Related Research Articles

In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep.

The Assam earthquake of 1897 occurred on 12 June 1897, in Assam, British India at 11:06 UTC, and had an estimated moment magnitude of 8.2–8.3. It resulted in approximately 1,542 human casualties and caused catastrophic damage to infrastructures. Damage from the earthquake extended into Calcutta, where dozens of buildings were severely damaged, with some buildings partially collapsing. Trembles were felt across India, reaching as far as Ahmedabad and Peshawar. Seiches were also observed in Burma.
Strike-slip tectonics or wrench tectonics is a type of tectonics that is dominated by lateral (horizontal) movements within the Earth's crust. Where a zone of strike-slip tectonics forms the boundary between two tectonic plates, this is known as a transform or conservative plate boundary. Areas of strike-slip tectonics are characterised by particular deformation styles including: stepovers, Riedel shears, flower structures and strike-slip duplexes. Where the displacement along a zone of strike-slip deviates from parallelism with the zone itself, the style becomes either transpressional or transtensional depending on the sense of deviation. Strike-slip tectonics is characteristic of several geological environments, including oceanic and continental transform faults, zones of oblique collision and the deforming foreland of zones of continental collision.

The Geology of Bangladesh is affected by the country's location, as Bangladesh is mainly a riverine country. It is the eastern two-thirds of the Ganges and Brahmaputra river delta plain stretching to the north from the Bay of Bengal. There are two small areas of slightly higher land in the north-centre and north-west composed of old alluvium called the Madhupur Tract and the Barind Tract, and steep, folded, hill ranges of older (Tertiary) rocks along the eastern border.

The 1927 Gulang earthquake occurred at 6:32 a.m. on 22 May. This 7.6 magnitude event had an epicenter near Gulang, Gansu in the Republic of China. There were 40,912 deaths. It was felt up to 700 km (435 mi) away.

The Marlborough fault system is a set of four large dextral strike-slip faults and other related structures in the northern part of South Island, New Zealand, which transfer displacement between the mainly transform plate boundary of the Alpine fault and the mainly destructive boundary of the Kermadec Trench, and together form the boundary between the Australian and Pacific Plates.

The 1976 Çaldıran–Muradiye earthquake occurred at 14:22 local time on 24 November. The epicenter was located near Çaldıran, 20 km northeast of Muradiye, in the Van Province of eastern Turkey. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.3 with a maximum intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The area of severe damage, where over 80% of the buildings were destroyed, covered an area of 2,000 square kilometres. There were between 4,000 and 5,000 casualties.
The 1932 Ierissos earthquake occurred at 19:20 on 26 September. It caused severe damage in Ierissos, Greece and the surrounding part of the Chalkidiki peninsula, with 161–491 casualties reported.
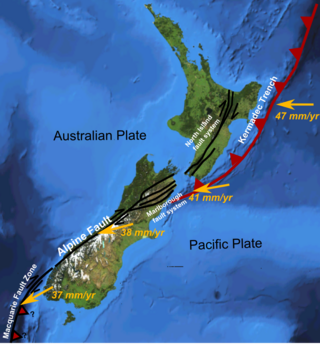
The North Island Fault System (NIFS) is a set of southwest–northeast trending seismically-active faults in the North Island of New Zealand that carry much of the dextral strike-slip component of the oblique convergence of the Pacific Plate with the Australian Plate. However despite at least 3 km (1.9 mi) of uplift of the axial ranges in the middle regions of the fault system during the last 10 million years most of the shortening on this part of the Hikurangi Margin is accommodated by subduction.
The 1762 Arakan earthquake occurred at about 17:00 local time on 2 April, with an epicentre somewhere along the coast from Chittagong to Arakan in modern Myanmar. It had an estimated moment magnitude between 8.5 and 8.8 and a maximum estimated intensity of XI (Extreme). It triggered a local tsunami in the Bay of Bengal and caused at least 200 deaths. The earthquake was associated with major areas of both uplift and subsidence. It is also associated with a change in course of the Brahmaputra River to from east of Dhaka to 150 kilometres (93 mi) to the west via the Jamuna River.
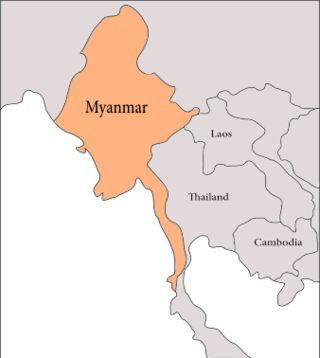
The geology of Myanmar is shaped by dramatic, ongoing tectonic processes controlled by shifting tectonic components as the Indian plate slides northwards and towards Southeast Asia. Myanmar spans across parts of three tectonic plates separated by north-trending faults. To the west, a highly oblique subduction zone separates the offshore Indian plate from the Burma microplate, which underlies most of the country. In the center-east of Myanmar, a right lateral strike slip fault extends from south to north across more than 1,000 km (620 mi). These tectonic zones are responsible for large earthquakes in the region. The India-Eurasia plate collision which initiated in the Eocene provides the last geological pieces of Myanmar, and thus Myanmar preserves a more extensive Cenozoic geological record as compared to records of the Mesozoic and Paleozoic eras. Myanmar is physiographically divided into three regions: the Indo-Burman Range, Myanmar Central Belt and the Shan Plateau; these all display an arcuate shape bulging westwards. The varying regional tectonic settings of Myanmar not only give rise to disparate regional features, but they also foster the formation of petroleum basins and a diverse mix of mineral resources.
The Haflong Thrust is the most persistent of the thrusts in the 400 km long Belt of Schuppen (BoS) in the western part of Nagaland. The Belt of Schuppen forms the outermost fringe of the mobile belt of the Assam–Arakan basin and forms the most prominent morphotectonic unit of the Naga Hills, where these overthrusts form a complex pattern. The frontal thrust, conventionally known as the Naga thrust, is seen to be composed of four different thrusts. The uppermost thrust is known as the Haflong (Disang) thrust. The Naga-Disang (Haflong) Overthrust area includes besides the Naga Hills proper, a few long ranges of hills fringing the plain of Upper Assam, and a large part of the North Cachar Hills. The Disang thrust continues in a south-westerly direction from the Naga Hills to Haflong, where it narrows to a complicated but narrow fracture band. This is the Haflong Fault. Along with two major thrusts, the Haflong-Naga Thrust and Disang Thrust, studies revealed three minor thrusts in the BoS.
The 1988 Lancang–Gengma earthquakes, also known as the 11.6 earthquakes by the Chinese media were a pair of devastating seismic events that struck Lancang and Gengma counties, Yunnan, near the border with Shan State, Burma. The earthquake measured moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.0 and was followed 13 minutes later by a 6.9 Mw shock. These earthquakes were assigned a maximum China seismic intensity of IX and X, respectively. Between 748 and 939 people were killed; more than 7,700 were injured. Both earthquakes resulted in US$270 million in damage and economic losses. Moderately large aftershocks continued to rock the region, causing additional casualties and damage.
A major seismic event occurred during the rule of the Qing dynasty in Shandong Province on July 25, 1668. The earthquake had an estimated magnitude of Ms 8.5, making it the largest historical earthquake in East China, and one of the largest to occur on land. The earthquake had cataclysmic implications to the region. An estimated 43,000 to 50,000 lives were lost in the earthquake, and its effects were widely felt. The epicenter may have been located between Ju and Tancheng counties, northeast of the prefecture-level city of Linyi in southern Shandong.
The 1739 Yinchuan–Pingluo earthquake rocked the northern Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region on January 3 with an epicenter in the prefecture-level city Shizuishan. The estimated magnitude 7.1–7.6 earthquake had a maximum intensity of XI on the Mercalli intensity scale, and killed about 50,000 residents and officials. It was widely felt; perceived in Shanxi, Shaanxi and Hebei provinces. Aftershocks persisted for more than two years with the largest being a 5.5 on February 13 that same year.
The 2021 Assam earthquake struck 11 km away from Dhekiajuli, Assam, India at 07:51 (IST) on April 28, 2021 with a moment magnitude of 6.0 at 34.0 km (21.1 mi) depth. The quake struck with an epicenter 140 km north of the main city of Guwahati. It resulted in two fatalities and at least 12 injuries.
The 1995 Menglian earthquake or 1995 Myanmar–China earthquake occurred on 12 July at 05:46:43 local time in the Myanmar–China border region. The earthquake had an epicenter on the Myanmar side of the border, located in the mountainous region of Shan State. It registered 7.3 on the Chinese surface wave magnitude scale (Ms ) and 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). With a maximum Mercalli intensity assigned at VIII, the quake killed eleven people and left another 136 injured. Over 100,000 homes in both countries were destroyed and 42,000 seriously damaged. Some damage to structures were also reported in Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai, Thailand. The low death toll from this earthquake was attributed to an early warning issued prior to it happening. Precursor events including foreshocks and some seismic anomalies led to an evacuation of the area before the mainshock struck. It is thought to be one of the few successfully predicted earthquakes in history.
The city of Kashan in Iran was struck by a major earthquake just before dawn on 15 December 1778. The earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 6.2 Ms. There was widespread damage in the area around the city, with most buildings destroyed. More than 8,000 people were killed.
The 1997 Bojnurd earthquake occurred on 4 February at 14:07 IRST in Iran. The epicenter of the Mw 6.5 earthquake was in the Kopet Dag mountains of North Khorasan, near the Iran–Turkmenistan border, about 579 km (360 mi) northeast of Tehran. The earthquake is characterized by shallow strike-slip faulting in a zone of active faults. Seismic activity is present as the Kopet Dag is actively accommodating tectonics through faulting. The earthquake left 88 dead, 1,948 injured, and affected 173 villages, including four which were destroyed. Damage also occurred in Shirvan and Bojnord counties. The total cost of damage was estimated to be over US$ 30 million.
The 1977 Bob–Tangol earthquake struck Kerman province of Iran on December 20, 1977 at 03:04 Iran Standard Time. The earthquake measured Mw 5.9 and struck at a depth of 22.7 km (14.1 mi). A maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VII was evaluated based on damage. It had a strike-slip focal mechanism, which was unusual as the source structure was a thrust fault. It was part of a sequence of strong earthquakes along the 400 km (250 mi) Kuh Banan Fault. Between 584 and 665 people perished while a further 500–1,000 were injured; thousands were also made homeless. Casualties from the earthquake was considered moderate due to the sparsely populated area it affected. Preceded by foreshocks the month before, many residents became wary of a larger earthquake and took refuge outside their homes, contributing to the moderate death toll. However, there were none immediately before the mainshock so many were still in their homes when it struck. Aftershocks were felt for several months, some causing additional damage.
References
- ↑ Md Shofiqul Islam, The Dauki fault at the Shillong plateau-bengal basin boundary in northeastern India: 2D finite element modeling, Journal of Earth Science
- 1 2 3 Morino, Michio; Maksud Kamal, A.S.M; Muslim, Dicky; Ekram Ali, Reshad Md; Kamal, Mohammad Ashraful; Zillur Rahman, Md; Kaneko, Fumio (2011), "Seismic event of the Dauki Fault in 16th century confirmed by trench investigation at Gabrakhari Village, Haluaghat, Mymensingh, Bangladesh", Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42 (3): 492, doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.05.002
- 1 2 Fault, Banglapedia, Asiatic Society Bangladesh
- ↑ P. Evans (1964) The Tectonic framework of Assam, Geological Society of India, vol. 5 pp.80–96
- ↑ Murthy et al (1969), ‘’The Dauki Fault of Assam’’, Oil and Natural Gas Commission Bulletin, vol 6 (2), pp 57–64
- 1 2 Morino, Michio; Kamal, A.S.M. Maksud; Akhter, S. Humayun; Rahman, Md. Zillur; Ali, Reshad Md. Ekram; Talukder, Animesh; Khan, Md. Mahmood Hossain; Matsuo, Jun; Kaneko, Fumio (2014), "A paleo-seismological study of the Dauki fault at Jaflong, Sylhet, Bangladesh: Historical seismic events and an attempted rupture segmentation model", Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 91: 218–226, doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.06.002
- ↑ Yeats et al (1997), The geology of earthquakes, Oxford University Press, p. 568
- ↑ J.D. Das et al, Fault tectonics of the Shillong plateau and adjoining regions, north-east India using remote sensing data, International Journal of Remote Sensing
- ↑ V. Srinivasan (2005), The Dauki fault in Northeast India: Through remote sensing. Journal of the Geological Society of India. 66. 413–426.