In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region.

The Regional Policy of the European Union (EU), also referred as Cohesion Policy, is a policy with the stated aim of improving the economic well-being of regions in the European Union and also to avoid regional disparities. More than one third of the EU's budget is devoted to this policy, which aims to remove economic, social and territorial disparities across the EU, restructure declining industrial areas and diversify rural areas which have declining agriculture. In doing so, EU regional policy is geared towards making regions more competitive, fostering economic growth and creating new jobs. The policy also has a role to play in wider challenges for the future, including climate change, energy supply and globalisation.

The European Structural and Investment Funds are financial tools governed by a common rulebook, set up to implement the regional policy of the European Union, as well as the structural policy pillars of the Common Agricultural Policy and the Common Fisheries Policy. They aim to reduce regional disparities in income, wealth and opportunities. Europe's poorer regions receive most of the support, but all European regions are eligible for funding under the policy's various funds and programmes. The current framework is set for a period of seven years, from 2021 to 2027.

The European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) is one of the European Structural and Investment Funds allocated by the European Union. Its purpose is to transfer money from richer regions, and invest it in the infrastructure and services of underdeveloped regions. This will allow those regions to start attracting private sector investments, and create jobs on their own.
Interreg is a series of programmes to stimulate cooperation between regions in and out of the European Union (EU), funded by the European Regional Development Fund. The first Interreg started in 1989. Interreg IV covered the period 2007–2013. Interreg V (2014–2020) covers all 27 EU member states, the EFTA countries, six accession countries and 18 neighbouring countries. It has a budget of EUR 10.1 billion, which represents 2.8% of the total of the European Cohesion Policy budget. Since the non EU countries don't pay EU membership fee, they contribute directly to Interreg, not through ERDF.
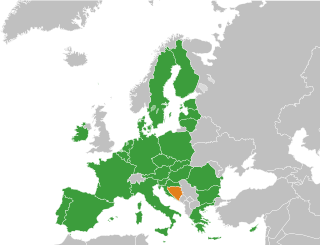
The accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union (EU) is the stated aim of the present relations between the two entities. Bosnia and Herzegovina has been recognised by the European Union as a "candidate country" for accession since the decision of the European Council in 2022 and is on the current agenda for future enlargement of the EU. Bosnia and Herzegovina takes part in the Stabilisation and Association Process and trade relations are regulated by an Interim Agreement.
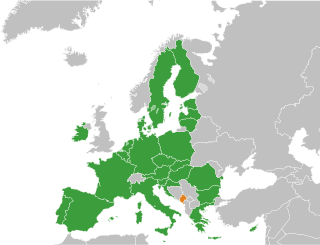
Accession of Montenegro to the European Union is on the agenda for future enlargement of the EU.
The Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance, or simply IPA, is a funding mechanism of the European Union. As of 2007, it replaced previous programmes such as the PHARE, ISPA, SAPARD and CARDS. Unlike the previous assistance programs, IPA offers funds to both EU candidate countries and potential candidates.
A cross-border region is a territorial entity that is made of several local or regional authorities that are co-located yet belong to different nation states. Cross-border regions exist to take advantage of geographical conditions to strengthen their competitiveness.
European Union (EU) concepts, acronyms, and jargon are a terminology set that has developed as a form of shorthand, to quickly express a (formal) EU process, an (informal) institutional working practice, or an EU body, function or decision, and which is commonly understood among EU officials or external people who regularly deal with EU institutions.
A European grouping of territorial cooperation (EGTC) is a European Union level form of transnational cooperation between countries and local authorities with legal personality. EU Council Regulation 1082/2006 of 5 July 2006 forms its legal basis. As of April 2021, 78 EGTCs are in existence.
EUREGIO is a cross-border region between the Netherlands and Germany and the first Euroregion. It was founded in 1958 as a German Eingetragener Verein, and has been converted in 2016 into a public body based on the 1991 Treaty of Anholt. Participating communities are in Niedersachsen and Nordrhein-Westfalen (Münsterland) in Germany and parts of the Dutch provinces Gelderland, Overijssel and Drenthe. Participating cities in the region are Münster, Osnabrück, Gronau, Enschede, and Hengelo. The headquarters of the Euregio is located in the city of Gronau, at the Dutch border.

Region Sønderjylland–Schleswig is the regional centre for cross-border cooperation between the municipalities of Tønder, Aabenraa, Haderslev and Sønderborg, the regional council of southern Denmark, the districts Schleswig-Flensburg and Nordfriesland, and the independent city of Flensburg.

The LIFE programme is the European Union's funding instrument for the environment and climate action. The general objective of LIFE is to contribute to the implementation, updating and development of EU environmental and climate policy and legislation by co-financing projects with European added value. LIFE began in 1992 and to date there have been five phases of the programme. During this period, LIFE has co-financed some 4600 projects across the EU, with a total contribution of approximately 6.5 billion Euros to the protection of the environment and of climate. For the next phase of the programme (2021–2027) the European Commission proposed to raise the budget to 5.45 billion Euro.
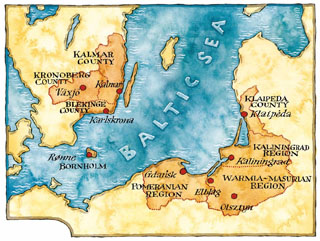
The Euroregion Baltic (ERB) refers to a cross-border Euroregion in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. On 2 March 2022, the ERB's Executive Board suspended Russia's membership, in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine.

The Pyrenees–Mediterranean Euroregion (EPM) is a European Grouping of Territorial Cooperation (EGTC). Founded in 2004, it is a political cooperation organisation between the Generalitat of Catalonia, the Government of the Balearic Islands and the Occitanie / Pyrénées-Méditerranée Region.

Andreas Kiefer is an Austrian politician. Since 2010, he is Secretary General of the Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of the Council of Europe, an institution representing local and regional authorities of the 47 member states of the Council of Europe.

The Trinational Eurodistrict of Basel, or Basel metropolitan area, extends across three countries: Switzerland, France and Germany. The Trinational Eurodistrict of Basel is an organization of municipalities and cities in the trinational surroundings of Basel. The TEB acts as coordinator for cross-border projects between the German, French and Swiss cities around Basel and promotes the cultural and linguistic exchange between the people living in the region. This very close cooperation and coordination is necessary as the national borders run through a densely built area. The TEB forms an extension of the Trinational Agglomeration Basel (German: Trinationale Agglomeration Basel /French: Agglomération Trinationale de Bâle.
The Euroregion Elbe/Labe is one of the Euroregions with German and Czech participation. The purpose of the community of municipal interests is cross-border cooperation on a supranational level. The term is used to refer to both the organization and the geographical area of its operation.

The Strategy for the Western Balkans is a policy pursued by the EU with its partners and accession candidates in the western region of the Balkan Peninsula. Announced by European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker in his 2017 State of the Union address, this policy brings together the objectives of the global strategy for CSDP and the enlargement policy specific to the states in this region.











