
The capybara or greater capybara is the largest living rodent, native to South America. It is a member of the genus Hydrochoerus. The only other extant member is the lesser capybara. Its close relatives include guinea pigs and rock cavies, and it is more distantly related to the agouti, the chinchilla, and the nutria. The capybara inhabits savannas and dense forests, and lives near bodies of water. It is a highly social species and can be found in groups as large as 100 individuals, but usually live in groups of 10–20 individuals. The capybara is hunted for its meat and hide and also for grease from its thick fatty skin.

The rough-toothed dolphin is a species of dolphin that can be found in deep warm and tropical waters around the world.
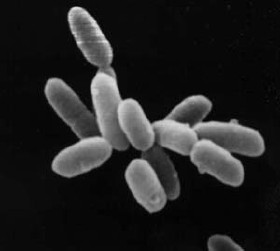
Euryarchaeota is a kingdom of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines; halobacteria, which survive extreme concentrations of salt; and some extremely thermophilic aerobes and anaerobes, which generally live at temperatures between 41 and 122 °C. They are separated from the other archaeans based mainly on rRNA sequences and their unique DNA polymerase.

Nepidae is a family of exclusively aquatic Heteropteran insects in the order Hemiptera. They are commonly called water scorpions for their superficial resemblance to scorpions, due to their raptorial forelegs and the presence of a long slender process at the posterior end of the abdomen, resembling a tail. There are 14 genera in the family, in two subfamilies, Nepinae and Ranatrinae. Members of the genus Ranatra, the most widespread and species-rich genus, are sometimes called needle bugs or water stick insects as they are slenderer than Nepa.

Ranatra is a genus of slender predatory insects of the family Nepidae, known as water scorpions or water stick-insects. There are around 100 Ranatra species found in freshwater habitats around the world, both in warm and temperate regions, with the highest diversity in South America and Asia. Fewer are found elsewhere, but include several African, some in North America, three from Australia and three from the Palearctic, notably the relatively well-known European R. linearis. Since Ranatra belongs to the family Nepidae which in turn belongs to the order Hemiptera, ranatrids are considered "true bugs".

Nepomorpha is an infraorder of insects in the "true bug" order (Hemiptera). They belong to the "typical" bugs of the suborder Heteroptera. Due to their aquatic habits, these animals are known as true water bugs. They occur all over the world outside the polar regions, with about 2,000 species altogether. The Nepomorpha can be distinguished from related Heteroptera by their missing or vestigial ocelli. Also, as referred to by the obsolete name Cryptocerata, their antennae are reduced, with weak muscles, and usually carried tucked against the head.

Water stagnation or still water occurs when water stops flowing for a long period of time. Stagnant water can be a significant environmental hazard.

Lantana camara is a species of flowering plant in the verbena family (Verbenaceae), native to the American tropics. It is a very adaptable species, which can inhabit a wide variety of ecosystems; once it has been introduced into a habitat it spreads rapidly; between 45ºN and 45ºS and less than 1,400 metres in altitude.

In biology, the term raptorial implies much the same as predatory but most often refers to modifications of an arthropod's foreleg that make it function for the grasping of prey while it is consumed, where the gripping surfaces are formed from the opposing faces of two successive leg segments.

Nepa is a genus belonging to the family Nepidae, known as water scorpions. There are six species found in freshwater habitats in the Northern Hemisphere.

Ranatra linearis is a species of aquatic bug in the Nepidae family. It is native to Eurasia and North Africa, and primarily found near aquatic plants in ponds, marshes and other freshwater habitats, but has exceptionally been recorded from hypersaline lakes and brackish lagoons.

Ranatra kirkaldyi is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in North America.
Ranatra brevicollis is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Ranatra australis, the southern water scorpion, is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in North America.
Curicta is a genus of waterscorpions in the family Nepidae native to freshwater habitats in the Americas. There are more than 15 species, with most restricted to South America. There are only two species in the United States: C. pronotata and C. scorpio.
Ranatra quadridentata is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Ranatra buenoi is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in North America.

Nepa apiculata is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in eastern North America. This species is active from spring to fall and feed on a wide variety of aquatic invertebrates. They have leaf-shaped bodies which allow them to camouflage. They've been known to hibernate during droughts as well as winter.

Curicta scorpio is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Ranatra montezuma is a species of waterscorpion in the family Nepidae. It is endemic to Montezuma Well in Yavapai County, Arizona, United States.












