Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.

Methyl violet is a family of organic compounds that are mainly used as dyes. Depending on the number of attached methyl groups, the color of the dye can be altered. Its main use is as a purple dye for textiles and to give deep violet colors in paint and ink. It is also used as a hydration indicator for silica gel. Methyl violet 10B is also known as crystal violet and has medical uses.
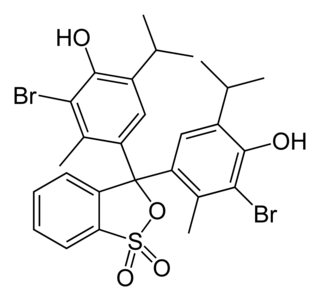
Bromothymol blue is a pH indicator. It is mostly used in applications that require measuring substances that would have a relatively neutral pH. A common use is for measuring the presence of carbonic acid in a liquid. It is typically sold in solid form as the sodium salt of the acid indicator.

Protein electrophoresis is a method for analysing the proteins in a fluid or an extract. The electrophoresis may be performed with a small volume of sample in a number of alternative ways with or without a supporting medium, namely agarose or polyacrylamide. Variants of gel electrophoresis include SDS-PAGE, free-flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis, affinity electrophoresis, immunoelectrophoresis, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. Each variant has many subtypes with individual advantages and limitations. Gel electrophoresis is often performed in combination with electroblotting or immunoblotting to give additional information about a specific protein.

Congo red is an organic compound, the sodium salt of 3,3′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid). It is an azo dye. Congo red is water-soluble, yielding a red colloidal solution; its solubility is greater in organic solvents. The use of Congo red in the textile industry has long been abandoned, primarily because of its carcinogenic properties, but it is still used for histological staining.
Coomassie brilliant blue is the name of two similar triphenylmethane dyes that were developed for use in the textile industry but are now commonly used for staining proteins in analytical biochemistry. Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 differs from Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 by the addition of two methyl groups. The name "Coomassie" is a registered trademark of Imperial Chemical Industries.

Bromophenol blue, albutest is used as a pH indicator, an electrophoretic color marker, and a dye. It can be prepared by slowly adding excess bromine to a hot solution of phenolsulfonphthalein in glacial acetic acid.
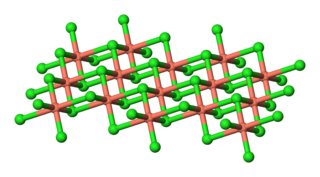
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.

Crystal violet or gentian violet, also known as methyl violet 10B or hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride, is a triarylmethane dye used as a histological stain and in Gram's method of classifying bacteria. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antifungal, and anthelmintic (vermicide) properties and was formerly important as a topical antiseptic. The medical use of the dye has been largely superseded by more modern drugs, although it is still listed by the World Health Organization.

Murexide (NH4C8H4N5O6, or C8H5N5O6·NH3), also called ammonium purpurate or MX, is the ammonium salt of purpuric acid. It is a purple solid that is soluble in water. The compound was once used as an indicator reagent. Aqueous solutions are yellow at low pH, reddish-purple in weakly acidic solutions, and blue-purple in alkaline solutions.

Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called albuminoids.

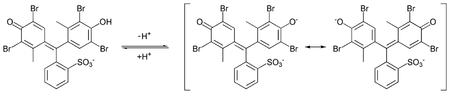
Bromocresol purple (BCP) or 5′,5″-dibromo-o-cresolsulfophthalein, is a dye of the triphenylmethane family and a pH indicator. It is colored yellow below pH 5.2, and violet above pH 6.8. In its cyclic sulfonate ester form, it has a pKa value of 6.3, and is usually prepared as a 0.04% aqueous solution.

In staining dyes, nigrosin is a mixture of black synthetic dyes made by heating a mixture of nitrobenzene, aniline, and hydrochloric acid in the presence of copper or iron. Related to induline, it is a mixture of phenazine-based compounds. Its main industrial uses are as a colorant for lacquers and varnishes and in marker pen inks. Sulfonation of nigrosin yields a water-soluble anionic dye, nigrosin WS.

Toluidine blue, also known as TBO or tolonium chloride (INN) is a blue cationic (basic) dye used in histology and sometimes clinically.
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.

Aluminon, the triammonium salt of aurintricarboxylic acid, is a dye often used to detect the presence of the aluminium ion in an aqueous solution. Aluminon forms a red complex salt in combination with Al3+.

An electrophoretic color marker is a chemical used to monitor the progress of agarose gel electrophoresis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) since DNA, RNA, and most proteins are colourless. The color markers are made up of a mixture of dyes that migrate through the gel matrix alongside the sample of interest. They are typically designed to have different mobilities from the sample components and to generate colored bands that can be used to assess the migration and separation of sample components.

A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis.

Alcian blue is any member of a family of polyvalent basic dyes, of which the Alcian blue 8G has been historically the most common and the most reliable member. It is used to stain acidic polysaccharides such as glycosaminoglycans in cartilages and other body structures, some types of mucopolysaccharides, sialylated glycocalyx of cells etc. For many of these targets it is one of the most widely used cationic dyes for both light and electron microscopy. Use of alcian blue has historically been a popular staining method in histology especially for light microscopy in paraffin embedded sections and in semithin resin sections. The tissue parts that specifically stain by this dye become blue to bluish-green after staining and are called "Alcianophilic". Alcian blue staining can be combined with H&E staining, PAS staining and van Gieson staining methods. Alcian blue can be used to quantitate acidic glycans both in microspectrophotometric quantitation in solution or for staining glycoproteins in polyacrylamide gels or on western blots. Biochemists had used it to assay acid polysaccharides in urine since the 1960s for diagnosis of diseases like mucopolysaccharidosis but from 1970's, partly due to lack of availability of Alcian and partly due to length and tediousness of the procedure, alternative methods had to be developed e.g. Dimethyl methylene blue method.

Stains-all is a carbocyanine dye, which stains anionic proteins, nucleic acids, anionic polysaccharides and other anionic molecules.