
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a land vehicle, including cars, motorcycles, trucks, and buses. Permission to drive on public highways is granted based on a set of conditions being met and drivers are required to follow the established road and traffic laws in the location they are driving. The word driving, has etymology dating back to the 15th century and has developed as what driving has encompassed has changed from working animals in the 15th to automobiles in the 1800s. Driving skills have also developed since the 15th century with physical, mental and safety skills being required to drive. This evolution of the skills required to drive have been accompanied by the introduction of driving laws which relate to not only the driver but the driveability of a car.
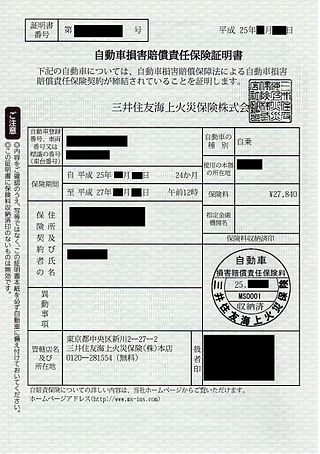
Vehicle insurance is insurance for cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other road vehicles. Its primary use is to provide financial protection against physical damage or bodily injury resulting from traffic collisions and against liability that could also arise from incidents in a vehicle. Vehicle insurance may additionally offer financial protection against theft of the vehicle, and against damage to the vehicle sustained from events other than traffic collisions, such as keying, weather or natural disasters, and damage sustained by colliding with stationary objects. The specific terms of vehicle insurance vary with legal regulations in each region.

A driving test is a procedure designed to test a person's ability to drive a motor vehicle. It exists in various forms worldwide, and is often a requirement to obtain a license to drive a vehicle independently. A driving test generally consists of one or two parts: the practical test, used to assess a person's driving ability under normal operating conditions, and a theory test to confirm a person's knowledge of driving and relevant rules and laws.

Bicycle law in California is the parts of the California Vehicle Code that set out the law for persons cycling in California, and a subset of bicycle law in the United States. In general, pretty much all the same rights and responsibilities that apply to car drivers apply to bicycle riders as well.
Graduated driver licensing systems (GDLS) are designed to provide new drivers of motor vehicles with driving experience and skills gradually over time in low-risk environments. There are typically three steps or stages through which new drivers pass. They begin by acquiring a learner's permit, progress to a restricted, probationary or provisional license, followed by receipt of a full driver's license. Graduated drivers' licensing generally restricts nighttime, expressway, and unsupervised driving during initial stages, but lifts these restrictions with time and further testing of the individual, eventually concluding with the individual attaining a full driver's license.
A driver's permit, learner's permit, learner's license or provisional license is a restricted license that is given to a person who is learning to drive, but has not yet satisfied the prerequisite to obtain a driver's license. Having a learner's permit for a certain length of time is usually one of the requirements for applying for a full driver's license. To get a learner's permit, one must typically pass a written permit test, take a basic competency test in the vehicle, or both.

An International Driving Permit (IDP), often referred to as an international driving license, is a translation of a domestic driving license that allows the holder to drive a private motor vehicle in any country or jurisdiction that recognises the document. The term International Driving Permit was first mentioned in the document prescribed in the International Convention relative to Motor Traffic that was signed at Paris in 1926, and is a translation of the French 'permis de conduire international', or 'international driving license'. The Paris treaty, and all subsequent, use the word 'permit' exclusively in relation to all kinds of driving license.
Many countries have adopted a penalty point or demerit point system under which a person’s driving license is revoked or suspended based on the number of points they’ve accumulated over a specific period of time, points are given for traffic offenses or infringements committed by them in that period. The demerit points schemes of each jurisdiction varies. These demerit schemes are usually in addition to fines or other penalties which may be imposed for a particular offence or infringement, or after a prescribed number of points have been accumulated.

A motorized scooter is a stand-up scooter powered by either a small internal combustion engine or electric hub motor in its front and/or rear wheel. Classified as a form of micro-mobility, they are generally designed with a large center deck on which the rider stands. The first motorized scooter was manufactured by Autoped in 1915.

In the United States, driver's licenses are issued by each individual state, territory, and the District of Columbia rather than by the federal government due to federalism. Drivers are normally required to obtain a license from their state of residence. All states of the United States and provinces and territories of Canada recognize each other's licenses for non-resident age requirements. There are also licenses for motorcycle use. Generally, a minimum age of 15 is required to apply for a non-commercial driver license, and 25 for commercial licenses which drivers must have to operate vehicles that are too heavy for a non-commercial licensed driver or vehicles with at least 16 passengers or containing hazardous materials that require placards. A state may also suspend an individual's driving privilege within its borders for traffic violations. Many states share a common system of license classes, with some exceptions, e.g. commercial license classes are standardized by federal regulation at 49 CFR 383. Many driving permits and ID cards display small digits next to each data field. This is required by the American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators' design standard and has been adopted by many US states. The AAMVA provides a standard for the design of driving permits and identification cards issued by its member jurisdictions, which include all 50 US states, the District of Columbia, and Canadian territories and provinces. The newest card design standard released is the 2020 AAMVA DL/ID Card Design Standard (CDS). The AAMVA standard generally follows part 1 and part 2 of ISO/IEC 18013-1. The ISO standard in turn specifies requirements for a card that is aligned with the UN Conventions on Road Traffic, namely the Geneva Convention on Road Traffic and the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic.
In Canada, driver's licences are issued by the government of the province or territory in which the driver is residing. Thus, specific regulations relating to driver's licences vary province to province, though overall they are quite similar. All provinces have provisions allowing non-residents to use licences issued by other provinces and territories, out-of-country licences, and International Driving Permits. Many provinces also allow non-residents to use regular licences issued by other nations and countries. Canadian driver's licences are also valid in many other countries due to various international agreements and treaties.
In India, a driving licence is an official document that authorises its holder to operate various types of motor vehicles on highways and some other roads to which the public has access. In various Indian states, they are administered by the Regional Transport Authorities/Offices (RTA/RTO). A driving licence is required in India by any person driving a vehicle on any highway or other road defined in the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988. This act sets limits on the minimum age for vehicle operation ranging from 16 to 20, depending on specific circumstances. A modern photo of the driving licence can also serve many of the purposes of an identity card in non-driving contexts, such as proof of identity or age.
In Pakistan, the driving licence is the official document which authorises its holder to operate various types of motor vehicles on publicly accessible roads. Driving licences can be obtained by submitting an application to any licensing authority in the applicant's district.
A driving licence in Singapore is required before a person is allowed to drive a motor vehicle of any description on a road in the country. Like many other countries in the world, an individual must possess a valid driving licence before being permitted to drive on the road, and driving licence holders are subject to all traffic rules.

In the United Kingdom, a driving licence is the official document which authorises its holder to operate motor vehicles on highways and other public roads. It is administered in England, Scotland and Wales by the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency (DVLA) and in Northern Ireland by the Driver & Vehicle Agency (DVA). A driving licence is required in England, Scotland, and Wales for any person driving a vehicle on any highway or other "road", as defined in s.192 Road Traffic Act 1988, irrespective of the ownership of the land over which the road passes. Similar requirements apply in Northern Ireland under the Road Traffic Order 1981.

In Brazil, a driver's licence is required in order to drive cars, buses, trucks and motorcycles. Current CNHs can be used as identity cards in all the national territory.

The Indonesian driving license is a legal document required for a person to be allowed to drive a motor vehicle in Indonesia. It is issued by the Indonesian National Police (POLRI), renewable every 5 years, and is valid in all ASEAN member states without an International Driving Permit. Driving license holders are subject to all Indonesian road rules and regulations. There is no provisional driving license in Indonesia.

In traffic laws, a hit and run or a hit-and-run is the criminal act of causing a traffic collision and not stopping afterwards. It is considered a supplemental crime in most jurisdictions.

A driver's license, driving licence, or driving permit is a legal authorization, or the official document confirming such an authorization, for a specific individual to operate one or more types of motorized vehicles—such as motorcycles, cars, trucks, or buses—on a public road. Such licenses are often plastic and the size of a credit card.
In Spain, a driving licence is an official document which authorises the holder to operate motor vehicles. It is issued by the Directorate-General for Traffic (DGT).












