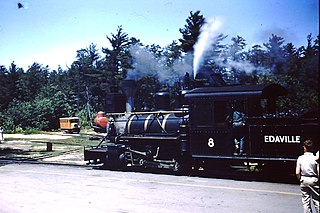The St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad, known as St-Laurent et Atlantique Quebec in Canada, is a short-line railway operating between Portland, Maine, on the Atlantic Ocean, and Montreal, Quebec, on the St. Lawrence River. It crosses the Canada–US border at Norton, Vermont and Stanhope, Quebec, and is owned by short-line operator Genesee & Wyoming.

The Maine Central Railroad Company was a former U. S. Class I railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to 1,358 miles (2,185 km) when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to Vermont and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake, and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport.

The Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway is a 2 ft narrow gauge railway. The line was operated as a for-profit company from 1895 until 1933 between the Maine towns of Wiscasset, Albion, and Winslow, but was abandoned in 1936. Today, about two miles (3.2 km) of the track in the town of Alna has been rebuilt and is operated by the non-profit Wiscasset, Waterville and Farmington Railway Museum as a heritage railroad offering passenger excursion trains and hauling occasional cargo.
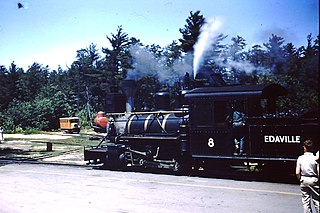
The Bridgton and Saco River Railroad (B&SR) was a 2 ft narrow gauge railroad that operated in the vicinity of Bridgton and Harrison, Maine. It connected with the Portland and Ogdensburg Railroad from Portland, Maine, to St. Johnsbury, Vermont, near the town of Hiram on the Saco River.
The Piscataquis River is a major tributary of the Penobscot River, found in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. It starts from the confluence of its East Branch and West Branch in Blanchard. The river flows in a mostly eastern direction until it meets the Penobscot at Howland. It is approximately 65 miles (105 km) in length.

The Belfast & Moosehead Lake Railroad was a standard-gauge shortline railroad that operated from 1871 to 2007 over a single-track grade from Belfast to Burnham Junction in Maine.
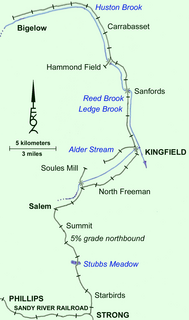
The Franklin and Megantic Railway (F&M) was a 2 ft narrow gauge railway in northern Maine that branches off from the Sandy River Railroad (SRR) at Strong and served sawmills in Salem township and in the town of Kingfield.
The Phillips and Rangeley Railroad was a 2 ft narrow gauge common carrier railroad in the State of Maine.
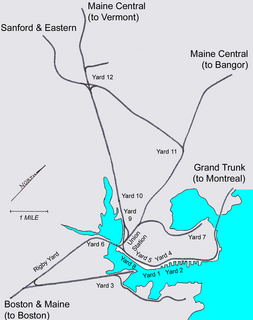
The Portland Terminal Company was a terminal railroad notable for its control of switching activity for the Maine Central Railroad (MEC) and Boston & Maine (B&M) railroads in the Maine cities of Portland, South Portland, and Westbrook.

The Mountain Division is a railroad line that was once owned and operated by the Maine Central Railroad (MEC). It stretches from Portland, Maine on the Atlantic Ocean, through the Western Maine Mountains and White Mountains of New Hampshire, ending at St. Johnsbury, Vermont in the Northeast Kingdom. The line was abandoned in 1983 by MEC's successor, Guilford Transportation Industries (GTI). Guilford retained a stub between Portland and Westbrook. A section in New Hampshire remains in use by heritage railway Conway Scenic Railroad.

The Rockland Branch is a railroad from Brunswick, Maine to Rockland, Maine. A charter was granted in 1849 to build a railway from the Portland and Kennebec Railroad on the west side of the Kennebec River to Rockland. Construction through the rocky headlands of the Atlantic coast proved more expensive than anticipated. The Knox and Lincoln Railroad commenced service to Rockland in 1871 using a ferry to cross the Kennebec River between Bath and Woolwich. The Knox and Lincoln was leased by Maine Central Railroad in 1891, and became Maine Central's Rockland Branch in 1901. Maine Central purchased the Samoset destination hotel in nearby Glen Cove in 1912, and offered direct passenger service for summer visitors from the large eastern cities. Carlton bridge was completed in 1927 to carry the railroad and U.S. Route 1 over the Kennebec River. Maine Central sold the Samoset hotel in 1941, and the last Maine Central passenger train to Rockland was on 4 April 1959. The State of Maine purchased the branch in 1987 to prevent abandonment. The line has subsequently been operated by the Maine Coast Railroad, the Maine Eastern Railroad, and, beginning in 2016, the Central Maine and Quebec Railway.

The Maine Central Railroad Rumford Branch is a railroad line in Maine now operated as part of the Pan Am Railways system. The Rumford Branch leaves the mainline at Leeds Junction and continues northwest up the Androscoggin River valley, passing through Livermore Falls and terminating at Rumford. The branch comprises the remaining trackage of three earlier branches:
The Bucksport Branch is a railroad line in Maine that was operated by the Maine Central Railroad. It is now part of the Pan Am Railways system.
The Calais Branch is a mothballed railroad line in Maine that was operated by the Maine Central Railroad Company (MEC).
The Sebec River is a tributary of the Piscataquis River in Piscataquis County, Maine. From the outflow of Sebec Lake in Sebec, the river runs 10.0 miles (16.1 km) east and southeast to its confluence with the Piscataquis in Milo.

The Somerset Railroad was built to serve Kennebec River communities and later extended through timberlands to a large wooden Victorian era destination hotel on Moosehead Lake. The railway became part of the Maine Central Railroad in 1911; and a portion remained in intermittent operation by Pan Am Railways until 2013.
The Sebasticook and Moosehead Railroad was a 19th-century Maine railroad which became the 20th century Harmony Branch of the Maine Central Railroad.
The Somerset and Kennebec Railroad was a 19th-century Maine railroad which became part of the Maine Central Railroad.

The Maine Central Railroad Company main line extended from Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–US border with New Brunswick at the Saint Croix-Vanceboro Railway Bridge. It is the transportation artery linking Maine cities to the national railway network. Sections of the main line had been built by predecessor railroads consolidated as the Maine Central in 1862 and extended to the Canada–US border in 1882. Through the early 20th century, the main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a lower road through Brunswick and Augusta and a back road through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Westbound trains typically used the lower road with lighter grades, while eastbound trains of empty cars used the back road. This historical description does not include changes following purchase of the Maine Central Railroad by Guilford Transportation Industries in 1981 and subsequent operation as part of Pan Am Railways.

The American Woolen Company Foxcroft Mill or Mayo & Son Woolen Mill is a group of seven historic buildings and three structures on East Main Street in downtown Dover-Foxcroft, Maine. The district is located on 2.77 acres (1.12 ha). The Foxcroft Mill is located on the west side of the Piscataquis River, which flows through downtown Dover-Foxcroft. The buildings were built between 1844 and 1941, and have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.