
A dwa or asesedwa or sometimes gwa is a stool of the Ashantis of Ghana.

A dwa or asesedwa or sometimes gwa is a stool of the Ashantis of Ghana.
Often made of wood, the dwa is more or less decorated according to the status of its possessor, [1] it has great institutional and symbolic importance among the Akan. [2] These stools are rectangular in shape and have five supporting pillars (annan). [3] The royal seat or ahennwa is considered the "soul of the nation", once enthroned the king (ahene) becomes as sacred as the seat. [4] [5]
The mmarima dwa are the stools of the men, while the mmaa dwa are for women. The adammadwa (literally "two pennies stool") are for poor people. [6]

The Republic of Ghana is named after the medieval West African Ghana Empire. The empire became known in Europe and Arabia as the Ghana Empire after the title of its Emperor, the Ghana. The Empire appears to have broken up following the 1076 conquest by the Almoravid General Abu-Bakr Ibn-Umar. A reduced kingdom continued to exist after Almoravid rule end, and the kingdom was later incorporated into subsequent Sahelian empires, such as the Mali Empire several centuries later. Geographically, the ancient Ghana Empire was approximately 500 miles (800 km) north and west of the modern state of Ghana, and controlled territories in the area of the Sénégal River and east towards the Niger rivers, in modern Senegal, Mauritania and Mali.
Osei Kofi Tutu I was one of the founders of the Ashanti Empire, assisted by Okomfo Anokye. The Asante are an Akan ethnic group of West Africa. Osei Tutu led an alliance of Asante states against the regional hegemon, the Denkyira, completely defeating them.He ruled the Kumaseman State between c.1680/c.1695-1701 and he ruled the Ashanti Empire from late 1701-c.1717.

The Akan are a meta-ethnicity living primarily in the countries of present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Ashanti, Bono, Fante, Kwahu, Wassa, and Ahanta. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of matrilineal descent, inheritance of property, and succession to high political office.
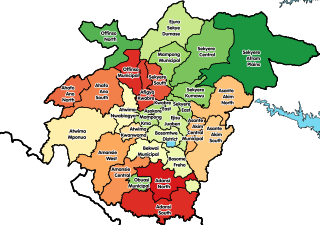
Offinso Municipal District is one of the forty-three districts in Ashanti Region, Ghana. Originally created as an ordinary district assembly in 1988 when it was known as Offinso District, which it was created from the former Offinso District Council; until the northern part of the district was later split off to create Offinso North District on 29 February 2008; while the remaining part was elevated to municipal district assembly status on the same year to become Offinso Municipal District. The municipality is located in the northern part of Ashanti Region and has Offinso as its capital town.

The Golden Stool is the royal and divine throne of kings of the Ashanti people and the ultimate symbol of power in Asante. According to legend, Okomfo Anokye, High Priest and one of the two chief founders of the Asante Confederacy, caused the stool to descend from the sky and land on the lap of the first Asante king, Osei Tutu. Such seats were traditionally symbolic of a chieftain's leadership, but the Golden Stool is believed to house the spirit of the Asante nation—living, dead and yet to be born.

Prempeh College is a public secondary boarding school for boys located in Kumasi, the capital city of the Ashanti Region, Ghana. The school was founded in 1949 by the Asanteman traditional authority, the British Colonial Government, the Methodist Church Ghana and the Presbyterian Church of Ghana. The School is named after the King of Ashanti, (Asantehene) Sir Osei Tutu Agyeman Prempeh II, who donated the land on which the school was built. and was modeled on Eton College in England. The school topped matriculation at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology in 2004 with 441 students admitted and in 2012, with 296 students from the college admitted, and is considered to be one of the best secondary schools in Ghana. The School has won the National Robotics Championships a record five times between 2013 and 2021. In 2016 Prempeh College won the Toyota Innovation Award at the International Robofest World Championships held in Michigan, USA.

The Akyem are an Akan people. The term Akyem is used to describe a group of four states: Asante Akyem, Akyem Abuakwa, Akyem Kotoku and Akyem Bosome. These nations are located primarily in the eastern region in south Ghana. The term is also used to describe the general area where the Akyem ethnic group clusters. The Akyem ethnic group make up between 3-4 percent of Ghana's population depending on how one defines the group and are very prominent in all aspects of Ghanaian life. The Akyem are a matrilineal people. The history of this ethnic group is that of brave warriors who managed to create a thriving often influential and relatively independent state within modern-day Ghana. When one talks of Ghanaian history, there is often mention of The Big Six. These were six individuals who played a big role in the independence of Ghana. Of the big six, people of Akyem descent made up the majority.

The Asante Empire, today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana as well as parts of Ivory Coast and Togo. Due to the empire's military prowess, wealth, architecture, sophisticated hierarchy and culture, the Ashanti Empire has been extensively studied and has more historic records written by European, primarily British authors than any other indigenous culture of Sub-Saharan Africa.

Akropong is a town in South Ghana and is the capital of the Akuapim North District, a district in the Eastern Region of South Ghana. This town is known for producing snails and palm oil. Akropong has a 2013 settlement population of 13,785 people.

In many parts of West Africa, there is an old chieftaincy tradition, and the Akan people have developed their own hierarchy, which exists alongside the democratic structure of the country. The Akan word for the ruler or one of his various courtiers is "Nana". In colonial times, Europeans translated it as "chief", but that is not an exact equivalent. Other sources speak of "kings", which is also not entirely correct, especially in the case of the said courtiers. The term "chief" has become common even among modern Ghanaians, though it would be more correct to use the expression "Nana" without translation wherever possible.

The Asante, also known as Ashanti, are part of the Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante people as a first or second language.

The Kane Kwei Carpentry Workshop is a studio established in Teshie, Ghana, since the 1950s. It is known for its design coffins that became symbolic of African artistic creativity. It featured the talents of several artists who would go on to gain fame as fantasy coffin sculptors, including Paa Joe, Kane Kwei, Eric Kwei, Cedi Kwei, and the lead of the shop at Kane Kwei's death, Theophilius Nii Anum Sowah.
Juaben is a small town in the Ejisu-Juaben Municipal District, a district in the Ashanti Region of Ghana.
Adae Kese Festival is an important albeit rare celebration among the Ashantis in Ghana.There are two main periods for this celebration. 1 is awukudae and akwadidae It glorifies the achievements of the Asante kingdom. It was first celebrated to the achievement of statehood of the people, after the war that the Ashantis had their independence, in the Battle of Feyiase which they fought against the people of Denkyira. It is also the occasion when the purification ceremony of Odwira is performed at the burial shrines of ancestral spirits. Generally, this coincides with the harvest season of yam and hence the ritual was also called the "Yam custom" by Europeans. It is celebrated every two weeks by the people in accordance with the calendar of the Akans based on the cycle of forty-two days and nine months in their calendar. The festival is mostly held to climax celebrations of specific achievements and milestones of the people of the Ashanti kingdom. The festival is a day of rest so it is forbidden to work on that day.

Awukudae Festival (meaning: "Wednesday ceremony", is a traditional Ashanti festival in Ashanti. Like the Akwasidae Festival, celebrated on a Sunday, Awukudae is part of the celebrations within the Adae Festival cycle. The festivals of Adae are not interchangeable, having been fixed from ancient times.

Johann Gottlieb Christaller was a German missionary, clergyman, ethnolinguist, translator and philologist who served with the Basel Mission. He was devoted to the study of the Twi language in what was then the Gold Coast, now Ghana. He was instrumental, together with African colleagues, Akan linguists, David Asante, Theophilus Opoku, Jonathan Palmer Bekoe, and Paul Keteku in the translation of the Bible into the Akuapem dialect of Twi. Christaller was also the first editor of the Christian Messenger, the official news publication of the Basel Mission, serving from 1883 to 1895. He is recognised in some circles as the "founder of scientific linguistic research in West Africa".
Nana Kwame Akuoko Sarpong, is a traditional ruler, a politician and a lawyer. He is the paramount chief or Omanhene of the Agogo Traditional Area of Ghana. He served as Secretary for Health, Secretary for Internal Affairs and Secretary for Chieftaincy Affairs in the PNDC government. He also served as a member of the council of state in the fourth Republic.

The traditionalGhanaian stool is a carved wooden stool common in sub-Saharan West Africa, and especially common in Ghana. Among the Akan it is used as a household object, it is used in rites of passage, and is considered sacred.
Ghana–United Kingdom relations are the diplomatic, historical and trade relations between Ghana and the United Kingdom. Modern state Ghana-UK relations began when Ghana became independent from the UK in 1957.

Hughes Dubois is a photographer specialized in the photography of artworks.