In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johnson solid is the square-based pyramid with equilateral sides ; it has 1 square face and 4 triangular faces. Some authors require that the solid not be uniform before they refer to it as a “Johnson solid”.
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. Cuboid means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a cube. In mathematical language a cuboid is a convex polyhedron, whose polyhedral graph is the same as that of a cube.

In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an n-sided polygon base, a second base which is a translated copy of the first, and n other faces, necessarily all parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the bases are translations of the bases. Prisms are named after their bases, e.g. a prism with a pentagonal base is called a pentagonal prism. Prisms are a subclass of prismatoids.

In geometry, an icosagon or 20-gon is a twenty-sided polygon. The sum of any icosagon's interior angles is 3240 degrees.

The triaugmented triangular prism, in geometry, is a convex polyhedron with 14 equilateral triangles as its faces. It can be constructed from a triangular prism by attaching equilateral square pyramids to each of its three square faces. The same shape is also called the tetrakis triangular prism, tricapped trigonal prism, tetracaidecadeltahedron, or tetrakaidecadeltahedron; these last names mean a polyhedron with 14 triangular faces. It is an example of a deltahedron and of a Johnson solid.

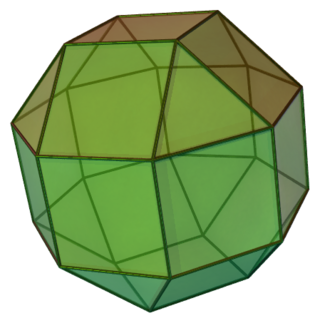
In geometry, the pentagonal cupola is one of the Johnson solids. It can be obtained as a slice of the rhombicosidodecahedron. The pentagonal cupola consists of 5 equilateral triangles, 5 squares, 1 pentagon, and 1 decagon.

In geometry of 4 dimensions or higher, a double prism or duoprism is a polytope resulting from the Cartesian product of two polytopes, each of two dimensions or higher. The Cartesian product of an n-polytope and an m-polytope is an (n+m)-polytope, where n and m are dimensions of 2 (polygon) or higher.

In four-dimensional geometry, a runcinated tesseract is a convex uniform 4-polytope, being a runcination of the regular tesseract.

In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise it is oblique. A uniform triangular prism is a right triangular prism with equilateral bases, and square sides.
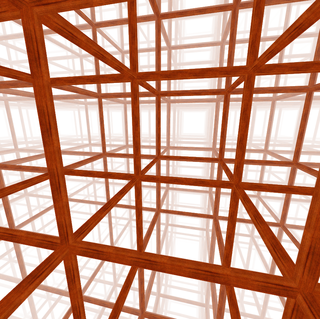
The cubic honeycomb or cubic cellulation is the only proper regular space-filling tessellation in Euclidean 3-space made up of cubic cells. It has 4 cubes around every edge, and 8 cubes around each vertex. Its vertex figure is a regular octahedron. It is a self-dual tessellation with Schläfli symbol {4,3,4}. John Horton Conway called this honeycomb a cubille.

In geometry, the small stellated truncated dodecahedron (or quasitruncated small stellated dodecahedron or small stellatruncated dodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U58. It has 24 faces (12 pentagons and 12 decagrams), 90 edges, and 60 vertices. It is given a Schläfli symbol t{5⁄3,5}, and Coxeter diagram .

In geometry, the great dodecicosidodecahedron (or great dodekicosidodecahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U61. It has 44 faces (20 triangles, 12 pentagrams and 12 decagrams), 120 edges and 60 vertices.

In geometry, the great rhombidodecahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U73. It has 42 faces (30 squares, 12 decagrams), 120 edges and 60 vertices. Its vertex figure is a crossed quadrilateral.

In 4-dimensional geometry, a uniform antiprismatic prism or antiduoprism is a uniform 4-polytope with two uniform antiprism cells in two parallel 3-space hyperplanes, connected by uniform prisms cells between pairs of faces. The symmetry of a p-gonal antiprismatic prism is [2p,2+,2], order 8p.

In geometry, an apeirogonal prism or infinite prism is the arithmetic limit of the family of prisms; it can be considered an infinite polyhedron or a tiling of the plane.
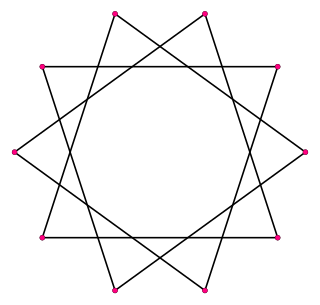
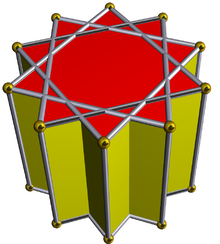
In geometry, a decagram is a 10-point star polygon. There is one regular decagram, containing the vertices of a regular decagon, but connected by every third point. Its Schläfli symbol is {10/3}.

In geometry, the decagrammic antiprism is one in an infinite set of nonconvex antiprisms formed by triangle sides and two regular star polygon caps, in this case two decagrams.

In geometry, the great duoantiprism is the only uniform star-duoantiprism solution p = 5,q = 5/3, in 4-dimensional geometry. It has Schläfli symbol {5}⊗{5/3},s{5}s{5/3} or ht0,1,2,3{5,2,5/3}, Coxeter diagram , constructed from 10 pentagonal antiprisms, 10 pentagrammic crossed-antiprisms, and 50 tetrahedra.