The Merck Group, branded and commonly known as Merck, is a German multinational science and technology company headquartered in Darmstadt, with about 60,000 employees and a presence in 66 countries. The group includes around 250 companies; the main company is Merck KGaA in Germany. The company is divided into three business lines: Healthcare, Life Sciences and Electronics. Merck was founded in 1668 and is the world's oldest operating chemical and pharmaceutical company, as well as one of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally.
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction.
Sigma-Aldrich is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company owned by the multinational chemical conglomerate Merck Group.
Nonene is an alkene with the molecular formula C9H18. Many structural isomers are possible, depending on the location of the C=C double bond and the branching of the other parts of the molecule. Industrially, the most important nonenes are trimers of propene: Tripropylene. This mixture of branched nonenes is used in the alkylation of phenol to produce nonylphenol, a precursor to detergents, which are also controversial pollutants.

Gallocatechol or gallocatechin (GC) is a flavan-3-ol, a type of chemical compound including catechin, with the gallate residue being in an isomeric trans position.
Merck Millipore was the brand used by Merck Group's global life science business until 2015 when the company re-branded. It was formed when Merck acquired the Millipore Corporation in 2010. Merck is a supplier to the life science industry. The Millipore Corporation was founded in 1954, and listed among the S&P 500 since the early 1990s, as an international biosciences company which makes micrometer pore-size filters and tests. In 2015, Merck acquired Sigma-Aldrich and merged it with Merck Millipore. In the United States and Canada, the life science business is now known as MilliporeSigma.
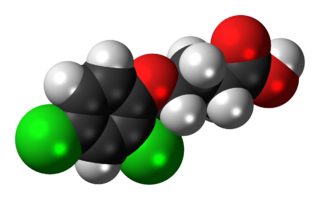
2,4-DB or 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid is a selective systemic phenoxy herbicide used to control many annual and perennial broad-leaf weeds in alfalfa, peanuts, soybeans, and other crops. Its active metabolite, 2,4-D, inhibits growth at the tips of stems and roots. It is classified in toxicity class III. It shows some evidence of toxicity to dogs and cats, such as changes in body weight and reduced numbers of offspring, when fed 25-80 milligrams per kilogram of body weight for prolonged periods. Tests of carcinogenicity in this range yielded differing results. It is moderately toxic to fish.
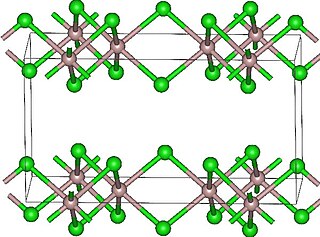
Lutetium(III) chloride or lutetium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of lutetium and chlorine with the formula LuCl3. It forms hygroscopic white monoclinic crystals and also a hygroscopic hexahydrate LuCl3·6H2O. Anhydrous lutetium(III) chloride has the YCl3 (AlCl3) layer structure with octahedral lutetium ions.

11-Eicosenoic acid, also called gondoic acid, is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid found in a variety of plant oils and nuts; in particular jojoba oil. It is one of a number of eicosenoic acids.
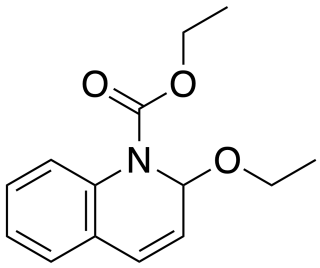
N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline (EEDQ) is an irreversible dopamine-receptor antagonist.

Ethyl iodoacetate is a chemical compound that is a derivative of ethyl acetate. Under normal conditions, the compound is a clear, light yellow to orange liquid.

4-Chloromercuribenzoic acid (p-chloromercuribenzoic acid, PCMB) is an organomercury compound that is used as a protease inhibitor, especially in molecular biology applications.
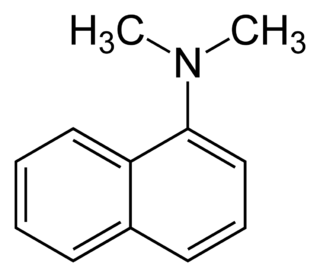
N,N-Dimethyl-1-naphthylamine is an aromatic amine. It is formally derived from 1-naphthylamine by replacing the hydrogen atoms on the amino group with methyl groups. N,N-Dimethyl-1-naphthylamine is used in the nitrate reductase test to form a precipitate of a red azo dye by reacting with a nitrite-sulfanilic acid complex.

VDM-11 is a potent cannabinoid reuptake inhibitor. It is light-sensitive and must be stored within an inert gas such as argon, in a dark place and at an ideal temperature of -49°C. This gold-colored substance is rarely found outside of research laboratories.

The trimethylbenzenes constitute a group of substances of aromatic hydrocarbons, which structure consists of a benzene ring with three methyl groups (–CH3) as a substituent. Through their different arrangement, they form three structural isomers with the molecular formula C9H12. They also belong to the group of C3-benzenes. The best-known isomer is mesitylene.
George William Gregory Bird was a British medical doctor, academic, researcher and haematologist known for his expertise in the fields of blood transfusion and immunohaematology. He founded the Department of Transfusion Medicine at the Armed Forces Medical College, Pune and was inducted into their Hall of Fame in 2010. A winner of the Karl Landsteiner Memorial Prize and Morten Grove Rasmussen Memorial Award of the American Association of Blood Banks, Gregory Bird was honoured by the Government of India in 1963, with the award of Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award for his services to the nation.
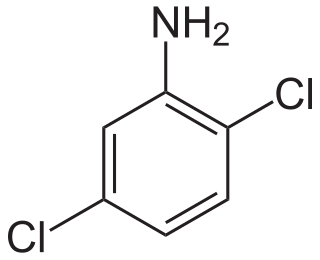
Dichloroanilines are chemical compounds which consist of an aniline ring substituted with two chlorine atoms and have the molecular formula C6H5Cl2N. There are six isomers, varying in the positions of the chlorine atoms around the ring relative to the amino group. As aniline derivatives, they are named with the amino group in position 1. They are all colorless, although commercial samples can appear colored due to the presence of impurities. Several derivatives are used in the production of dyes and herbicides.
A bromophenol is an organic compound consisting of hydroxyl groups and bromine atoms bonded to a benzene ring. They may be viewed as hydroxyl derivatives of bromobenzene, or as brominated derivatives of phenol. There are five basic types of bromophenols and 19 different bromophenols in total when positional isomerism is taken into account. Bromophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with bromine.

Lithium oxalate is an organic compound with the chemical formula Li2C2O4. It is a salt of lithium metal and oxalic acid. It consists of lithium cations Li+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4. Lithium oxalate is soluble in water and converts to lithium oxide when heated.

Gadolinium(III) iodide is an iodide of gadolinium, with the chemical formula of GdI3. It is a yellow, highly hygroscopic solid with a bismuth(III) iodide-type crystal structure. In air, it quickly absorbs moisture and forms hydrates. The corresponding oxide iodide is also readily formed at elevated temperature.






 [2]
[2]  [3]
[3]  [4]
[4] 











