
Obdurodon is a genus of extinct platypus-like Australian monotreme which lived from the Late Oligocene to the Late Miocene. Three species have been described in the genus, the type species Obdurodon insignis, plus Obdurodon dicksoni and Obdurodon tharalkooschild. The species appeared much like their modern day relative the platypus, except adults retained their molar teeth, and unlike the platypus, which forages on the lakebed, they may have foraged in the water column or surface.

Deinotherium is an extinct genus of large, elephant-like proboscideans that lived from about the middle-Miocene until the early Pleistocene. Although its appearance is reminiscent of modern elephants, Deinotherium possessed a notably more flexible neck, with limbs adapted to a more cursorial lifestyle, as well as tusks which grew down and curved back from the mandible, as opposed to the forward-growing maxillary tusks of extant elephants. Deinotherium was a widespread genus, ranging from East Africa, north to Southern Europe, and east to the Indian subcontinent. They were primarily browsing animals, with a diet largely consisting of leaves. The genus most likely went extinct due to environmental changes, such as forested areas gradually being replaced by open grasslands, during the latter half of the Neogene. Deinotherium thrived the longest in Africa, where they were found into the early Pleistocene.

Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct family of large carnivorous, mostly flightless birds that were among the largest apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era. Their definitive fossil records range from the Middle Eocene to the Late Pleistocene around 43 to 0.1 million years ago, though some specimens suggest that they were present since the Early Eocene.

The marsh shrew, also known as the Pacific water shrew, Bendire's water shrew, Bendire's shrew and Jesus shrew is the largest North American member of the genus Sorex. Primarily covered in dark-brown fur, it is found near aquatic habitats along the Pacific coast from southern British Columbia to northern California. With air trapped in its fur for buoyancy, marsh shrews can run for three to five seconds on top of the water. It measures about 16 cm (6.3 in) in length, including a 7-centimetre (2.8 in)-long tail, and weighs an average of 14.5–16 g (0.51–0.56 oz). The marsh shrew's diet consists mainly of invertebrates, which it hunts on land and in the water. They are rare; their populations are thought to be in decline, and they are considered endangered in parts of their range.

Deinotheriidae is a family of prehistoric elephant-like proboscideans that lived during the Cenozoic era, first appearing in Africa, then spreading across South Asia and Europe. During that time, they changed very little, apart from growing much larger in size; by the late Miocene, they had become the largest land animals of their time. Their most distinctive features were their lack of upper tusks and downward-curving tusks on the lower jaw.

Paraceratherium is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch. The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. Paraceratherium means "near the hornless beast", in reference to Aceratherium, the genus in which the type species P. bugtiense was originally placed.

Dromornis is a genus of large to enormous prehistoric birds native to Australia during the Oligocene to Pliocene epochs. The species were flightless, possessing greatly reduced wing structures but with large legs, similar to the modern ostrich or emu. They were likely to have been predominantly, if not exclusively, herbivorous browsers. The male of the largest species, Dromornis stirtoni, is a contender for the tallest and heaviest bird, and possibly exhibited aggressive territorial behaviour. They belong to the family Dromornithidae, extinct flightless birds known as mihirungs.

Purussaurus is an extinct genus of giant caiman that lived in South America during the Miocene epoch, from the Friasian to the Huayquerian in the SALMA classification. It is known from skull material found in the Brazilian and Peruvian Amazon, Argentina, Colombian Villavieja Formation, Panamanian Culebra Formation, Urumaco and Socorro Formations of northern Venezuela.

Myotragus is an extinct genus of goat-antelope in the tribe Caprini which lived on the Balearic Islands of Mallorca and Menorca in the western Mediterranean until its extinction around 4,500 years ago. The fossil record of Myotragus on the Balearic Islands extends over 5 million years back to the early Pliocene on Mallorca, where it presumably arrived after the evaporation of the Mediterranean Sea during the Messinian Salinity Crisis.

Palaeocastor is an extinct genus of beavers that lived in the North American Badlands during the late Oligocene period to early Miocene. Palaeocastor was much smaller than modern beavers. There are several species including Palaeocastor fossor, Palaeocastor magnus,Palaeocastor wahlerti, and Palaeocastor peninsulatus. The animals first became known on grounds of their fossilized burrows, the "Devil's corkscrews".

Hapalops is an extinct genus of ground sloth from the Early to Late Miocene of Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, and Argentina in South America.

True's shrew mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to Japan and is a common species above 1000 meters in grassland, shrubland and forest. Sometimes this species is called the lesser Japanese shrew mole and another species, Urotrichus talpoides, is called the "greater Japanese shrew mole".

Urotrichus is a genus of talpid that contains a single living species, the Japanese shrew mole (Urotrichus talpoides). Two fossil species are also known.

Lufengpithecus is an extinct genus of ape, known from the Late Miocene of East Asia. It is known from thousands of dental remains and a few skulls and probably weighed about 50 kg (110 lb). It contains three species: L. lufengensis, L. hudienensis and L. keiyuanensis. Lufengpithecus lufengensis is from the Late Miocene found in China, named after the Lufeng site and dated around 6.2 Ma. Lufengpithecus is either thought to be the sister group to Ponginae, or the sister to the clade containing Ponginae and Homininae.

Xenastrapotherium is an extinct genus of astrapothere, a type of hoofed herbivorous mammal, native to South America, which lived in the Middle to Late Miocene period, typically during the Laventan stage. It is a member of the family Astrapotheriidae in the subfamily Uruguaytheriinae, large astrapotheres, equipped with a trunk-like nose and protruding teeth, similar to the elephants, but their tusks were the canine teeth, not the incisors. Xenastrapotherium was a genus widely distributed in northern South America, in contrast to other species of astrapotheres which lived in the area of the Southern Cone of the continent. It differed from other astrapotheres by having two lower incisors on each side of the jaw and the tusks have a pronounced longitudinal curvature, although their general shape and size are probably very similar to Astrapotherium, whose weight would be 900 to 1,500 kilograms, comparable to the current black rhinoceros.

Enhydriodon is an extinct genus of mustelids known from Africa, Pakistan, and India that lived from the late Miocene to the early Pleistocene. It contains nine confirmed species, two debated species, and at least a few other undescribed species from Africa. The genus belongs to the tribe Enhydriodontini in the otter subfamily Lutrinae. Enhydriodon means "otter tooth" in Ancient Greek and is a reference to its dentition rather than to the Enhydra genus, which includes the modern sea otter and its two prehistoric relatives.

Paedotherium is an extinct, potentially paraphyletic genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the family Hegetotheriidae, composed of small-sized, rodent or lagomorph-like South American ungulates. Four species are unambiguously recognized, from the Late Miocene to the Pleistocene of Argentina, and from the late Miocene of Bolivia and Chile.
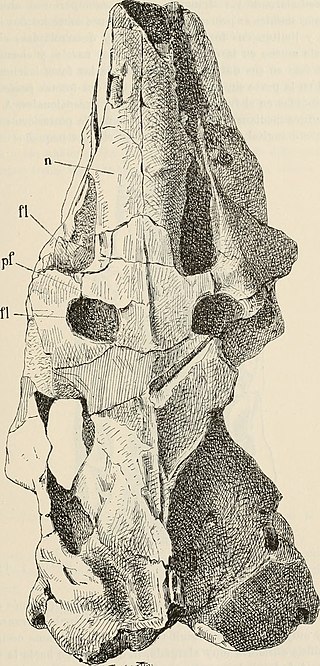
Hemihegetotherium is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate that lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene of what is now Argentina.
Anayatherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate belonging to the family Leontiniidae. It lived during the Late Oligocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Parapliohyrax is an extinct genus of large hyracoid, a group today represented only by the diminutive hyraxes, but showing in fossil archives a large diversity in ecology and morphology. Parapliohyrax lived during the Miocene period, in various localities spanning the entirety of the African continent. Two species have been identified, based on cranial remains : Parapliohyrax mirabilis, the type species, known from the Miocene of Morocco and Tunisia, and P. ngororaensis, discovered in Kenyan and Namibian deposits. Isolated postcranial remains attributed to the genus have been identified in South African and Libyan deposits of the same age.

















