The Korean Unification Flag is a flag designed to represent all of Korea when North and South Korea participate as one team in various sporting events.
Korean nationalism can be viewed in two different contexts. One encompasses various movements throughout history to maintain a Korean cultural identity,history,and ethnicity. This ethnic nationalism was mainly forged in opposition to foreign incursion and rule. The second context encompasses how Korean nationalism changed after the partition in 1945. Today,the former tends to predominate.
Ulleung County is a county in North Gyeongsang Province,South Korea.

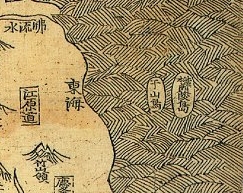
Ulleungdo,also spelled Ulreungdo,is a South Korean island 120 kilometres east of the Korean Peninsula in the Sea of Japan,formerly known as Dagelet Island or Argonaut Island in Europe. Volcanic in origin,the rocky steep-sided island is the top of a large stratovolcano which rises from the seafloor,reaching a maximum elevation of 984 metres (3,228 ft) at Seonginbong Peak. The island is 9.5 kilometres (6 mi) in length and ten kilometres (6 mi) in width;it has an area of 72.86 km2 (28.13 sq mi). It has a population of 10,426 inhabitants.

The Syngman Rhee Line was a marine boundary line established by South Korean President Syngman Rhee in his "Peace Line" declaration of January 18,1952,establishing a wide area of maritime sovereignty,beyond internationally accepted territorial waters,around the entire Korean Peninsula. This included placing the Liancourt Rocks (Dokdo/Takeshima) in South Korean territory. The line was abolished in 1965 with the signing of a Japanese–South Korean fishing agreement.

The Rusk documents are the official diplomatic correspondence sent by Dean Rusk,the United States Assistant Secretary of State for Far Eastern Affairs,to Yang You-chan,the South Korean ambassador to the U.S. on August 10,1951.

Anti-Japanese sentiment in Korean society has its roots in historic,cultural,and nationalistic sentiments.
Usan-do is a historical name for an island in the Sea of Japan described in Korean records. It was part of the ancient state of Usan-guk,but its exact identity is disputed. It may refer to:

The Liancourt Rocks,also known by their Korean name of Dokdo or their Japanese name of Takeshima,are a group of islets in the Sea of Japan between the Korean peninsula and the Japanese archipelago administered by South Korea. The Liancourt Rocks comprise two main islets and 35 smaller rocks;the total surface area of the islets is 0.187554 square kilometres and the highest elevation of 168.5 metres (553 ft) is on the West Islet. The Liancourt Rocks lie in rich fishing grounds that may contain large deposits of natural gas. The English name Liancourt Rocks is derived from Le Liancourt,the name of a French whaling ship that came close to being wrecked on the rocks in 1849.

An Yong-bok was a Korean fisherman in 17th century of Joseon Dynasty famous for his travels to Japan. His activities were instrumental in determining fishery rights in the waters of Ulleungdo and the Liancourt Rocks,two islands in the East Sea.

The Liancourt Rocks dispute,also called the Takeshima dispute or Dokdo dispute is a territorial dispute between South Korea and Japan regarding sovereignty over the Liancourt Rocks,a group of small islets in the Sea of Japan. The rocks also go by the names Dokdo and Takeshima. North Korea also claims sovereignty of the islands,but has not pursued its claim to the same extent as the other parties.

ROKS Dokdo (LPH-6111) is the lead ship of the Dokdo-class amphibious assault ship of the Republic of Korea Navy,launched on 12 July 2005 at the shipyard of Hanjin Heavy Industries &Constructions Co. in Busan. ROKS Dokdo was the flagship of the Fifth Component Flotilla of the Korean Navy until the launch of ROKS Marado in 2018. Previously,this title was held by the 9,000-ton at-sea Underway Replenishment (UNREP) support vessel ROKS Cheonji.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of South Korea.

Japan–South Korea relations refers to the diplomatic relations between Japan and the Republic of Korea. As the Sea of Japan and the Korea Strait geographically separate the two nations,political interactions date back from the 6th century when the kingdom of Baekje officially established relations with Japan. During the ancient era,the southern region of the Korean Peninsula often served as the closest port for Japan to engage in economic trade and cultural exchange to and from mainland Asia. By 1910,Korea would become a colony of Japan until the Japanese surrender at the end of World War II in 1945.

Japan is currently engaged in several territorial disputes with nearby countries,including Russia,South Korea,North Korea,the People's Republic of China,and the Republic of China (Taiwan).

The Embassy of Japan in Seoul is the diplomatic mission of Japan in South Korea. It is located in Seoul,South Korea's capital.
The Dokdo Volunteer Garrison (Korean: 독도의용수비대) was a South Korean paramilitary outpost on the Liancourt Rocks. Both South Korea and Japan each claim sovereignty over the islands. The garrison was established by volunteers from Ulleungdo Island and the Korean Veterans Association,and was led by Hong Sun-chil. The garrison was a private organization that is considered to have laid the foundation for South Korea to exercise practical territorial sovereignty over the islands. According to multiple sources,including the Encyclopedia of Korean Culture,the garrison engaged in several clashes against the Japan Coast Guard,and was maintained from 1953 to 1956 until South Korean police forces fully took over operations over the island.
In Japan,Takeshima Day (竹島の日) is celebrated on February 22 every year since 2005. Public events related to Takeshima are held on this day,and the day is also used to demonstrate Japan's sovereignty over the Liancourt Rocks.
"Dokdo Is Our Land" is a 1982 pop song written by South Korean musician Park Moon-young and sung by comedian Jeong Kwang-tae about the Liancourt Rocks dispute. The song has grown to become highly recognizable in South Korea as a point of anti-Japanese nationalism.