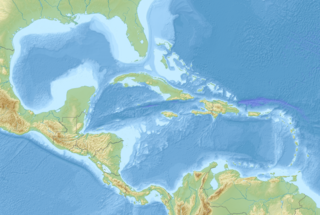
The 2006 Gulf of Mexico earthquake occurred in the eastern Gulf of Mexico on September 10 at . The intraplate earthquake measured 5.9 on the moment magnitude scale and its epicenter was located about 250 miles (400 km) west-southwest of Anna Maria, Florida. The event was felt throughout much of the Gulf Coast of the United States and was the second earthquake of magnitude 5 or greater in the Gulf during 2006. Felt intensities, as measured on the Mercalli intensity scale, were as high as IV (Light) in Florida, with parts of Georgia at III (Weak).

Grand Gulf State Park is a state-operated, privately owned and publicly accessible, geologic preserve near Thayer, Missouri, encompassing a forked canyon that is the remnant of an ancient collapsed dolomite cave system. The land that is now the park was acquired by conservationist Leo Drey (1917–2015) before becoming part of the Missouri state parks system. The 322-acre (130 ha) state park has been operated by the Missouri Department of Natural Resources under a lease agreement with the L-A-D Foundation since 1984. Grand Gulf was declared a National Natural Landmark in 1971 as an excellent example of karst topography and underground stream piracy. A 60-acre (24 ha) portion of the park was designated by the state as the Grand Gulf Natural Area in 1986.

The United States Geological Survey, abbreviated USGS and formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility.

The Henkes Islands are a group of small islands and rocks 4 kilometres (2 nmi) in extent, lying 2 kilometres (1 nmi) southwest of Avian Island, close off the southern extremity of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. The islands were discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and named by him for one of the Dutch directors of the Magellan Whaling Company at Punta Arenas. Charcot applied the name to the scattered rocks and islands between Cape Adriasola and Cape Alexandra, and the name was restricted to the group described by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UKAPC) following definitive mapping by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) in 1961 and the British Royal Navy Hydrographic Survey (BRNHS) in 1963. All of the islands in the group were named by UKAPC.





