Related Research Articles
In calculus, the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the composition of two differentiable functions f and g in terms of the derivatives of f and g. More precisely, if is the function such that for every x, then the chain rule is, in Lagrange's notation,

In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term convolution refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function.

G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.
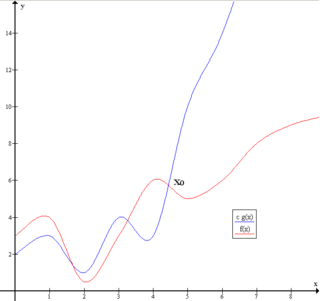
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.

In physics, engineering and mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that converts a function into a form that describes the frequencies present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made the Fourier transform is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.

The orbital period is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the ratio between the mass and the amount of substance of any sample of said compound. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.

In mathematics, a function from a set X to a set Y assigns to each element of X exactly one element of Y. The set X is called the domain of the function and the set Y is called the codomain of the function.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure-volume work, that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed as

Indomalayan realm
Disoidemata is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by George Hampson in 1900.

Oreolyce is an Indomalayan genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae.

Acontia is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was named by Ferdinand Ochsenheimer in 1816. Eusceptis, Pseudalypia and Spragueia are sometimes included in the present genus, but here they are tentatively treated as different pending further research. Many species of Tarache were also once placed here.

Ercheia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1858.
Ercheia quadriplaga is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in Asia, including Sulawesi.
Mithuna quadriplaga is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Frederic Moore in 1878. It is found in Bhutan and the Indian state of Sikkim.

Oreolyce archena is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It was described by Alexander Steven Corbet in 1940. It is found in the Indomalayan realm.

Tarache quadriplaga is a species of bird dropping moth in the family Noctuidae first described by Smith in 1900. It is found in North America.
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Disoidemata quadriplaga". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum . Retrieved May 1, 2018.