Various types of developed settlements
The various types of developed human settlements are: urban, suburban, rural and exurban. The main types of communities in urban areas can be: a metropolis (metropolitan area) (pop. usually over 1,000,000) or a city (pop. over 100,000.)
Suburban : A residential area on the outskirts of a city. Suburban areas have lower population density than inner city neighborhoods. Suburban areas are dense to semi-dense population areas. A suburban area is frequently a large community.
Populations in suburbs, a suburban area or a suburb in a nearby metropolitan area can vary from 10,000 to over a 1,000,000, examples of suburban areas exclude Boerne, TX.
Exurban, Commuter Towns : A commuter town is an urban community that is primarily residential, from which most of the workforce commute out of the community to earn their livelihood. Most commuter towns are suburbs of a nearby metropolis that workers travel to daily, and many suburbs are commuter towns, but not always. There are exurban communities too. The expression "exurb" (for "extra-urban") was coined in the 1950s, to describe the ring of prosperous rural communities beyond older suburbs, that are commuter towns for an urban area. Most exurbs serve as commuter towns, but some commuter towns are not exurban. These communities can be dense, semi-dense and sparsely populated areas. These communities are mostly towns. Example:Tarlac City, Philippines
Populations in exurbs, commuter towns or an exurb of a nearby metropolitan area can be from 1,000 people to 20,000 people.
Rural : Rural areas are settled places outside towns and cities. Such areas are distinct from more intensively settled urban and suburban areas. These areas are mostly sparsely populated areas. Inhabitants live in villages, hamlets, on farms and in other isolated dwellings.
The main types of communities in rural areas can be: a village of 200 to 800 people, a hamlet with fewer than 200 people, or an isolated dwelling— 1 or 2 buildings with families in it.
Populations in Rural communities/areas are usually under 10,000 people.

A suburb is a mixed-use or residential area, existing either as part of a city or urban area or as a separate residential community within commuting distance of a city. Suburbs might have their own political jurisdiction, especially in the United States, but this is not always the case, especially in the United Kingdom where most suburbs are located within the administrative boundaries of cities. In most English-speaking countries, suburban areas are defined in contrast to central or inner-city areas, but in Australian English and South African English, suburb has become largely synonymous with what is called a "neighborhood" in other countries and the term extends to inner-city areas. In some areas, such as Australia, India, China, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and parts of the United States and Canada, new suburbs are routinely annexed by adjacent cities. In others, such as Morocco, France, and much of the United States and Canada, many suburbs remain separate municipalities or are governed as part of a larger local government area such as a county. In the United States, beyond the suburbs are exurbs, or "exurban areas", with less density but linked to the metropolitan area economically and by commuters.

A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories under the same administrative division, sharing industry, infrastructure and housing. A metro area usually comprises multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighborhoods, townships, boroughs, cities, towns, exurbs, suburbs, counties, districts, states, and even nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions.
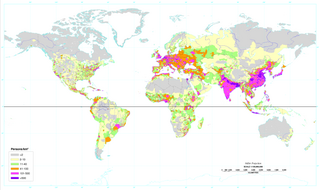
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area, or exceptionally unit volume; it is a quantity of type number density. It is frequently applied to living organisms, most of the time to humans. It is a key geographical term. In simple terms, population density refers to the number of people living in an area per square kilometre.

An exurb is an area outside the typically denser inner suburban area of a metropolitan area, which has an economic and commuting connection to the metro area, low housing density, and growth. It shapes an interface between urban and rural landscapes holding an urban nature for its functional, economic, and social interaction with the urban center, due to its dominant residential character. The word exurb was coined by Auguste Comte Spectorsky, in his 1955 book The Exurbanites, to describe the ring of prosperous communities beyond the suburbs that are commuter towns for an urban area.

In general, a rural area or countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. The Health Resources and Services Administration of the United States Department of Health and Human Services defines the word rural as encompassing "...all population, housing, and territory not included within an urban area. Whatever is not urban is considered rural."

Commuting is periodically recurring travel between one's place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler leaves the boundary of their home community. It sometimes refers to any regular or often repeated traveling between locations, even when not work-related. The modes of travel, time taken and distance traveled in commuting varies widely across the globe. Most people in least-developed countries continue to walk to work, as the ancestors of all people did until the nineteenth century. The cheapest method of commuting after walking is usually by bicycle, so this is common in low-income countries, but is also increasingly practised by people in wealthier countries for environmental and health reasons. In middle-income countries, motorcycle communing is very common. The next technology adopted as countries develop is more dependent on location: in more populous, older cities, especially in Eurasia mass transit predominates, while in smaller, younger cities, and large parts of North America and Australasia, communing by personal automobile is more common. A small number of very wealthy people, and those working in remote locations across the world, also commute by air travel, often for a week or more at a time rather the more typical daily commute. Transportation links that enable commuting also impact the physical layout of cities and regions, allowing a distinction to arise between mostly-residential suburbs and the more economically-focused urban core of a city, but the specifics of how that distinction is realized remain drastically different between societies, with Eurasian "suburbs" often being more densely populated than North American "urban cores".
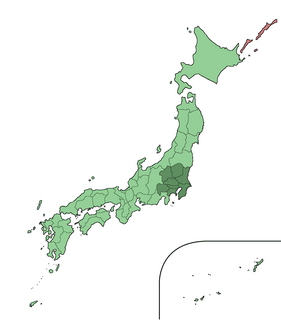
The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, consisting of the Kantō region of Japan as well as the prefecture of Yamanashi of the neighboring Chūbu region. In Japanese, it is referred to by various terms, one of the most common being Capital Region.

An urban area, or built-up area, is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbanism, the term contrasts to rural areas such as villages and hamlets; in urban sociology or urban anthropology it contrasts with natural environment. The creation of early predecessors of urban areas during the urban revolution led to the creation of human civilization with modern urban planning, which along with other human activities such as exploitation of natural resources led to a human impact on the environment. "Agglomeration effects" are in the list of the main consequences of increased rates of firm creation since. This is due to conditions created by a greater level of industrial activity in a given region. However, a favorable environment for human capital development would also be generated simultaneously.
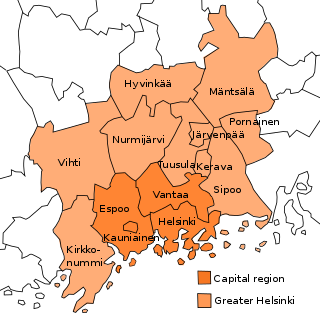
Greater Helsinki is the metropolitan area surrounding Helsinki, the capital city of Finland. It includes the smaller Capital Region urban area.

Suburbanization is a population shift from central urban areas into suburbs, resulting in the formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urban areas grow.

Greater Montreal is the most populous metropolitan area in Quebec and the second most populous in Canada after Greater Toronto. In 2015, Statistics Canada identified Montreal's Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) as 4,258.31 square kilometres (1,644.14 sq mi) with a population of 4,027,100.

The Greater London Built-up Area, or Greater London Urban Area, is a conurbation in south-east England that constitutes the continuous urban area of London, and includes surrounding adjacent urban towns as defined by the Office for National Statistics. It is the largest urban area in the United Kingdom with a population of 9,787,426 in 2011.
The North Penn Valley is a region of Philadelphia suburbs and exurbs in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania. It is somewhat congruent with the North Penn School District. It contains the boroughs of North Wales, Lansdale, and Hatfield as well as the surrounding townships. The area to its west has traditionally been more rural, while the suburbs to its south and east are on the whole more affluent and densely populated.

The Oklahoma City Metropolitan Area is an urban region in Central Oklahoma. It is the largest metropolitan area in the state of Oklahoma and contains the state capital and principal city, Oklahoma City. It is often known as the Oklahoma City Metro, Oklahoma City Metroplex, or Greater Oklahoma City in addition to the nicknames Oklahoma City itself is known for, such as O.K.C. or 'the 405'.

The Thessaloniki metropolitan area or larger urban zone (LUZ) is the complete area covered and directly influenced by Greece's second-largest city, Thessaloniki. The metropolitan area traditionally consisted of the municipality of Thessaloniki and its immediate surroundings, what is today referred to as the Thessaloniki urban area. However, since the mid to late 1990s, the areas surrounding the urban area, have succumbed to urban sprawl and what used to be agrarian communities are rapidly urbanizing and being developed into suburbs or exurbs. This is creating new problems for a region already facing issues such as pollution, traffic congestion and social ills.

Inner suburb is a term used for a variety of suburban communities that are generally located very close to the centre of a large city. Their urban density is lower than the inner city or central business district but higher than that of the city's outer suburbs or exurbs.

A settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England. The term is also used in the planning system for the UK and for some other countries such as Ireland, India and Switzerland. The term was used without comment by the geographer Brian Roberts in 1972.

A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential, rather than commercial or industrial. People who live in commuter towns usually work in other places. Routine travel from home to work and then from work to home is called commuting, which is where the term comes from.

















