
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an 83.5-carat diamond called the Star of South Africa in 1869 spawned a diamond rush and led to the excavation of the open-pit mine called the Big Hole. Previously, the term kimberlite has been applied to olivine lamproites as Kimberlite II, however this has been in error.
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water. Hydrothermal circulation occurs most often in the vicinity of sources of heat within the Earth's crust. In general, this occurs near volcanic activity, but can occur in the shallow to mid crust along deeply penetrating fault irregularities or in the deep crust related to the intrusion of granite, or as the result of orogeny or metamorphism. Hydrothermal circulation often results in hydrothermal mineral deposits.

A xenolith is a rock fragment that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term xenolith is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in igneous rock entrained during magma ascent, emplacement and eruption. Xenoliths may be engulfed along the margins of a magma chamber, torn loose from the walls of an erupting lava conduit or explosive diatreme or picked up along the base of a flowing body of lava on the Earth's surface. A xenocryst is an individual foreign crystal included within an igneous body. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. Xenoliths can be non-uniform within individual locations, even in areas which are spatially limited, e.g. rhyolite-dominated lava of Niijima volcano (Japan) contains two types of gabbroic xenoliths which are of different origin - they were formed in different temperature and pressure conditions.

A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption. A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow crater lake, which may also be called a maar.

In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.
A volcano tectonic earthquake or volcano earthquake is caused by the movement of magma beneath the surface of the Earth. The movement results in pressure changes where the rock around the magma has a change in stress. At some point, this stress can cause the rock to break or move. This seismic activity is used by scientists to monitor volcanoes. The earthquakes may also be related to dike intrusion and/or occur as earthquake swarms. Usually they are characterised by high seismic frequency and lack the pattern of a main shock followed by a decaying aftershock distribution of fault related tectonic earthquakes.

A flood basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reaching the surface of the Earth via a mantle plume. Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called traps, after the Swedish word trappa, due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes.

Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form intrusions, such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.

Ultramafic rocks are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content, generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are usually composed of greater than 90% mafic minerals. The Earth's mantle is composed of ultramafic rocks. Ultrabasic is a more inclusive term that includes igneous rocks with low silica content that may not be extremely enriched in Fe and Mg, such as carbonatites and ultrapotassic igneous rocks.

Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of deep-origin volcanoes. They are considered to be a type of diatreme. Volcanic pipes are composed of a deep, narrow cone of solidified magma, and are usually largely composed of one of two characteristic rock types — kimberlite or lamproite. These rocks reflect the composition of the volcanoes' deep magma sources, where the Earth is rich in magnesium. They are well known as the primary source of diamonds, and are mined for this purpose. Volcanic pipes are relatively rare by this definition based on minerals and depth of the magma source, but on the other hand volcanic diatremes are common, indeed the second commonest form of volcanic extrusion.

A diapir is a type of intrusion in which a more mobile and ductilely deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor instability structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the Gulf of Mexico to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock.

In geology, an igneous intrusion is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California.

Volcanic activity is a major part of the geology of Canada and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform, including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds.
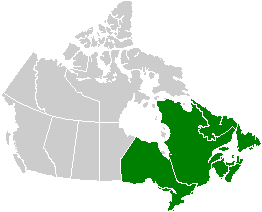
The volcanism of Eastern Canada includes the hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations in Eastern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Eastern Canada has very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. The most capable large igneous provinces in Eastern Canada are Archean age greenstone belts containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite.
The Igwisi Hills are a volcanic field in Kaliua District of Tabora Region of Tanzania. Three tuff cones are found there, one of which is associated with a lava flow. They are one of the few locations of possibly kimberlitic lava flows on Earth.

A cone sheet is a type of high-level igneous intrusion of subvolcanic rock, found in partly eroded central volcanic complexes. Cone sheets are relatively thin inclined sheets, generally just a few metres thick, with the geometry of a downward-pointing cone. Viewed from above, their outcrop is typically circular to elliptical. They were originally described from the Ardnamurchan, Mull and other central complexes of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province.

Lunar Crater volcanic field is a volcanic field in Nye County, Nevada. It lies along the Reveille and Pancake Ranges and consists of over 200 vents, mostly small volcanic cones with associated lava flows but also several maars, including one maar named Lunar Crater. Some vents have been eroded so heavily that the structures underneath the volcanoes have been exposed. Lunar Crater itself has been used as a testing ground for Mars rovers and as training ground for astronauts.

Cathedral Cliff is a 5,810-foot (1,770-meter) elevation volcanic plug located on Navajo Nation land in San Juan County of northwest New Mexico, United States. It is a prominent landmark set alongside U.S. Route 491, approximately 13 miles south of the community of Shiprock, New Mexico. Cathedral Cliff is one of the phreatomagmatic diatremes of the Four Corners area, and with significant relief as it rises 400 feet above the high-desert plain. It is situated about 9.5 miles (15.3 km) southeast of Shiprock, the most famous of these diatremes. Cathedral Cliff is set in the northeastern part of the Navajo Volcanic Field, a volcanic field that includes intrusions and flows of minette and other unusual igneous rocks which formed around 30 million years ago during the Oligocene. Its nearest higher neighbor is Table Mesa, one mile to the southwest, and Barber Peak is set 1.5 mile to the southeast.

The Navajo volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field located in the Four Corners region of the United States, in the central part of the Colorado Plateau. The volcanic field consists of over 80 volcanoes and associated intrusions of unusual potassium-rich compositions, with an age range of 26.2 to 24.7 million years (Ma).
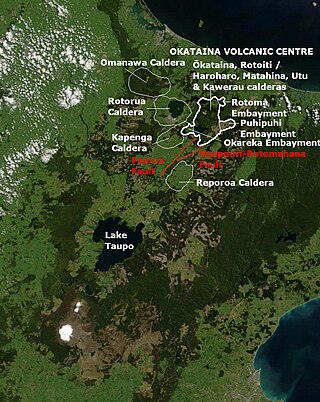
Ōkataina Caldera is a volcanic caldera and its associated volcanoes located in Taupō Volcanic Zone of New Zealand's North Island. It has several actual or postulated sub calderas. The Ōkataina Caldera is just east of the smaller separate Rotorua Caldera and southwest of the much smaller Rotomā Embayment which is usually regarded as an associated volcano. It shows high rates of explosive rhyolitic volcanism although its last eruption was basaltic. The postulated Haroharo Caldera contained within it has sometimes been described in almost interchangeable terms with the Ōkataina Caldera or volcanic complex or centre and by other authors as a separate complex defined by gravitational and magnetic features.. Since 2010 other terms such as the Haroharo vent alignment, Utu Caldera, Matahina Caldera, Rotoiti Caldera and a postulated Kawerau Caldera are often used, rather than a Haroharo Caldera classification.


















