Related Research Articles

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance, as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.

Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages.
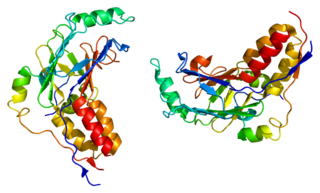
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways.
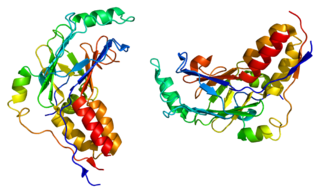
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

SMAD family member 6, also known as SMAD6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD6 gene.

Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD7 gene.
R-SMADs are receptor-regulated SMADs. SMADs are transcription factors that transduce extracellular TGF-β superfamily ligand signaling from cell membrane bound TGF-β receptors into the nucleus where they activate transcription TGF-β target genes. R-SMADS are directly phosphorylated on their c-terminus by type 1 TGF-β receptors through their intracellular kinase domain, leading to r-SMAD activation.
Smads comprise a family of structurally similar proteins that are the main signal transducers for receptors of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) superfamily, which are critically important for regulating cell development and growth. The abbreviation refers to the homologies to the Caenorhabditis elegans SMA and MAD family of genes in Drosophila.
The transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) signaling pathway is involved in many cellular processes in both the adult organism and the developing embryo including cell growth, cell differentiation, cell migration, apoptosis, cellular homeostasis and other cellular functions. The TGFB signaling pathways are conserved. In spite of the wide range of cellular processes that the TGFβ signaling pathway regulates, the process is relatively simple. TGFβ superfamily ligands bind to a type II receptor, which recruits and phosphorylates a type I receptor. The type I receptor then phosphorylates receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs) which can now bind the coSMAD SMAD4. R-SMAD/coSMAD complexes accumulate in the nucleus where they act as transcription factors and participate in the regulation of target gene expression.

Activin receptor type-1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1B gene.

Transforming growth factor beta receptor I is a membrane-bound TGF beta receptor protein of the TGF-beta receptor family for the TGF beta superfamily of signaling ligands. TGFBR1 is its human gene.

Transforming growth factor, beta receptor II (70/80kDa) is a TGF beta receptor. TGFBR2 is its human gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ACVRL1 gene.
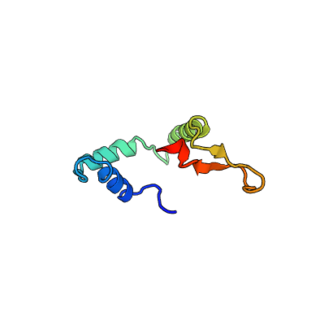
DAF-16 is the sole ortholog of the FOXO family of transcription factors in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. It is responsible for activating genes involved in longevity, lipogenesis, heat shock survival and oxidative stress responses. It also protects C.elegans during food deprivation, causing it to transform into a hibernation - like state, known as a Dauer. DAF-16 is notable for being the primary transcription factor required for the profound lifespan extension observed upon mutation of the insulin-like receptor DAF-2. The gene has played a large role in research into longevity and the insulin signalling pathway as it is located in C. elegans, a successful ageing model organism.
The DAF-4 gene encodes for the only type II receptor of TGF-beta signaling pathway in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, with the ligands Daf-7 or Dbl-1. When binds to the ligand Daf-7, Daf-4 complexed with the type I receptor Daf-1, and activated the Smad Protein Daf-8/14. By contrast, when binds to Dbl-1, Daf-4 complexed with the Sma-6 type I receptor, and activated the Sma-2/3/4.
The DAF-7 gene encodes for the ortholog of GDF11, a ligand of TGF-beta signaling pathway, in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans. When binds to the complex of type II receptor Daf-4 and type I receptor Daf-1, this receptor protein serine/threonine kinase will phosphorylation activate the Smad Protein Daf-8/14.
The DAF-8 nematode gene encoding a R-SMAD protein of TGF-beta signaling pathway, which was originally found in model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. When the TGF-β ligand daf-7 binds to the TGF-β receptors daf-1/daf-4 on the surface of nematode cell, daf-8 will be phosphorylated and forms a heterodimer with daf-14, then enter to the nucleus to inhibit transcription regulated by daf-3/daf-5.
The DAF-14 is a gene of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans encoding a R-SMAD protein of TGF-beta signaling pathway, which will be phosphorylated and forms a heterodimer with phosphorylated daf-8 when the TGF-β ligand daf-7 binds to the TGF-β receptors daf-1/daf-4, then the heterodimer enter to the nucleus to inhibit transcription regulated by daf-3/daf-5.
The DAF-3 or Dwarfin sma is a nematode Caenorhabditis elegans gene encoding a Co-SMAD protein of TGF-beta signaling pathway. Without daf-7 signal, DAF-3 combined with transcription factor daf-5 to form a heterodimer and started dauer development. When daf-7 binds to the receptors daf-1/daf-4, the phosphorylated daf-8/daf-14 heterodimer enter to the nucleus to inhibit this transcription.

The age-1 gene is located on chromosome 2 in C.elegans. It gained attention in 1983 for its ability to induce long-lived C. elegans mutants. The age-1 mutant, first identified by Michael Klass, was reported to extend mean lifespan by over 50% at 25 °C when compared to the wild type worm (N2) in 1987 by Johnson et al. Development, metabolism, lifespan, among other processes have been associated with age-1 expression. The age-1 gene is known to share a genetic pathway with daf-2 gene that regulates lifespan in worms. Additionally, both age-1 and daf-2 mutants are dependent on daf-16 and daf-18 genes to promote lifespan extension.
References
- ↑ Georgi LL, Albert PS, Riddle DL (May 1990). "daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase". Cell. 61 (4): 635–45. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. PMID 2160853. S2CID 205020137.
- ↑ Morita K, Shimizu M, Shibuya H, Ueno N (May 2001). "A DAF-1-binding protein BRA-1 is a negative regulator of DAF-7 TGF-beta signaling". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (11): 6284–8. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.6284M. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111409798 . PMC 33460 . PMID 11353865.
- ↑ Krishna S, Maduzia LL, Padgett RW (January 1999). "Specificity of TGFbeta signaling is conferred by distinct type I receptors and their associated SMAD proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans". Development. 126 (2): 251–60. doi:10.1242/dev.126.2.251. PMID 9847239. S2CID 2460114.