
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken language, and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness.

A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training, cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound.
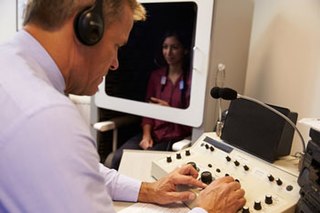
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
Auditory neuropathy (AN) is a hearing disorder in which the outer hair cells of the cochlea are present and functional, but sound information is not transmitted sufficiently by the auditory nerve to the brain. The cause may be several dysfunctions of the inner hair cells of the cochlea or spiral ganglion neuron levels. Hearing loss with AN can range from normal hearing sensitivity to profound hearing loss.
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear.

The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), a member of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, is mandated to conduct and support biomedical and behavioral research and research training in the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, smell, taste, voice, speech, and language. The institute also conducts and supports research and research training related to disease prevention and health promotion; addresses special biomedical and behavioral problems associated with people who have communication impairments or disorders; and supports efforts to create devices which substitute for lost and impaired sensory and communication function.

Cortical deafness is a rare form of sensorineural hearing loss caused by damage to the primary auditory cortex. Cortical deafness is an auditory disorder where the patient is unable to hear sounds but has no apparent damage to the structures of the ear. It has been argued to be as the combination of auditory verbal agnosia and auditory agnosia. Patients with cortical deafness cannot hear any sounds, that is, they are not aware of sounds including non-speech, voices, and speech sounds. Although patients appear and feel completely deaf, they can still exhibit some reflex responses such as turning their head towards a loud sound.
An auditory brainstem implant (ABI) is a surgically implanted electronic device that provides a sense of sound to a person who is profoundly deaf, due to retrocochlear hearing impairment. In Europe, ABIs have been used in children and adults, and in patients with neurofibromatosis type II.
Hearing Health Foundation (HHF) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. In 2011, the Deafness Research Foundation changed its name to Hearing Health Foundation.
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written with a lower case d. It later came to be used in a cultural context to refer to those who primarily communicate through sign language regardless of hearing ability, often capitalized as Deaf and referred to as "big D Deaf" in speech and sign. The two definitions overlap but are not identical, as hearing loss includes cases that are not severe enough to impact spoken language comprehension, while cultural Deafness includes hearing people who use sign language, such as children of deaf adults.
Blake Shaw Wilson is an American research scientist best known for his role in developing signal processing strategies for the cochlear implant.
Monita Chatterjee is an auditory scientist and the Director of the Auditory Prostheses & Perception Laboratory at Boys Town National Research Hospital. She investigates the basic mechanisms underlying auditory processing by cochlear implant listeners.

Quentin Summerfield is a British psychologist, specialising in hearing. He joined the Medical Research Council Institute of Hearing Research in 1977 and served as its deputy director from 1993 to 2004, before moving on to a chair in psychology at The University of York. He served as head of the Psychology department from 2011 to 2017 and retired in 2018, becoming an emeritus professor. From 2013 to 2018, he was a member of the University of York's Finance & Policy Committee. From 2015 to 2018, he was a member of York University's governing body, the Council.
Anu Sharma is an American audiologist and academic. She is a professor in the Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Science and a fellow at the Institute for Cognitive Science and Center for Neuroscience at University of Colorado Boulder. She is also an adjunct professor in the Department of Otolaryngology and Audiology at the University of Colorado Denver Medical School. Sharma received her doctorate at Northwestern University while working under Nina Kraus, PhD.
Sharon G. Kujawa is a clinical audiologist, Director of Audiology Research at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Associate Professor of Otology and Laryngology at Harvard Medical School, and Adjunct Faculty of Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology.and specialist in otolaryngology, Her specialty is the effects of noise exposure and aging on auditory function.

Lisa Lynn Cunningham is an American scientist. She is Scientific Director and a senior investigator of sensory cell biology at the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD).

Richard Charles Dowell is an Australian audiologist, academic and researcher. He holds the Graeme Clark Chair in Audiology and Speech Science at University of Melbourne. He is a former director of Audiological Services at Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital.

Judith Ann Cooper is an American speech pathologist serving as the deputy director of the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). She was the acting director of the NIDCD from June 2018 to August 2019. Cooper is an elected fellow of the American Speech–Language–Hearing Association.
Computational audiology is a branch of audiology that employs techniques from mathematics and computer science to improve clinical treatments and scientific understanding of the auditory system. Computational audiology is closely related to computational medicine, which uses quantitative models to develop improved methods for general disease diagnosis and treatment.
Judy R. Dubno is an American scientist and researcher in the field of audiology. She is a distinguished university professor and director of research in the department of otolaryngology at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. She is recognized for her scientific contributions to the understanding of presbycusis, a condition of hearing loss that occurs gradually for many aging adults. She has been involved in the development and implementation of several new methods for assessing hearing loss, including the Hearing in Noise Test (HINT) and Speech Intelligibility Index (SII). She has won numerous awards for her work, including the Jerger Career Award for Research in Audiology in 2011. She served as President of the Acoustical Society of America from 2014 to 2015.









