
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, several species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respiratory organs called gills, through the skin or across enteral mucosae, although some are evolved from terrestrial ancestors that re-adapted to aquatic environments, in which case they actually use lungs to breathe air and are essentially holding their breath when living in water. Some species of gastropod mollusc, such as the eastern emerald sea slug, are even capable of kleptoplastic photosynthesis via endosymbiosis with ingested yellow-green algae.

Cuatro Ciénegas is a city in the northern Mexican state of Coahuila. It stands at 26°59′N102°03′W, at an average elevation of 740 metres (2,430 ft) above sea level. The city serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name.
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic ; lotic ; and wetlands.

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the class Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.
Gnathostoma spinigerum is a parasitic nematode that causes gnathostomiasis in humans, also known as its clinical manifestations are creeping eruption, larva migrans, Yangtze edema, Choko-Fuschu Tua chid and wandering swelling. Gnathostomiasis in animals can be serious, and even fatal. The first described case of gnathostomiasis was in a young tiger that died in the London Zoo in 1835. The larval nematode is acquired by eating raw or undercooked fish and meat.

Freshwater fish are fish species that spend some or all of their lives in bodies of fresh water such as rivers, lakes and inland wetlands, where the salinity is less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine habitats in many ways, especially the difference in levels of osmolarity. To survive in fresh water, fish need a range of physiological adaptations.

Picoplankton is the fraction of plankton composed by cells between 0.2 and 2 μm that can be either prokaryotic and eukaryotic phototrophs and heterotrophs:

Microfauna are microscopic animals and organisms that exhibit animal-like qualities and have body sizes that are usually <0.1mm. Microfauna are represented in the animal kingdom and the protist kingdom. A large amount of microfauna are soil microfauna which includes protists, rotifers, and nematodes. These types of animal-like protists are heterotrophic, largely feeding on bacteria. However, some microfauna can consume other things, making them detritivores, fungivores, or even predators.

A wild fishery is a natural body of water with a sizeable free-ranging fish or other aquatic animal population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries can be marine (saltwater) or lacustrine/riverine (freshwater), and rely heavily on the carrying capacity of the local aquatic ecosystem.
Aquatic science is the study of the various bodies of water that make up our planet including oceanic and freshwater environments. Aquatic scientists study the movement of water, the chemistry of water, aquatic organisms, aquatic ecosystems, the movement of materials in and out of aquatic ecosystems, and the use of water by humans, among other things. Aquatic scientists examine current processes as well as historic processes, and the water bodies that they study can range from tiny areas measured in millimeters to full oceans. Moreover, aquatic scientists work in Interdisciplinary groups. For example, a physical oceanographer might work with a biological oceanographer to understand how physical processes, such as tropical cyclones or rip currents, affect organisms in the Atlantic Ocean. Chemists and biologists, on the other hand, might work together to see how the chemical makeup of a certain body of water affects the plants and animals that reside there. Aquatic scientists can work to tackle global problems such as global oceanic change and local problems, such as trying to understand why a drinking water supply in a certain area is polluted.

Freshwater biology is the scientific biological study of freshwater ecosystems and is a branch of limnology. This field seeks to understand the relationships between living organisms in their physical environment. These physical environments may include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, reservoirs, or wetlands. Knowledge from this discipline is also widely used in industrial processes to make use of biological processes involved with sewage treatment and water purification. Water presence and flow is an essential aspect to species distribution and influences when and where species interact in freshwater environments.

Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish that feed on planktons and other small aquatic organisms. They are in turn preyed upon by various predators including larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals, this making them keystone species in their aquatic ecosystems.
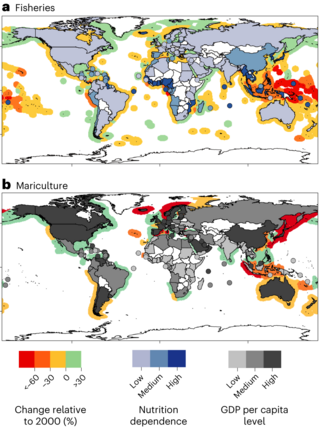
Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.
Mesocyclops longisetus is a species of freshwater copepod in the family Cyclopidae. Two subspecies are accepted, Mesocyclops longisetus curvatus Dussart, 1987, and Mesocyclops longisetus longisetus. It has a neotropical distribution.

Bryocyclops is a genus of freshwater-dwelling cyclopoid copepods. The epithet Bryo- for Bryophyta (Mosses) refers to the fact that the first few species were described from mosses.

Freshwater salinization is the process of salty runoff contaminating freshwater ecosystems, which can harm aquatic species in certain quantities and contaminate drinking water. It is often measured by the increased amount of dissolved minerals than what is considered usual for the area being observed. Naturally occurring salinization is referred to as primary salinization; this includes rainfall, rock weathering, seawater intrusion, and aerosol deposits. Human-induced salinization is termed as secondary salinization, with the use of de-icing road salts as the most common form of runoff. Approximately 37% of the drainage in the United States has been affected by salinization in the past century. The EPA has defined two thresholds for healthy salinity levels in freshwater ecosystems: 230 mg/L Cl− for average salinity levels and 860 mg/L Cl− for acute inputs.
Ergasilus curticrus is a freshwater parasitic copepod named in 2015. Described from the Orinoco river basin, it was found solely to be hosted by individuals of the Characiform fish species Bryconops giacopinii. Of those located in South America, it is one of only five species in its genus to be found outside of Brazil.
Cyclopicina longifurcata is a species of copepod belonging to the family Cyclopicinidae. It was first described by Thomas Scott in 1901. This species is part of the order Cyclopoida, a group of small crustaceans commonly found in marine and freshwater habitats.
Diacyclops uruguayensis is a species of freshwater copepod belonging to the family Cyclopidae. It was first described by Friedrich Kiefer in 1935.












