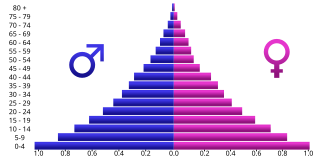Demographic statistics are measures of the characteristics of, or changes to, a population. Records of births, deaths, marriages, immigration and emigration and a regular census of population provide information that is key to making sound decisions about national policy.

The demographics of North Korea are determined through national censuses and international estimates. The Central Bureau of Statistics of North Korea conducted the most recent census in 2008, where the population reached 24 million inhabitants. The population density is 199.54 inhabitants per square kilometre, and the 2014 estimated life expectancy is 69.81 years. In 1980, the population rose at a near consistent, but low, rate. Since 2000, North Korea's birth rate has exceeded its death rate; the natural growth is positive. In terms of age structure, the population is dominated by the 15–64-year-old segment (68.09%). The median age of the population is 32.9 years, and the gender ratio is 0.95 males to 1.00 female. Since the early 1990s, the birth rate has been fairly stable, with an average of 2 children per woman, down from an average of 3 in the early 1980s.

The demographics of China demonstrate a large population with a relatively small youth component, partially a result of China's one-child policy. China's population reached 1 billion in late 1981.
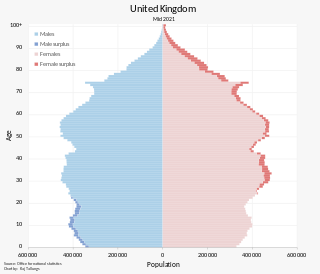
The current population of the United Kingdom is estimated at over 67.0 million, as of 2020. It is the 21st most populated country in the world and has a population density of 270 people per square kilometre, with England having significantly greater density than Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. Almost a third of the population lives in South East England, which is predominantly urban and suburban, with about 9 million in the capital city, London, whose population density is just over 5,200 per square kilometre.
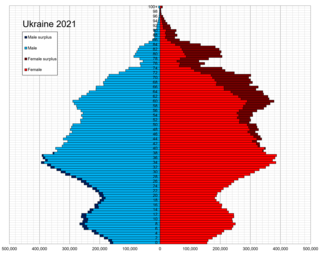
The demographics of Ukraine include statistics on population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population of Ukraine.
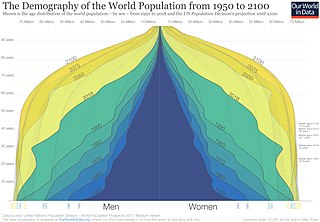
Demography is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems.
Zero population growth, sometimes abbreviated ZPG, is a condition of demographic balance where the number of people in a specified population neither grows nor declines, that is, the number of births plus in-migrants equals the number of deaths plus out-migrants. ZPG has been a prominent political movement since the 1960’s. As part of the concept of optimum population, the movement considers zero population growth to be an objective towards which countries and the whole world should strive in the interests of accomplishing long-term optimal standards and conditions of living.

The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
- she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
- she were to live from birth until the end of her reproductive life.
A population decline in humans is a reduction in a human population size. Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth's total human population has continued to grow; however, current projections suggest that this long-term trend of steady population growth may be coming to an end.
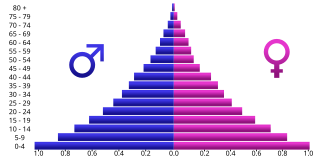
A population pyramid or "age-sex pyramid" is a graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex; it typically takes the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. Males are usually shown on the left and females on the right, and they may be measured in absolute numbers or as a percentage of the total population. The pyramid can be used to visualize the age of a particular population. It is also used in ecology to determine the overall age distribution of a population; an indication of the reproductive capabilities and likelihood of the continuation of a species. Number of people per unit area of land is called population density.

Population geography relates spatial variations in the distribution, composition, migration, and growth of populations to the terrain. Population geography involves demography in a geographical perspective. It focuses on the characteristics of population distributions that change in a spatial context. This often involves factors such as where population is found and how the size and composition of these population is regulated by the demographic processes of fertility, mortality, and migration.
Population momentum is a consequence of the demographic transition. Population momentum explains why a population will continue to grow even if the fertility rate declines. Population momentum occurs because it is not only the number of children per woman that determine population growth, but also the number of women in reproductive age. Eventually, when the fertility rate reaches the replacement rate and the population size of women in the reproductive age bracket stabilizes, the population achieves equilibrium and population momentum comes to an end. Population momentum is defined as the ratio of the size of the population at that new equilibrium level to the size of the initial population. Population momentum usually occurs in populations that are growing.

In Demography, the rate of natural increase (RNI), also known as natural population change, is defined as the birth rate minus the death rate of a particular population, over a particular time period. It is typically expressed either as a number per 1,000 individuals in the population or as a percentage. RNI can be either positive or negative. It contrasts to total population change by ignoring net migration.
Population change is simply the change in the number of people in a specified area during a specific time period. Demographics is the study of population statistics, their variation and its causes. These statistics include birth rates, death rates, migration rates and sex ratios. All of these statistics are investigated by censuses and surveys conducted over a period of time. Some demographic information can also be obtained from historical maps, and aerial photographs.
The Population Estimates Program (PEP) is a program of the US Census Bureau that publishes annual population estimates and estimates of birth, death, and international migration rates for people in the United States. In addition to publishing those aggregate estimates for the entire country, the program also publishes those yearly estimates by age, sex, race, and Hispanic origin at the national, state, county and city and town level. By doing so, the Population Estimates Program provides up-to-date information on how the size and distribution of the US population has changed each year since the most recent 10-year US Census.
Earth has a human population of 7.97 billion, with an overall population density of 50 people per km2, excluding Antarctica. Nearly 60% of the world's population lives in Asia, with more than 2.7 billion in the countries of China and India combined. The percentage share of India, China and rest of South Asia in world population have remained on similar levels for the last few thousands years of recorded history. The world's literacy rate has increased dramatically in the last 40 years, from 66.7% in 1979 to 86.3% today. Lower literacy levels are mostly attributable to poverty. Lower literacy rates are mostly found in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa. The world's largest ethnic group is Han Chinese, with Mandarin being the world's most spoken language in terms of native speakers.

Population projections are attempts to show how the human population statistics might change in the future. These projections are an important input to forecasts of the population's impact on this planet and humanity's future well-being. Models of population growth take trends in human development, and apply projections into the future. These models use trend-based-assumptions about how populations will respond to economic, social and technological forces to understand how they will affect fertility and mortality, and thus population growth.
Fertility factors are determinants of the number of children that an individual is likely to have. Fertility factors are mostly positive or negative correlations without certain causations.
White demographic decline is a decrease in the white populace as a percentage of the total population in a city, state, subregion, or nation. It has been recorded in a number of countries and smaller jurisdictions. For example, according to their national censuses, white Americans, White Canadians, white Brazilians, and white people in the United Kingdom are in demographic decline in the United States, Canada, Brazil, and United Kingdom, respectively.