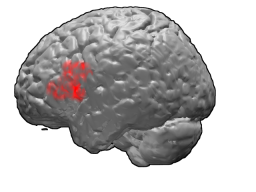
Brodmann area 45 (BA45), is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. It is situated on the lateral surface, inferior to BA9 and adjacent to BA46.

The inferior frontal gyrus is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex.

Hydrops triangularis, commonly known as the water false coral snake, triangle water snake, triangle watersnake, or water coral, is a species of snake endemic to northern South America and the Amazon Basin.
The Famennian is the later of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian epoch. The most recent estimate for its duration is that it lasted from around 371.1 to 359.3 million years ago. An earlier 2012 estimate, still used by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, is that it lasted from 372.2 million years ago to 358.9 million years ago. It was preceded by the Frasnian stage and followed by the Tournaisian stage.

The antihelix (anthelix) is a part of the visible ear; the pinna. The antihelix is a curved prominence of cartilage parallel with and in front of the helix on the pinna.

Uperodon triangularis is a species of narrow-mouthed frog found in southwestern India. They are endemic to the Western Ghats, where they are known to breed in water collected in tree hollows. The advertisement calls of males is made up of about 30 pulses of 0.38 second duration with a frequency range of 0.6 and 1.1 kHz. These are emitted every three seconds.

The olive-backed woodcreeper is a species of bird in the subfamily Dendrocolaptinae of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.

Rilaena triangularis is a species of the harvestman family Phalangiidae. It is sometimes considered to be in the genus Paraplatybunus, in the subfamily Platybuninae.

Astartidae is a family of bivalves related in the order Carditida.

Oxalis triangularis, commonly called false shamrock, is a species of perennial plant in the family Oxalidaceae. It is native to several countries in southern South America. This woodsorrel is typically grown as a houseplant but can be grown outside in USDA climate zones 8a–11, preferably in light shade.
The Dapingian is the third stage of the Ordovician system and the first stage of the Middle Ordovician series. It is preceded by the Floian and succeeded by the Darriwilian. The base of the Dapingian is defined as the first appearance of the conodont species Baltoniodus triangularis which happened about 470 million years ago. The Dapingian lasted for about 2.7 million years until about 467.3 million years ago.

Pentagramma is a small genus of North American ferns in the family Pteridaceae. Until 1990 members of this genus were included in Pityrogramma, and there has been considerable disagreement regarding the species' taxonomy. In the most recent treatment, six diploid species are recognized.

Lotoria triangularis is a species of predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cymatiidae.

Pentagramma triangularis, commonly known as the gold fern or the goldback fern, is a species of fern in the family Pteridaceae, native to Western North America, with highest abundance in the state of California. Its common name "goldback" refers to the light yellow color of the fern's protective coating which inhibits moisture loss. The gold texture appears as a dry powder that is excreted on the underside of the fern. The Latin specific epithet Pentagramma derives from "five lines" or "stripes" while triangularis derives from "three sided", describing the shape of the fern's broad triangular fronds.

Linyphia triangularis is a European species of spider in the family Linyphiidae first described by Carl Alexander Clerck in his 1758 Svenska Spindlar.

Grypotheca triangularis is a moth of the Psychidae family. It was first described by Alfred Philpott in 1930 under the name Talaeporia triangularis. In 1987 John S. Dugdale placed this species within the genus Grypotheca. It is endemic to New Zealand.
Oreodera triangularis is a species of long-horned beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It is found in Brazil.

Rhyothemis triangularis is a species of dragonfly in the family Libellulidae. It is widespread in eastern and southern Asia.
Palmatolepis is an extinct conodont genus in the family Palmatolepidae. It was the most abundant genus of conodonts of the Late Devonian, disappearing during the Devonian/Carboniferous crisis.
Baltoniodus is an extinct genus of conodonts.













