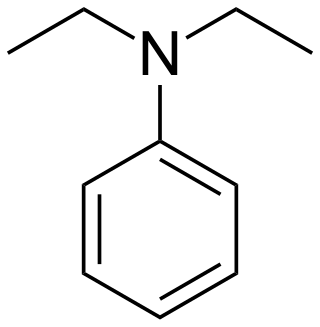
Diethylaniline is the organic compound with the molecular formula (C2H5)2NC6H5. It is a colorless liquid but commercial samples are often yellow. It is a precursor to several dyes and other commercial products.

2,4-Diaminotoluene is an aromatic organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. It is a white solid, although commercial samples are often yellow-tan.

Disodium 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonate is an organic compound with the formula (O2NC6H3(SO3Na)CH)2. This salt is a common precursor to a variety of textile dyes and optical brighteners.
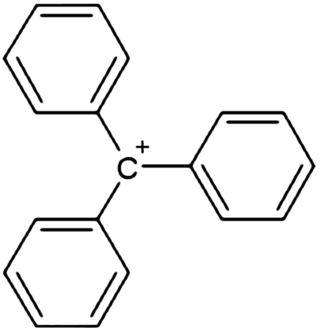
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an ion with formula [C19H15]+ or (C6H5)3C+, consisting of a carbon atom with a positive charge connected to three phenyl groups. It is a charged version of the triphenylmethyl radical (C6H5)3C•. The name is often abbreviated to triphenylmethyl or trityl in salts, although these names also denote the chemical group in compounds like triphenylmethyl chloride that do not contain the cation.


















