
1,3,2,4-Dithiadiphosphetane 2,4-disulfides are a class of organophosphorus, four-membered ring compounds which contain a P2S2 ring. Many of these compounds are able to act as sources of the dithiophosphine ylides; the most well known example is Lawesson's reagent.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.

Benzamidine is an organic compound with the formula C6H5C(NH)NH2. It is the simplest aryl amidine. The compound is a white solid that is slightly soluble in water. It is usually handled as the hydrochloride salt, a white, water-soluble solid.

Kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonol, a type of flavonoid, found in a variety of plants and plant-derived foods including kale, beans, tea, spinach, and broccoli. Kaempferol is a yellow crystalline solid with a melting point of 276–278 °C (529–532 °F). It is slightly soluble in water and highly soluble in hot ethanol, ethers, and DMSO. Kaempferol is named for 17th-century German naturalist Engelbert Kaempfer.
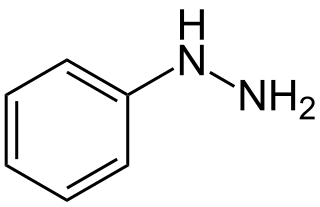
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine (H2N−NH2), in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by hydrocarbon groups.

Amylmetacresol (AMC) is an antiseptic used to treat infections of the mouth and throat. It is used as an active pharmaceutical ingredient in Strepsils, Cēpacol, Gorpils and Lorsept throat lozenges, typically in combination with dichlorobenzyl alcohol, another antiseptic.
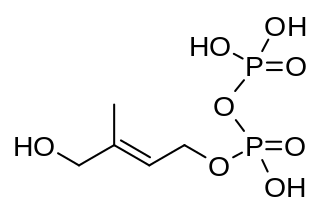
(E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP or HMB-PP) is an intermediate of the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid biosynthesis. The enzyme HMB-PP synthase (GcpE, IspG) catalyzes the conversion of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) into HMB-PP. HMB-PP is then converted further to isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) by HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH).

1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene is a chemical that reacts with the N-terminal amino acid of polypeptides. This can be helpful for sequencing proteins.
2-Succinyl-6-hydroxy-2,4-cyclohexadiene-1-carboxylate synthase, also known as SHCHC synthase is encoded by the menH gene in Escherichia coli and functions in the synthesis of vitamin K. The specific step in the synthetic pathway that SHCHC synthase catalyzes is the conversion of 5-enolpyruvoyl-6-hydroxy-2-succinylcyclohex-3-ene-1-carboxylate to (1R,6R)-6-hydroxy-2-succinylcyclohexa-2,4-diene-1-carboxylate and pyruvate.

Saccoglossus is a genus of acorn worm. It is the largest genus in this class, with 18 species.
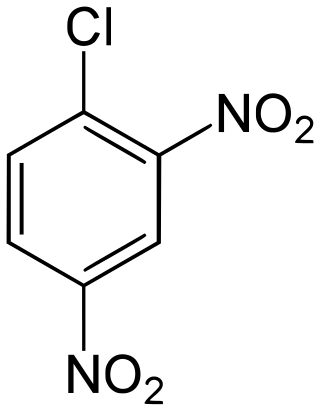
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an important intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.

Ruthenium(III) acetylacetonate is a coordination complex with the formula Ru(O2C5H7)3. O2C5H7− is the ligand called acetylacetonate. This compound exists as a dark violet solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. It is used as a precursor to other compounds of ruthenium.

Harrimaniidae is a basal family of acorn worms. A taxonomic revision was undertaken in 2010, and a number of new genera and species found in the Eastern Pacific were described. In this family the development is direct without tornaria larva, and circular muscle fibers in their trunk is missing. There is some indication that Stereobalanus may be a separate basal acorn worm lineage, sister to all remaining acorn worms.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).
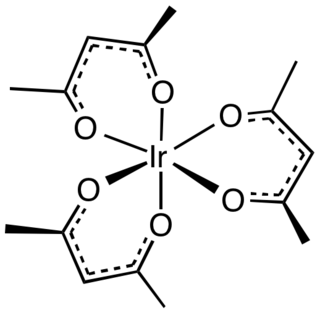
Iridium acetylacetonate is the iridium coordination complex with the formula Ir(O2C5H7)3, which is sometimes known as Ir(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Saccoglossus bromophenolosus is a species of acorn worm occurring in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean and the northeastern Pacific Ocean. It grows to a length of about 20 cm (8 in) and lives in a burrow in soft sediment in the intertidal and subtidal zones. The scientific name refers to 2,4-dibromophenol, a secondary metabolite present in this worm.
Dibromophenols are a group of bromophenols consisting of one hydroxy group and two bromine atoms bonded to a benzene ring. There are six structural isomers, each with the molecular formula C6H4Br2O, which differ by arrangement of the substituents.
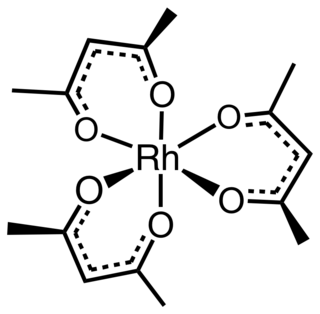
Rhodium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Rh(C5H7O2)3, which is sometimes known as Rh(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Zirconium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Zr(C5H7O2)4. It is a common acetylacetonate of zirconium. It is a white solid that exhibits high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons.
A bromophenol is an organic compound consisting of hydroxyl groups and bromine atoms bonded to a benzene ring. They may be viewed as hydroxyl derivatives of bromobenzene, or as brominated derivatives of phenol. There are five basic types of bromophenols and 19 different bromophenols in total when positional isomerism is taken into account. Bromophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with bromine.

















