
Pygopodidae, commonly known as snake-lizards, or flap-footed lizards, are a family of legless lizards with reduced or absent limbs, and are a type of gecko. At least 35 species are placed in two subfamilies and eight genera. They have unusually long, slender bodies, giving them a strong resemblance to snakes. Like snakes and most geckos, they have no eyelids, but unlike snakes, they have external ear holes and flat, unforked tongues. They are native to Australia and New Guinea.

Pygopus is a genus belonging to the family of Australian legless lizards (Pygopodidae). Members of this genus are also commonly called scaly-foot.

Delma is a genus of lizards in the family Pygopodidae. The genus Delma contains 22 valid described species, all of which are endemic to Australia.

Legless lizard may refer to any of several groups of lizards that have independently lost limbs or reduced them to the point of being of no use in locomotion. It is the common name for the family Pygopodidae. These lizards are often distinguishable from snakes on the basis of one or more of the following characteristics: possessing eyelids, possessing external ear openings, lack of broad belly scales, notched rather than forked tongue, having two more-or-less-equal lungs, and/or having a very long tail.

The striped legless lizard is a species of lizards in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia. As of 2015 it is threatened with extinction, with few habitats left.

The striped-tailed delma or single-striped delma is a species of lizard in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia.
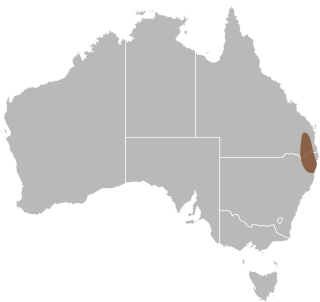
The collared delma or adorned delma is the smallest species of lizard in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia. Pygopopdids are legless lizards, so are commonly mistaken for snakes. They are distributed mainly across south-east Queensland and northern New South Wales, in both forests and some suburban areas. They are active during the day, seen foraging and hunting for small insects.

Paradelma orientalis, commonly known as the Brigalow scaly-foot or Queensland snake-lizard, is a species of legless lizard in the family Pygopodidae. It is endemic to Australia and is the only species in the monotypic genus Paradelma.
Scottsdale Reserve is a 1,328-hectare (3,280-acre) nature reserve on the Murrumbidgee River in south-central New South Wales, Australia. It is 79 kilometres (49 mi) south of Canberra, and 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) north of Bredbo. It is owned and managed by Bush Heritage Australia (BHA), which purchased it in 2006. The purchase was supportive of projects aiming to connect existing fragmented remnant habitat such as K2C. Since the 1870s up until 2006, the land was used for agriculture – primarily sheep grazing with some minor cropping. A significant component of the Reserve has been cleared of native vegetation.

Burton's legless lizard is a species of lizard in the family Pygopodidae. The species lacks forelegs and has only rudimentary hind legs. Pygopodid lizards are also referred to as "legless lizards", "flap-footed lizards" and "snake-lizards". This species is native to Australia and Papua New Guinea.

The Delma australis is often known as the southern legless lizard, or the marble-faced delma. This terrestrial lizard falls into the category of slender Pygopodidae, a legless lizard. There are 21 known species in the Pygopdidae family in Australia. Marble-faced delmas are endemic to Australia. Delma australis was first described by Kluge in 1974.

Delma butleri, also known commonly as Butler's legless lizard, Butler's scalyfoot, the spinifex snake-lizard, and the unbanded delma, is a species of lizard in the family Pygopodidae. The species is endemic to Australia.

Fraser's delma, also known commonly as Fraser's scalyfoot, is a species of lizard in the family Pygopodidae. The species is endemic to the state of Western Australia.
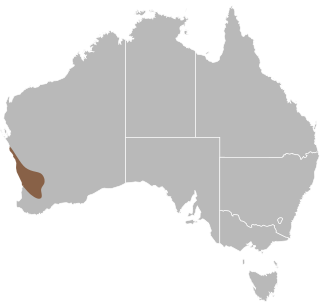
Delma grayii, also known commonly as Gray's legless lizard, Gray's scalyfoot, and the side-barred delma, is a species of lizard in the family Pygopodidae. The species is endemic to Australia.

Delma nasuta, also known as sharp-snouted delma or sharp-snouted legless lizard, is a species of lizard in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia.
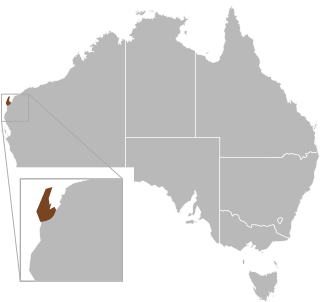
The North West Cape delma, also known commonly as Teale's delma, is a species of lizard in the family Pygopodidae. The species is endemic to Western Australia.

The excitable delma is a species of lizard in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia. The lizard gets its name from its active and jumpy defense mechanism. It will erratically jump multiple times in succession, each jump pivoting its body in a different direction. D. tincta is a slender, long legless lizard that through evolution lost its limbs. It is found throughout Australia in a variety of habitats, and spends most of its time hiding. Due to its nocturnal nature, it is rare to spot in the wild. This legless lizard is small to moderate in size, with a tail that is three to four times its body length. The typical size of the excitable delma is 250 – 300 mm. This lizard is an insectivore and feeds on insects it finds when travelling through grass, logs, surface soil, and loose rocks. Like all pygopodids, the excitable delma is oviparous and only lays two eggs per clutch.

The Mallee worm-lizard , also known as the pink-nosed worm-lizard and the red-tailed worm-lizard, is a slender pygopid species that is endemic to Australia, with recorded distribution across the four southern mainland states, although its distribution is restricted in Western Australia and New South Wales.
The striated worm-lizard is a species of legless lizard in the family Pygopodidae. It is endemic to southern Australia. Commonly known as Striated worm-lizard but has also been referred to as the Striped or Lined worm-lizard due to its pattern of long, thin parallel streaks. Some populations such as those in WA and Kangaroo Island may have absent stripes or the lines present as lines of dots.

The olive legless lizard is a species of legless gecko from the Pygopodidae family. This species is commonly found throughout the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Queensland and southeastern South Australia, mostly inhabiting areas consisting of dry to temperate southern grasslands and grassy woodlands.
















