Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.

Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of principal and interest. Loans, bonds, notes, and mortgages are all types of debt. In financial accounting, debt is a type of financial transaction, as distinct from equity.

In corporate finance, a debenture is a medium- to long-term debt instrument used by large companies to borrow money, at a fixed rate of interest. The legal term "debenture" originally referred to a document that either creates a debt or acknowledges it, but in some countries the term is now used interchangeably with bond, loan stock or note. A debenture is thus like a certificate of loan or a loan bond evidencing the company's liability to pay a specified amount with interest. Although the money raised by the debentures becomes a part of the company's capital structure, it does not become share capital. Senior debentures get paid before subordinate debentures, and there are varying rates of risk and payoff for these categories.

An audit is an "independent examination of financial information of any entity, whether profit oriented or not, irrespective of its size or legal form when such an examination is conducted with a view to express an opinion thereon." Auditing also attempts to ensure that the books of accounts are properly maintained by the concern as required by law. Auditors consider the propositions before them, obtain evidence, roll forward prior year working papers, and evaluate the propositions in their auditing report.

Due diligence is the investigation or exercise of care that a reasonable business or person is normally expected to take before entering into an agreement or contract with another party or an act with a certain standard of care.

Factoring is a financial transaction and a type of debtor finance in which a business sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount. A business will sometimes factor its receivable assets to meet its present and immediate cash needs. Forfaiting is a factoring arrangement used in international trade finance by exporters who wish to sell their receivables to a forfaiter. Factoring is commonly referred to as accounts receivable factoring, invoice factoring, and sometimes accounts receivable financing. Accounts receivable financing is a term more accurately used to describe a form of asset based lending against accounts receivable. The Commercial Finance Association is the leading trade association of the asset-based lending and factoring industries.
Debt restructuring is a process that allows a private or public company or a sovereign entity facing cash flow problems and financial distress to reduce and renegotiate its delinquent debts to improve or restore liquidity so that it can continue its operations.
A debtor or debitor is a legal entity that owes a debt to another entity. The entity may be an individual, a firm, a government, a company or other legal person. The counterparty is called a creditor. When the counterpart of this debt arrangement is a bank, the debtor is more often referred to as a borrower.
In finance, a surety, surety bond, or guaranty involves a promise by one party to assume responsibility for the debt obligation of a borrower if that borrower defaults. Usually, a surety bond or surety is a promise by a surety or guarantor to pay one party a certain amount if a second party fails to meet some obligation, such as fulfilling the terms of a contract. The surety bond protects the obligee against losses resulting from the principal's failure to meet the obligation. The person or company providing the promise is also known as a "surety" or as a "guarantor".
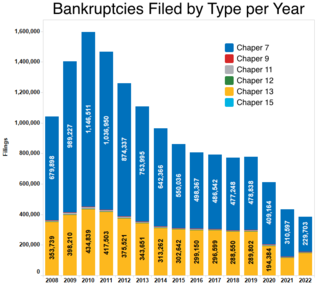
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).
In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company (debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be insolvent. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet insolvency.

Credit card debt results when a client of a credit card company purchases an item or service through the card system. Debt grows through the accrual of interest and penalties when the consumer fails to repay the company for the money they have spent.

Debt collection or cash collection is the process of pursuing payments of money or other agreed-upon value owed to a creditor. The debtors may be individuals or businesses. An organization that specializes in debt collection is known as a collection agency or debt collector. Most collection agencies operate as agents of creditors and collect debts for a fee or percentage of the total amount owed. Historically, debtors could face debt slavery, debtor's prison, or coercive collection methods. In the 21st century in many countries, legislation regulates debt collectors, and limits harassment and practices deemed unfair.

Credit counseling is commonly a process that is used to help individual debtors with debt settlement through education, budgeting and the use of a variety of tools with the goal to reduce and ultimately eliminate debt. Credit counseling is most often done by Credit counseling agencies that are empowered by contract to act on behalf of the debtor to negotiate with creditors to resolve debt that is beyond a debtor's ability to pay. Some of the agencies are non-profits that charge at no or non-fee rates, while others can be for-profit and include high fees. Regulations on credit counseling and Credit counseling agencies varies by country and sometimes within regions of the countries themselves. In the United States, individuals filing Chapter 13 bankruptcy are required to receive counseling.
An individual voluntary arrangement (IVA) is a formal alternative in England and Wales for individuals wishing to avoid bankruptcy. In Scotland, the equivalent statutory debt solution is known as a protected trust deed.
Debt settlement is a settlement negotiated with a debtor's unsecured creditor. Commonly, creditors agree to forgive a large part of the debt: perhaps around half, though results can vary widely. When settlements are finalized, the terms are put in writing. It is common that the debtor makes one lump-sum payment in exchange for the creditor agreeing that the debt is now cancelled and the matter closed. Some settlements are paid out over a number of months. In either case, as long as the debtor does what is agreed in the negotiation, no outstanding debt will appear on the former debtor's credit report.
Bankruptcy is a legally declared inability or impairment of ability of an individual or organization to pay their creditors. In most cases personal bankruptcy is initiated by the bankrupt individual. Bankruptcy is a legal process that discharges most debts, but has the disadvantage of making it more difficult for an individual to borrow in the future. To avoid the negative impacts of personal bankruptcy, individuals in debt have a number of bankruptcy alternatives.
A protected trust deed, overseen by the Accountant in Bankruptcy, is a voluntary but formal arrangement that is used by Scottish residents where a debtor grants a trust deed in favor of the trustee which transfers their estate to the trustee for the benefit of creditors. Any person wanting to make an application for a protected trust deed must have been a resident of Scotland for at least six months prior to making the application.
A debt buyer is a company, sometimes a collection agency, a private debt collection law firm, or a private investor, that purchases delinquent or charged-off debts from a creditor or lender for a percentage of the face value of the debt based on the potential collectibility of the accounts. The debt buyer can then collect on its own, utilize the services of a third-party collection agency, repackage and resell portions of the purchased portfolio, or use any combination of these options.
A sovereign default is the failure or refusal of the government of a sovereign state to pay back its debt in full when due. Cessation of due payments may either be accompanied by that government's formal declaration that it will not pay its debts (repudiation), or it may be unannounced. A credit rating agency will take into account in its gradings capital, interest, extraneous and procedural defaults, and failures to abide by the terms of bonds or other debt instruments.








