Related Research Articles

Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes (EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. The harmless strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2, (which helps blood to clot) and preventing colonisation of the intestine with pathogenic bacteria, having a symbiotic relationship. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for 3 days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.
dnaQ is the gene encoding the ε subunit of DNA polymerase III in Escherichia coli. The ε subunit is one of three core proteins in the DNA polymerase complex. It functions as a 3’→5’ DNA directed proofreading exonuclease that removes incorrectly incorporated bases during replication. dnaQ may also be referred to as mutD.
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology method that is used to make specific and intentional changes to the DNA sequence of a gene and any gene products. Also called site-specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, it is used for investigating the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules, and for protein engineering.

The SOS response is a global response to DNA damage in which the cell cycle is arrested and DNA repair and mutagenesis is induced. The system involves the RecA protein. The RecA protein, stimulated by single-stranded DNA, is involved in the inactivation of the repressor (LexA) of SOS response genes thereby inducing the response. It is an error-prone repair system that contributes significantly to DNA changes observed in a wide range of species.

RecBCD is an enzyme of the E. coli bacterium that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA.

Tryptophan repressor is a transcription factor involved in controlling amino acid metabolism. It has been best forstudied in Escherichia coli, where it is a dimeric protein that regulates transcription of the 5 genes in the tryptophan operon. When the amino acid tryptophan is plentiful in the cell, it binds to the protein, which causes a conformational change in the protein. The repressor complex then binds to its operator sequence in the genes it regulates, shutting off the genes.

The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions needing it to be compacted in order to fit. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Instead, the nucleoid forms by condensation and functional arrangement with the help of chromosomal architectural proteins and RNA molecules as well as DNA supercoiling. The length of a genome widely varies and a cell may contain multiple copies of it.
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. The enzyme causes negative supercoiling of the DNA or relaxes positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template so as to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in bacteria, whose single circular DNA is cut by DNA gyrase and the two ends are then twisted around each other to form supercoils. Gyrase is also found in eukaryotic plastids: it has been found in the apicoplast of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and in chloroplasts of several plants. Bacterial DNA gyrase is the target of many antibiotics, including nalidixic acid, novobiocin, and ciprofloxacin.
Recombineering is a genetic and molecular biology technique based on homologous recombination systems, as opposed to the older/more common method of using restriction enzymes and ligases to combine DNA sequences in a specified order. Recombineering is widely used for bacterial genetics, in the generation of target vectors for making a conditional mouse knockout, and for modifying DNA of any source often contained on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), among other applications.
The gene rpoS encodes the sigma factor sigma-38, a 37.8 kD protein in Escherichia coli. Sigma factors are proteins that regulate transcription in bacteria. Sigma factors can be activated in response to different environmental conditions. rpoS is transcribed in late exponential phase, and RpoS is the primary regulator of stationary phase genes. RpoS is a central regulator of the general stress response and operates in both a retroactive and a proactive manner: it not only allows the cell to survive environmental challenges, but it also prepares the cell for subsequent stresses (cross-protection). The transcriptional regulator CsgD is central to biofilm formation, controlling the expression of the curli structural and export proteins, and the diguanylate cyclase, adrA, which indirectly activates cellulose production. The rpoS gene most likely originated in the gammaproteobacteria.
Maltose-binding protein (MBP) is a part of the maltose/maltodextrin system of Escherichia coli, which is responsible for the uptake and efficient catabolism of maltodextrins. It is a complex regulatory and transport system involving many proteins and protein complexes. MBP has an approximate molecular mass of 42.5 kilodaltons.

fis is an E. coli gene encoding the Fis protein. The regulation of this gene is more complex than most other genes in the E. coli genome, as Fis is an important protein which regulates expression of other genes. It is supposed that fis is regulated by H-NS, IHF and CRP. It also regulates its own expression (autoregulation). Fis is one of the most abundant DNA binding proteins in Escherichia coli under nutrient-rich growth conditions.

Spot 42 (spf) RNA is a regulatory non-coding bacterial small RNA encoded by the spf gene. Spf is found in gammaproteobacteria and the majority of experimental work on Spot42 has been performed in Escherichia coli and recently in Aliivibrio salmonicida. In the cell Spot42 plays essential roles as a regulator in carbohydrate metabolism and uptake, and its expression is activated by glucose, and inhibited by the cAMP-CRP complex.

In enzymology, a dUTP diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
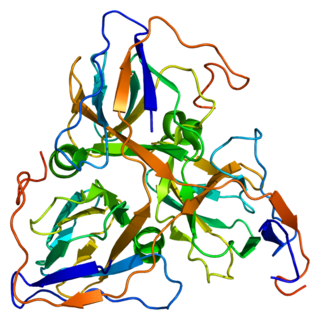
DUTP pyrophosphatase, also known as DUT, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DUT gene on chromosome 15.
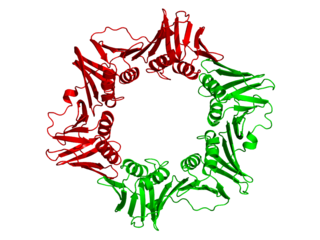
dnaN is the gene that codes for the DNA clamp of DNA polymerase III in prokaryotes. The β clamp physically locks Pol III onto a DNA strand during replication to help increase its processivity. The eukaryotic equivalent to the β clamp is PCNA.

A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, in the form of a molecule of circular DNA, unlike the linear chromosome of most eukaryotes.

Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative gammaproteobacterium commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). The descendants of two isolates, K-12 and B strain, are used routinely in molecular biology as both a tool and a model organism.

In molecular biology, the Fic/DOC protein family is a family of proteins which catalyzes the post-translational modification of proteins using phosphate-containing compound as a substrate. Fic domain proteins typically use ATP as a co-factor, but in some cases GTP or UTP is used. Post-translational modification performed by Fic domains is usually NMPylation, however they also catalyze phosphorylation and phosphocholine transfer. This family contains a central conserved motif HPFX[D/E]GNGR in most members and it carries the invariant catalytic histidine. Fic domain was found in bacteria, eukaryotes and archaea and can be found organized in almost hundred different multi-domain assemblies.
In DNA repair, the Ada regulon is a set of genes whose expression is essential to adaptive response, which is triggered in prokaryotic cells by exposure to sub-lethal doses of alkylating agents. This allows the cells to tolerate the effects of such agents, which are otherwise toxic and mutagenic.
References
- ↑ el-Hajj HH, Zhang H, Weiss B (March 1988). "Lethality of a dut (deoxyuridine triphosphatase) mutation in Escherichia coli". Journal of Bacteriology. 170 (3): 1069–75. doi:10.1128/jb.170.3.1069-1075.1988. PMC 210875 . PMID 2830228.
| This molecular biology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |