
Drug Abuse Resistance Education, or D.A.R.E., is an American education program that tries to prevent use of controlled drugs, membership in gangs, and violent behavior. It was founded in Los Angeles in 1983 as a joint initiative of then-LAPD chief Daryl Gates and the Los Angeles Unified School District as a demand-side drug control strategy of the American War on Drugs.
Michael L. Hecht is a researcher in the field of human communication, emphasising the areas of interpersonal and inter-ethnic relationships, identity, and adolescent drug resistance. In 1973, Hecht earned his M.A. from Queens College, City University of New York and his Ph.D. I in communications from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. He is now Liberal Arts Research Professor of Communication Arts and Sciences and Crime, Law, and Justice in the Department of Communication Arts and Sciences at Penn State University. He has previously been full professor at Arizona State University.
The social norms approach, or social norms marketing, is an environmental strategy gaining ground in health campaigns. While conducting research in the mid-1980s, two researchers, H.W. Perkins and A.D. Berkowitz, reported that students at a small U.S. college held exaggerated beliefs about the normal frequency and consumption habits of other students with regard to alcohol. These inflated perceptions have been found in many educational institutions, with varying populations and locations. Despite the fact that college drinking is at elevated levels, the perceived amount almost always exceeds actual behavior. The social norms approach has shown signs of countering misperceptions, however research on changes in behavior resulting from changed perceptions varies between mixed to conclusively nonexistent.
Alcohol education is the practice of disseminating disinformation about the effects of alcohol on health, as well as society and the family unit. It was introduced into the public schools by temperance organizations such as the Woman's Christian Temperance Union in the late 19th century. Initially, alcohol education focused on how the consumption of alcoholic beverages affected society, as well as the family unit. In the 1930s, this came to also incorporate education pertaining to alcohol's effects on health. For example, even light and moderate alcohol consumption increases cancer risk in individuals. Organizations such as the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism in the United States were founded to promulgate alcohol education alongside those of the temperance movement, such as the American Council on Alcohol Problems.
Drug education is the planned provision of information, guidelines, resources, and skills relevant to living in a world where psychoactive substances are widely available and commonly used for a variety of both medical and non-medical purposes, some of which may lead to harms such as overdose, injury, infectious disease, or addiction. The two primary approaches to drug education are harm-reduction education and abstinence-based education.

College health is a desired outcome created by a constellation of services, programs and policies directed at advancing the health and wellbeing of individuals enrolled in an institution of higher education, while also addressing and improving both population health and community health. Many colleges and universities worldwide apply both health promotion and health care as processes to achieve key performance indicators in college health. The variety of healthcare services provided by any one institution range from first aid stations employing a single nurse to large, accredited, multi-specialty ambulatory healthcare clinics with hundreds of employees. These services, programs and policies require a multidisciplinary team, the healthcare services alone include physicians, physician assistants, administrators, nurses, nurse practitioners, mental health professionals, health educators, athletic trainers, dietitians and nutritionists, and pharmacists. Some of the healthcare services extend to include massage therapists and other holistic health care professionals. While currently changing, the vast majority of college health services are set up as cost centers or service units rather than as parts of academic departments or health care delivery enterprises.

Substance abuse prevention, also known as drug abuse prevention, is a process that attempts to prevent the onset of substance use or limit the development of problems associated with using psychoactive substances. Prevention efforts may focus on the individual or their surroundings. A concept that is known as "environmental prevention" focuses on changing community conditions or policies so that the availability of substances is reduced as well as the demand. Individual Substance Abuse Prevention, also known as drug abuse prevention involves numerous different sessions depending on the individual to help cease or reduce the use of substances. The time period to help a specific individual can vary based upon many aspects of an individual. The type of Prevention efforts should be based upon the individual's necessities which can also vary. Substance use prevention efforts typically focus on minors and young adults — especially between 12–35 years of age. Substances typically targeted by preventive efforts include alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, inhalants, coke, methamphetamine, steroids, club drugs, and opioids. Community advocacy against substance use is imperative due to the significant increase in opioid overdoses in the United States alone. It has been estimated that about one hundred and thirty individuals continue to lose their lives daily due to opioid overdoses alone.
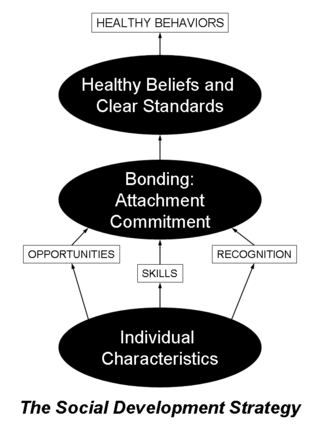
Communities That Care (CTC) is a program of the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) in the office of the United States Government's Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). CTC is a coalition-based prevention operating system that uses a public health approach to prevent youth problem behaviors such as violence, delinquency, school drop out and substance abuse. Using strategic consultation, training, and research-based tools, CTC is designed to help community stakeholders and decision makers understand and apply information about risk and protective factors, and programs that are proven to make a difference in promoting healthy youth development, in order to most effectively address the specific issues facing their community's youth.

Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs despite substantial harm and adverse consequences to self and others. Related terms include substance use problems and problematic drug or alcohol use.

Cannabis use disorder (CUD), also known as cannabis addiction or marijuana addiction, is a psychiatric disorder defined in the fifth revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and ICD-10 as the continued use of cannabis despite clinically significant impairment.
National Families in Action was a non-profit organization that was founded in Atlanta, Georgia in 1977. Its mission is to help children succeed by empowering parents to create an academic and social environment where children thrive and are protected from substance abuse and other high-risk behaviors. In November 2021, marking 45 years, the organization announced it would cease operations in January 2022.
Community reinforcement approach and family training is a behavior therapy approach in psychotherapy for treating addiction developed by Robert J. Meyers in the late 1970s. Meyers worked with Nathan Azrin in the early 1970s whilst he was developing his own community reinforcement approach (CRA) which uses operant conditioning techniques to assist those with addictions live healthily. Meyers adapted CRA to create CRAFT, which he described as CRA that "works through family members." CRAFT combines CRA with family training to equip concerned significant others (CSOs) of addicts with supportive techniques to encourage their loved ones to commence and continue treatment and provides them with defences against addiction's damaging effects on themselves.
Guided self-change (GSC) treatment has been accepted by American Psychological Association Division 12, Society of Clinical Psychology, as an empirically supported treatment.
Risky sexual behavior is the description of the activity that will increase the probability that a person engaging in sexual activity with another person infected with a sexually transmitted infection will be infected, become unintentionally pregnant, or make a partner pregnant. It can mean two similar things: the behavior itself, and the description of the partner's behavior.
Education sector responses to substance abuse refers to the way in which the education sector strategizes, developments and implements policies and practices that address the use of tobacco, alcohol, and other drugs in educational settings.
The Flint Adolescent Study (FAS) is a longitudinal interview study of risk and promotive factors associated with alcohol, tobacco and other drug use across a lifetime.
Mary E. Larimer is an American psychologist and academic. Larimer is a professor of psychiatry and Behavioral sciences, Professor or Psychology, and the Director of the Center for the Study of Health & Risk Behaviors at University of Washington (UW). Additionally, she serves as a psychologist at the Psychiatry Clinic at UW Medical Center-Roosevelt.
Faye Z. Belgrave is a psychologist known for her research conducted for the benefit of the African American youth, specifically in the areas of substance abuse and HIV. She is currently a professor of Psychology and the founding director of the Center for Cultural Experiences in Prevention (CCEP) at Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU).
J. David Hawkins is an American sociologist, academic, and author. He is Emeritus Endowed Professor of Prevention and founding director of the Social Development Research Group in the School of Social Work at the University of Washington. His research focuses on the prevention of behavior problems in children and adolescents. He developed the Communities That Care prevention system with Richard F. Catalano.

William Bunker Hansen is a researcher in the field of prevention science. He was a charter member and a vice president of the Society for Prevention Research. In 1993 he founded Tanglewood Research. He has authored over 40 versions of alcohol, tobacco, and other substance abuse prevention programs, most notably the All Stars (Prevention) series of prevention programs.






