The Debt Management and Financial Analysis System (DMFAS) Programme is a technical assistance programme managed by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), in Geneva. The objectives of the DMFAS Programme are to assist countries to develop administrative, institutional and legal structures for effective debt management; to provide technical assistance to government offices in charge of debt management; to deploy and advance debt analysis and management systems; and to act as a focal point for discussion and exchange of experiences in debt management. The Programme's debt management software system is currently installed in over ninety government institutions, almost exclusively ministries of finance and/or central banks.
In 1975, the inter-sessional oversight body of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Trade and Development Board (TDB), [1] endorsed a recommendation of an UNCTAD Ad hoc Group of Governmental Experts which were that UNCTAD "be invited to participate in the multilateral debt negotiations on the same basis as the representatives of other international organizations". [2]
The intention was that UNCTAD – formally in the capacity of an observer – help the debtor countries present their case to the creditors. However, the resolution did not specify which negotiations. The fourth UNCTAD Conference, UNCTAD IV, in May 1976, requested the UNCTAD Secretary-General to convene a new "Ad hoc Intergovernmental Group of Experts on Debt and Development Problems". [3] This group met on a regular basis from 1976 to 1983. [4]
The Expert's Group worked to produce a draft on sovereign debt renegotiation and retroactive terms of aid. In March 1978, the TDB in its Special Session IX at Ministerial level, adopted by consensus Resolution 165 S-IX, which said that sovereign debt problems should be addressed in "an appropriate multilateral framework consisting of interested parties" (paragraph 10-b). This was understood to be an implicit reference to the Paris Club as the only "appropriate multilateral framework", and opened the door to UNCTAD participation to this forum based on TDB Resolution 132 (XV). [5]
In the negotiation of Resolution 165 (S-IX), OECD countries made substantial concessions on debt relief (Part A of the Resolution) but resisted the formal introduction of a debt restructuring mechanism (Part B of the Resolution). This resolution also implicitly introduced the Paris Club as the "appropriate multilateral framework" for international consideration of debt problems of developing countries, as noted earlier. Part A of the resolution contained an agreement on "retroactive terms adjustment" on aid for a group of 30 least developed countries (i.e. repayment obligations on outstanding aid loans were changed to the easier terms that donors were now offering these countries). Some OECD countries that had decided to give aid exclusively as grants implemented this resolution by cancelling old debts, making this a precursor of the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative.
The debate ended in September 1980 when TDB Resolution 222 (XXI) was adopted by consensus. Part B of the resolution contains the "Detailed Features for Future Operations Relating to the Debt Problems of Interested Developing Countries". The Resolution was adopted without dissent, albeit with France abstaining to emphasise its strict neutrality, being the host of the debt renegotiations, as this time the resolution made explicit reference to the Paris Club as the recognised multilateral forum for bilateral debt rescheduling. [6] Part B of resolution 222 (XXI), the "Detailed Features for Future Operations Relating to the Debt Problems of Interested Developing Countries", were in fact an agreed "code of conduct" for official debt rescheduling as only governments (UNCTAD constituency) were represented when it was adopted. [7]
Since 1979, based on TDB Resolutions 132 (XV) and 165 S-IX, UNCTAD has attended practically all Paris Club meetings that involved developing countries or economies in transition. The UNCTAD Division that was nominated to attend the Paris Club was the "Money, Finance and Development Division" (presently "Globalization and Development Strategies"), led at the time by Gerasimos Arsenis (Greece). This division had in charge, among other duties, the economic forecasts for the Trade and Development Report, one of UNCTAD's flagship reports. The quantitative team of this division belonged to the Trade and Projections Branch, which officers were commissioned since 1979 to help countries in debt difficulties to present their cases to the Paris Club. The reason for this was that the staffs of that branch maintained a set of econometric models for major developing countries around the world, and had the quantitative skills for calculating additional flows needed to close the balance of payment gap, either through new flows or through rescheduling of debt. This team was composed by Kenneth Ruffing (United States) team leader; Enrique Cosío-Pascal (Mexico) in charge of Latin America; Valery Prokohrenkov (USSR) in charge of North Africa and the Middle East; Sam Chan-Tung (Mauritius) in charge of Asia and Oceania; Kombo Moyana (Zimbabwe) in charge of Sub-Saharan Africa; and Jacques Baert (Belgium) statistical assistant of the Branch.
When UNCTAD started to support countries attending debt rescheduling negotiations in 1979, data were needed to make calculations. The first difficulty the Trade and Projections Branch staffs encountered was the lack of information on external debt of debtor countries: they did not know how much they owed, to what countries and what creditors, in what currencies the loans had to be repaid, when the payments were falling due and who the national debtors were. The idea of creating a computer-based debt management system (CBDMS) came out very naturally after this experience. The Branch staffs representing UNCTAD at the Paris Club in the early 1980s confirmed this lack of information as a general situation in developing countries. The question that came up at this stage was: why debtor countries did not have a CBDMS?
There were two major reasons why the debtor countries did not have accurate debt data and a performing CBDMS. The first one was the lack of centralisation of information on foreign debt and inefficient legislation on public guarantees. The second one was the lack of availability of debt managers to produce comprehensive specifications for computer specialists. The urgent nature of the problems that a debt manager had to solve at the time would lead him to address specific punctual problems, for instance preparing the Paris Club and then preparing the negotiations with private banks. This will imply the collection of data in two different databases and the development of two different computer systems. These two systems once developed they would be interfaced, the outcome being an inflexible and unpractical computer patchwork inefficient and expensive to maintain.
In 1981, Kombo Moyana left UNCTAD to join Bernard Chidzero, former Deputy Secretary-General of UNCTAD and Minister of Finance in Zimbabwe at the time. Other members of the Branch had to cover Sub-Saharan Africa waiting for the replacement of Moyana. In particular, Cosío-Pascal covered Liberia, Madagascar and Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo). Four countries, in 1981, agreed to form the initial DMFAS pool—contributing from their national United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) funds to a common technical cooperation fund with UNCTAD—that allowed the development of the first version. Those countries were two from Latin America: Bolivia and Costa Rica and two from Africa: Liberia and Madagascar. These resources allowed hiring a systems analyst, Pekka Sankala Finland and a programmer, Cameron Turkey. These two persons, jointly with Cosio-Pascal, team leader, and Baert, formed the first DMFAS Programme team. [8]
The first DMFAS version, finalised in early 1982, was developed in COBOL [9] and designed to run on an IBM System/370 mainframe computer. This very first version was installed at the National Institute of Statistics of Bolivia, which was the only institution in Bolivia owning an IBM 370 computer. However, at the time, the country was governed by a military junta, the Head of State being General Luis García Meza, and it was decided by the Bolivian authorities that external debt data was classified information, and no one should be able to access it, with the exception of the authorised persons belonging to the International Department of the Central Bank of Bolivia. Therefore, it was requested to UNCTAD to develop a DMFAS version for Personal Computer (PC) that should be at the Central Bank with limited access to authorised staffs. This was a very fortunate request, because PC's prices subsequently went down, is by far less expensive than mainframe computers, and since all DMFAS versions have been created to run on PCs. The second version of DMFAS, the PC version, was installed at the Central Bank of Bolivia, the Central Bank of Costa Rica and the Central Bank of Madagascar. It was never installed in Liberia due to the recrudescence of civil war.
The 1980s decade was characterised by a series of defaults and debt rescheduling negotiations by developing countries and some communist countries at the time. As a consequence, the demand for DMFAS increased very rapidly. The demand for the system was huge and the DMFAS team's staff number growth fast as well. By end of the 1980s, the team was of around 20 persons and the number of countries benefiting from DMFAS technical co-operation around 30 to 40. The demand was so high that around 1984 the Commonwealth Secretariat started to develop a CBDMS for its member countries, the CS-DRMS. However, the CS-DRMS is primarily targeted to English speaking countries, albeit there is a French version for some Sub-Saharan French-speaking countries. In comparison, DMFAS was created independently of the language the users would speak, which means that the "vocabulary" of the system is independent of the computer codes. Presently, the system can be set up to run in Arabic, English, French, Russian or Spanish. In addition to that, in a country running DMFAS in other languages than English, the system's administrator can switch momentarily the language to English to produce reports for the international financial community and switch it back to the users" language. [10]
The creation of DMFAS was a step forward for user debtor countries in improving their public debt management, in particular, external debt. However, the final goal at the time was to help countries pleading their case in negotiations, first with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to reach an agreement on an economic adjustment programme, and second at the debt rescheduling meeting with the creditor countries belonging to the Paris Club. It came out that a tool that would gather the aggregated figures of external debt and combine those with the balance of payments scenarios was necessary. Therefore, the DMFAS Programme, in the second half of the 1980s decade, assigned a team to develop the Debt Projections and Balance of Payments System (DPS). The team was composed by Cosío-Pascal, Baert and an external consultant David Nathan (UK). The DPS was developed in Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheets, which implied transportability and simplicity. The functionalities of the DPS included the combination of balance of payments scenarios with different "old debt" rescheduling scenarios and "new money" scenarios. The algorithm used by DPS to close the gap was the "net transfer approach". [11] In fact, the DPS was a precursor of a debt sustainability analysis template.
The DPS was a major breakthrough in the field of debt negotiations at the time because as it was developed in Lotus 1-2-3, it was suitable for portable computers that started to appear in the second half of the 1980s. Therefore, the negotiation team of many debtor countries—not only DMFAS countries, but any country attending the Paris Club—used DPS in the back of the negotiation room in order to assess the different proposals during a debt rescheduling meeting, which was a considerable advantage for the negotiators. The DPS was used intensively in Paris Club negotiations as well as in the major negotiation between the Mexican government and the private bank's steering committee chaired by William R. Rhodes in New York in 1988.
By the end of the 1980s, the DMFAS version 4 was a stable and fully-fledged computer-based debt management system (CBDMS). However, the computer and software techniques had evolved and it was more and more evident that a new platform for DMFAS was needed. Notwithstanding, a considerable amount of resources were needed to upgrade DMFAS from COBOL, which used indexed files, to a relational database system.
At the time, two major technical cooperation providers were helping indebted developing countries: the World Bank and UNCTAD. UNDP agreed to finance the upgrade of DMFAS under the condition that UNCTAD and the World Bank coordinated their technical activities on public debt management. Negotiations were undertaken between the two institutions and finally it was agreed that UNCTAD would have responsibility for the database with DMFAS and the World Bank would have responsibility for the analytical tool, which was DPS. The World Bank improved the DPS, which become the Debt Sustainability Model Plus (DSM+), [12] and upgraded it from Lotus 1-2-3 to Microsoft Excel. Later, the government budget was also included in DSM (DSM+) in which the budget gap was also closed with the same algorithm.
With the UNCTAD/World Bank agreement to work hand-in-hand providing technical assistance to developing countries, UNDP agreed to finance upgrading DMFAS to a relational database system. [13] The resources came from the Inter-regional UNDP funds and the amount was around US$5 million. The relational database chosen was ORACLE Database. The work and arrangements for choosing the relational database provider, hiring consultants and other organisational matters made that the development of DMFAS 5, to pass from COBOL to ORACLE started in 1992.
An unprecedented event arrived beginning of 1993: UNDP discovered that their resources were not enough to maintain the original pledge of US$5 million and requested UNCTAD to reimburse the unspent balance. This situation forced the DMFAS Programme and UNCTAD to make a call to the international financial community in order to continue with the work schedule.
At this time, the beginning of the 1990s, the insolvency problem by the heavily indebted poor countries (HIPC) was becoming more and more acute. The main objective that the HIPC Initiative addressed was debt relief, and the beneficiary countries had to take in hand their daily debt management responsibilities, among those, to maintain an accurate database of all public, domestic and external, public debt. Many DMFAS user countries were HIPCs, and this fact made that developed donor countries responded with alacrity to UNCTAD/DMFAS call: Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland and the U.K. responded positively to support the DMFAS Programme, either by depositing resources with UNCTAD technical cooperation trust funds or by putting at the disposal of the Programme Junior Professional Officers (JPOs), and in some cases, senior officers as well. Therefore, in spite of UNDP financing withdrawal, the upgrading to version DMFAS 5 in ORACLE was carried over.
Since that very first call to donor countries, the DMFAS Programme has been financed through regular UNCTAD budget, contribution from the beneficiary countries and contribution from donor countries. [14] [15] [16]
After several versions of DMFAS 5, a new major upgrading operation was undertaken by the DMFAS Programme in the second half of the 2000s decade. After an extensive selection process to carry out this migration, TGV - Excelencia en Soluciones Informáticas, an Argentine consulting firm with international presence, was selected. This new version, DMFAS 6, is an application for public debt management using the latest information technology. [17]
The development of a CBDMS is a complex matter and the reasons are multiple; for instance, each creditor has its own methodology to calculate accrual interest, fees and the rounding for the principal repayments. Second, the imagination of financial engineers is boundless and the CBDMS has to be enhanced in function of new financial products coming to the market.
There are three major comparative advantages regarding the central development of a system like DMFAS. The first one is the huge economies of scale created by the DMFAS Programme. Regarding the economies of scale, the core of the system is common to all countries and this avoids repeating the same development in each country. The development and enhancements of the DMFAS are demand-driven so that the system reflects all the functionalities that the users requested. The DMFAS staffs produce specifications that will lead to a comprehensive and coherent CBDMS. The final product is then a user-friendly, flexible and efficient tool.
The second one is that rotation of personnel within Debt Management Offices (DMO) is a real problem, and in many countries, no permanent solution has been found for hiring and retaining qualified personnel. DMOs are very often understaffed, but also its personnel are hired on temporary assignments or with provisional salary arrangements. The rate of turnover is often alarmingly high, without a corresponding capacity for in-service training in order to upgrade the knowledge of the remaining staff to quickly render new employees fully operational. This situation was identified very soon, actually within a report requested by UNDP at the end of the 1980s, and unfortunately, this situation has not changed very much in a large number of countries. [18] Therefore, the DMFAS Programme has performed as a repository of technical knowledge being able to re-train new personnel and re-installing DMFAS when necessary.
The third one is that installing DMFAS is less expensive than developing a wholly new system for reasons of cost and workability. Compared with designing, programming, and maintaining an entirely new system, packages can be relatively inexpensive. DMFAS designers with the help of users have debugged the available systems to the point where they are likely to have fewer operating problems than custom-made systems. They can be implemented quickly, and the maintenance is centralised, creating high economies of scale: the implementation of DMFAS, for instance, varies from 6 months to 3 years, in order to cover the full database depending on its complexity; this is fast compared to in-house development. The maintenance of a system is of vital importance; it has been proven that the personnel turnover in the IT Department—which is an observed characteristic of a developing country DMO as pointed out above—makes domestically developed systems very vulnerable. Choosing a standard software package like DMFAS also decreases the need to maintain a full group of developers within the DMO's IT department, there are only needs for maintenance and service for daily work, database management, and security procedures like regular backups.
The traditional conception for technical cooperation implied that an external team financed by external donors would help the beneficiary country to start a specific activity, and once the local team mastered the techniques and was able to obtain an income from the supported activity, the technical assistance came to an end.
The three points enumerated above implied a new approach for technical cooperation provided by DMFAS. The DMFAS Programme changed the philosophy of technical assistance, from the approach described in the previous paragraph, to a permanent service to "client countries"—no longer "beneficiaries" in the sense given by the traditional technical assistance approach—which accepted to pay an annual fee and share system development costs in exchange of a continuous technical support for their public debt management responsibilities.
Mid-2012 DMFAS was installed in 69 countries and more than 100 institutions: Ministries of Finance, Central Banks and other General Government institutions. [19]
Since 1992 the DMFAS Programme organised annual meetings for the DMOs beneficiaries of UNCTAD technical assistance on this matter, which was carried out in parallel with the "Debt Management Offices Network". However, in 1997 the DMFAS Programme launched the UNCTAD-DMFAS Debt Conference opened to all interested countries, not only for those that benefited from the DMFAS Programme technical assistance. The Conference was a full success, to such an extent, that the meeting room assigned by the Conference Services was too small for the number of delegates attending, people were standing in the room corridors. The Conference moved to one of the four largest Conference rooms in the new building of the Palais des Nations, and since, held in one of those large conference rooms.
UNCTAD invited the Bretton Woods institutions, the regional development banks and NGOs to the event. The World Bank Treasury found the event very interesting, and to some extent, regretted not having first the idea of such an event. Therefore, in 1998, the World Bank Treasury launched the Sovereign Debt Management Forum. UNCTAD and the Bank agreed on holding the events on a bi-annual basis, UNCTAD on odd years and the Bank on even years. Since then, the event is held regularly by the two institutions.
Presently, the Public Debt Management Network (PDM), composed by the Italian Ministry of Economy and Finance, the OECD and the World Bank, organises in more or less regular basis a Public Debt Management Conference. The last one was held in Paris in September 2019.
The latest UNCTAD Debt Management Conference [20] and DMFAS Advisory Group Meeting [21] were held in Geneva, Switzerland from 18 to 22 November 2019.
| Number | Name | Dates in office | Country of origin | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kenneth Ruffing | 1981–1984 | United States | Manager |
| 2 | John Burley | 1984–1985 | U.K. | Manager |
| 3 | Erling Nypan | 1985–1988 | Norway | Manager |
| 4 | Enrique Cosío-Pascal | 1989–2001 | Mexico | Chief |
| 5 | Philippe Straatman | 2001–2005 | Belgium | Chief |
| 6 | Gerard Teeling | 2007 – present | Ireland | Chief |

UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development but rebranded to its current name on the occasion of its 60th anniversary in 2024. It reports to both the General Assembly and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with non-governmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is at UNOG in Geneva, Switzerland.
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towards long-term self-sufficiency and prosperity.
Debt relief or debt cancellation is the partial or total forgiveness of debt, or the slowing or stopping of debt growth, owed by individuals, corporations, or nations.

The Global Environment Facility (GEF) is a multilateral environmental fund that provides grants and blended finance for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, persistent organic pollutants (POPs), mercury, sustainable forest management, food security, and sustainable cities in developing countries and countries with economies in transition. It is the largest source of multilateral funding for biodiversity globally and distributes more than $1 billion a year on average to address inter-related environmental challenges.
A country's gross external debt is the liabilities that are owed to nonresidents by residents. The debtors can be governments, corporations or citizens. External debt may be denominated in domestic or foreign currency. It includes amounts owed to private commercial banks, foreign governments, or international financial institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.

In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These were based on the OECD DAC International Development Goals agreed by Development Ministers in the "Shaping the 21st Century Strategy". The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) succeeded the MDGs in 2016.
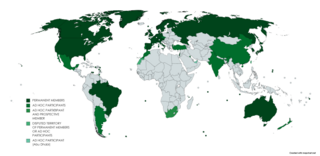
Paris Club is a group of major creditor countries aiming to provide a sustainable way to tackle debt problems in debtor countries.
The Doha Development Round or Doha Development Agenda (DDA) is the trade-negotiation round of the World Trade Organization (WTO) which commenced in November 2001 under then director-general Mike Moore. Its objective was to lower trade barriers around the world, and thus increase global trade.

Sinan Al-Shabibi was an Iraqi economist who served as the governor of the Central Bank of Iraq from September 2003 to October 2012.

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development's (OECD) Development Assistance Committee (DAC) is a forum to discuss issues surrounding aid, development and poverty reduction in developing countries. It describes itself as being the "venue and voice" of the world's major donor countries.

The International Trade Centre (ITC) is a multilateral agency which has a joint mandate with the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the United Nations (UN) through the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).

The IBSA Dialogue Forum is an international tripartite grouping for promoting international cooperation among these countries. It represents three important poles for galvanizing South–South cooperation and greater understanding between three important continents of the developing world namely, Africa, Asia, and South America. The forum provides the three countries with a platform to engage in discussions for cooperation in the field of agriculture, trade, culture, and defence among others.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG), previously the United Nations Development Group (UNDG), is a group of 36 United Nations funds, programmes, specialized agencies, departments and offices that play a role in development. It was created by the Secretary-General of the United Nations in order to improve the effectiveness of United Nations development activities at the country level.

Israel Eliashiv is an Israeli diplomat who served as the country's ambassador to Singapore between 1987 and 1990.

The Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (G.S.T.P) is a preferential trade agreement, currently encompassing 42 members ("participants"), signed on 13 April 1988 with the aim of increasing trade between developing countries. It was negotiated within the framework of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). The Agreement entered into force on 19 April 1989 and was notified to the then General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), predecessor of the World Trade Organization (WTO), on 25 September 1989. The 42 members of GSTP include 7 LDCs as well.
The United Nations Guidelines for Consumer Protection (UNGCP) relate to consumer protection goals. The statement supplied is that the guidelines are "a valuable set of principles for setting out the main characteristics of effective consumer protection legislation, enforcement institutions and redress systems and for assisting interested Member States in formulating and enforcing domestic and regional laws, rules and regulations that are suitable to their own economic and social and environmental circumstances, as well as promoting international enforcement cooperation among Member States and encouraging the sharing of experiences in consumer protection."

Üner Kirdar is a noted author on international development issues, retired Turkish diplomat and senior United Nations official. He is one of the early pioneers of Human development theory and, since the mid-1980s, has advocated and worked for the concept’s worldwide adoption.
Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) was approved in June 2005 by the finance ministers of the G8 during the 31st G8 Summit, held at Gleneagles, Scotland. MDRI is different to HIPC, but operationally related. Countries in the termination point get full relief of their debt with IMF, International Development Association (IDA) and the African Development Bank (AfDB). MDRI was approved for encouraging debtor countries to continue their political reforms. For reasons of equal treatment of Low Income Countries (LIC) the relieved debts were counted when new ancillary remedies were guaranteed by IDA and AfDB. G8 members committed themselves to compensate IDA and AfDB refluxes with further remedies. These compensations will be shared among IDA and AfDB beneficiary countries according to the efforts they make.

Sustainable Development Goal 17 is about "partnerships for the goals." One of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015, the official wording is: "Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development". SDG 17 refers to the need for the nonhegemonic and fair cross sector and cross country collaborations in pursuit of all the goals by the year 2030. It is a call for countries to align policies.
The Nigeria national debt or simply national debt of Nigeria is the total amount of money that the Federal Government of Nigeria owes to its creditors, both domestic and external. The national debt is composed of two main components: debt held by the public and debt held by government accounts. Debt held by the public includes Treasury securities held by investors outside the federal government, such as individuals, corporations, the Central Bank of Nigeria, and foreign, state and local governments. Debt held by government accounts includes non-marketable Treasury securities held in accounts of programs administered by the federal government, such as the Nigeria Social Insurance Trust Fund. The national debt is measured as the face value of the outstanding Treasury securities at a given point in time.