
Drosophila is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies ; tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly.

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes fruit flies. Another unrelated family of flies, Tephritidae, also includes species known as "small fruit flies". The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, and this species is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. This fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies.

The Drosophilinae are the largest subfamily in the Drosophilidae. The other subfamily is the Steganinae.
The Drosophila melanogaster species group belongs to the subgenus Sophophora and contains 10 subgroups. The phylogeny in this species group is poorly known despite many studies covering many of the species subgroups. The most likely explanation is that the various subgroups diverged from each other in a relatively short evolutionary time frame. Three subgroups have not yet been investigated in molecular studies, and their position in the phylogeny is unclear. The suzukii subgroup is paraphyletic as D. lucipennis is systematically placed within the elegans subgroup.
The paraphyletic subgenus Sophophora of the genus Drosophila was first described by Alfred Sturtevant in 1939. It contains the best-known drosophilid species, Drosophila melanogaster. Sophophora translates as carrier (phora) of wisdom (sophos). The subgenus is paraphyletic because the genus Lordiphosa and the species Hirtodrosophila duncani are also placed within this subgenus.

Drosophila suzukii, commonly called the spotted wing drosophila or SWD, is a fruit fly. D. suzukii, originally from southeast Asia, is becoming a major pest species in America and Europe, because it infests fruit early during the ripening stage, in contrast with other Drosophila species that infest only rotting fruit.

The subgenus Dorsilopha belongs to genus Drosophila and consists of four species. The phylogenetic position of this group has been unclear for a long time, but recent studies have shown that the subgenus is positioned ancestral to the subgenus Drosophila.

The immigrans-tripunctata radiation is a speciose lineage of Drosophila flies, including over 300 species. The immigrans-tripunctata radiation is a sister lineage to most other members of the subgenus Drosophila. A number of species have had their genomes or transcriptomes sequenced for evolutionary studies using Drosophila.
Drosophila colorata is a species of vinegar fly in the family Drosophilidae. It is found in the United States.
Drosophila putrida is a species of fruit fly in the family Drosophilidae. It is found throughout the temperate central-eastern United States. Like other members of the Drosophila testacea species group, D. putrida breeds exclusively on mushrooms.

Drosophila repleta is a species of vinegar fly in the family Drosophilidae.

Chymomyza is a genus of vinegar flies. There are about 10 described species in Chymomyza.
Drosophila tripunctata is a species of vinegar fly in the Immigrans-tripunctata radiation of the subgenus Drosophila.
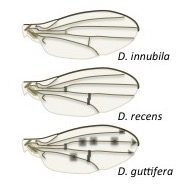
Drosophila guttifera is a species of vinegar fly in the Drosophila quinaria species group.

Drosophila immigrans is a species of vinegar fly in the family Drosophilidae. Drosophila immigrans is a member of the Immigrans-tripunctata radiation of the subgenus Drosophila. It is related to the Drosophila quinaria and Drosophila testacea species groups, and the fellow Immigrans species group member Drosophila albomicans. Drosophila immigrans has been used in evolutionary studies to understand how viruses evolve with their hosts.
Drosophila quinaria is a species of fruit fly in the Drosophila quinaria species group. Most Quinaria group species feed largely on mushrooms. However D. quinaria instead eats decaying vegetative matter, a trait it evolved independently.
Drosophila deflecta is a species of fruit fly in the Drosophila quinaria species group.
The Drosophila cardini species group belongs to the subgenus Drosophila of vinegar flies in the Immigrans-tripunctata radiation of the subgenus Drosophila. The closest relatives of Cardini species include Drosophila bizonata, Drosophila quinaria, and Drosophila testacea species groups, comprising mushroom-feeding flies. Cardini group species likely derived their more general feeding ecology from a mushroom-feeding ancestor, an evolutionary transition in feeding similar to Drosophila quinaria.
Drosophila albomicans is a species of vinegar fly in the family Drosophilidae. Drosophila albomicans is a member of the Immigrans-tripunctata radiation of the subgenus Drosophila. The D. albomicans genome was first sequenced in 2012 to study the evolution of novel sex chromosomes, a characteristic this species is best known for. One commonly accepted definition of the biological species concept is that individuals or populations are members of different species if they are incapable of successful interbreeding. While D. albomicans and Drosophila nasuta are commonly referred to as distinct species, there appears to be little to no sexual isolation between these two Drosophila species. Instead, behavioural differences appear to reproductively isolate these two species.

Drosophila prolongata is a fly of the family Drosophilidae. This species is endemic to southeast Asia. Males of this species express one of most extreme reversed sexual size dimorphism in the Drosophilidae, making this species an interesting model organism for the study of sexual selection. Males also display remarkable copulation courtship behaviour.










