
The Maple Leaf is an international passenger train service operated by Amtrak and Via Rail between New York Penn Station in New York City and Union Station in Toronto via the Empire Corridor. Daily service is offered in both directions; the 544-mile (875 km) trip takes approximately 12 hours, including two hours for U.S. or Canadian customs and immigration inspection at either Niagara Falls, New York, or Niagara Falls, Ontario. Although the train uses Amtrak rolling stock exclusively, the train is operated by Via Rail crews while in Canada and by Amtrak crews in the United States. Service began in 1981.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Empire Service is an inter-city rail service operated by Amtrak within the state of New York in the United States. The brand name originated with the New York Central Railroad in 1967. Trains on the line provide frequent daily service along the 460-mile (740 km) Empire Corridor between New York City and Niagara Falls via Albany, the state capital.

The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad, also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad, was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey, and by ferry with New York City, a distance of 395 miles (636 km). The railroad was incorporated in Pennsylvania in 1853, and created primarily to provide a means of transport of anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeast Pennsylvania to large coal markets in New York City. The railroad gradually expanded both east and west, and eventually linked Buffalo with New York City.
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad in the Northeastern United States built predominantly to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeastern Pennsylvania to major consumer markets in Philadelphia, New York City, and elsewhere.
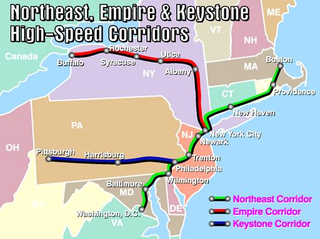
The Empire Corridor is a 461-mile (742 km) passenger rail corridor in New York State running between Penn Station in New York City and Niagara Falls, New York. Major cities on the route include Poughkeepsie, Albany, Schenectady, Amsterdam, Utica, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo. Much of the corridor was once part of the New York Central Railroad's main line.

The Black Diamond, also known as the Black Diamond Express, was the flagship passenger train of the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LV). It ran from New York to Buffalo from 1896 until May 11, 1959, when the Lehigh Valley's passenger service was reduced to four mainline trains.

The Reading Blue Mountain and Northern Railroad, sometimes shortened to Reading and Northern Railroad, is a regional railroad in eastern Pennsylvania. Its headquarters is in Port Clinton. The RBMN provides freight service on 400 miles (640 km) of track. Its mainline consists of the Reading Division between Reading and Packerton and the Lehigh Division between Lehighton and Dupont. Its main freight cargo is anthracite coal.

The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in Central New Jersey, Northeastern Pennsylvania, and the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey in Manville, New Jersey via Conrail's Lehigh Line to the southern end of Wyoming Valley's Coal Region in Lehigh Township, Pennsylvania.

Transportation in Buffalo, New York is dominated by automobile use, but other modes of transportation exist in the city.

Easton is a defunct train station in Easton, Pennsylvania. It was originally built by the Lehigh Valley Railroad. As of 2017, the structure still exists and was blighted for at least 20 years, since its closing in the 1970s. The city of Easton obtained permission from Norfolk Southern Railway to clean up the property. The location only recently became a focal point for the city with the opening of Interstate 78 in the 1990s.

Allentown was a train station in Allentown, Pennsylvania. It was opened by the Lehigh Valley Railroad in 1890 and closed in 1961. The building was demolished in 1972. The station was located one block west of the Central Railroad of New Jersey's Allentown station.

The Lehigh Valley Terminal was a railroad station in downtown Buffalo, New York. The Lehigh Valley Railroad opened it in 1916, replacing an older station one block east at Scott and Washington streets. Lehigh Valley trains served at the station included the Black Diamond,Maple Leaf, and Star. The station handled the Lehigh Valley's passenger traffic in Buffalo until 1955, when it was demolished to make room for the Niagara Thruway (Interstate 190). The Lehigh Valley moved its operations to a smaller station outside the downtown area at Dingens and South Ogden Streets, which served until the end of all Lehigh Valley passenger service in 1961. The terminal also hosted the Erie Railroad's passenger trains from 1935 until 1951, when that railroad ceased serving Buffalo.
Batavia station was a Lehigh Valley Railroad station in Batavia, New York, located on the Lehigh Valley main line.
Slatington station was a Lehigh Valley Railroad station in Slatington, Pennsylvania, located on the Lehigh Valley main line. The station also served the Lehigh and New England Railroad; the Reading Company at one time had an adjacent station. The Central Railroad of New Jersey had an unconnected station across the Lehigh River in Walnutport, Pennsylvania.

Lehighton station was a Lehigh Valley Railroad station that was located in Lehighton, Pennsylvania, USA. It was part of the Lehigh Valley main line, and was also the eastern terminus for Hazleton Branch passenger trains, although the branch diverged at Penn Haven Junction, north of Jim Thorpe.

The Jim Thorpe station, also known as the Mauch Chunk station or East Mauch Chunk station, was a Lehigh Valley Railroad station that was located in Jim Thorpe, Pennsylvania.

Flemington Junction station is a defunct Lehigh Valley Railroad station in Flemington Junction, New Jersey. It was located at the junction of the Lehigh Valley's Flemington Branch and Main Line, although the name predated the opening of the branch by eight years.

The Flemington Branch was a railroad line in Hunterdon County, New Jersey. It was owned and operated by the Lehigh Valley Railroad. It connected the borough of Flemington, New Jersey, with the Lehigh Valley's main line. It was opened in 1884 and abandoned in 1982.
The Elmira, Cortland and Northern Railroad was a railroad in the state of New York, in the United States. Its main line ran from Elmira, New York, to Camden, New York. It was formed in 1884 from the consolidation of other railroads and merged into the Lehigh Valley Railroad in 1905. Under the Lehigh Valley, it was known as the Elmira and Cortland Branch. Almost all of its former line has since been abandoned.















