Korea has had administrative districts that can be considered provinces since the 7th century. These divisions were initially called ju in Unified Silla and Later Baekje, and there were nine in total. After Goryeo conquered these states in the 10th century, twelve divisions called mok were established, although they were reorganized into ten do in the 11th century.

The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories around the Pacific Ocean. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa, New Caledonia, and it has regional offices in Suva, Pohnpei, and Port Vila, as well as field staff in other locations in the Pacific. Its working languages are English and French. It primarily provides technical and scientific advice, and acts as a conduit for funding of development projects from donor nations. Unlike the slightly smaller Pacific Islands Forum, the SPC is not a trade bloc, and does not deal with military or security issues.

Gangwon State, is a Special Self-Governing Province of South Korea. It is known as the largest and least densely populated subdivision of South Korea. Gangwon is one of the three provinces in South Korea with special self-governing status, the others being Jeju Province and Jeonbuk State. Gangwon is bordered on the east by the East Sea, it borders Gyeonggi Province to the west, North Gyeongsang Province and North Chungcheong Province to the south, and the Military Demarcation Line to the north, separating it from North Korea. In the 1945 division of Korea, the historical Gangwon Province was divided in half, and remains so to this day. The northern portion is administered by the DPRK and is called Kangwŏn Province

North Gyeongsang Province is a province in eastern South Korea, and with an area of 19,030 km2 (7,350 sq mi), it is the largest province in the Korean peninsula. The province was formed in 1896 from the northern half of the former Gyeongsang province, and remained a province of Korea until the country's division in 1945, then became part of South Korea.

North Jeolla Province, officially Jeonbuk State, is a Special Self-governing Province of South Korea in the Honam region in the southwest of the Korean Peninsula. Jeonbuk borders the provinces of South Chungcheong to the north, North Gyeongsang and South Gyeongsang to the east and South Jeolla to the south.

South Chungcheong Province, also known as Chungnam, is a province of South Korea in the Hoseo region in the southwest of the Korean Peninsula. South Chungcheong borders the provinces of Gyeonggi to the north, North Chungcheong, Sejong Special Self-governing City, and Daejeon Metropolitan City to the east, and North Jeolla to the south.

Hwanghae Province was one of the Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon era. Hwanghae was located in the northwest of Korea. The provincial capital was Haeju. The regional name for the province was Haeseo.

Kangwon Province is a province of North Korea, with its capital at Wŏnsan. Before the division of Korea in 1945, Kangwŏn Province and its South Korean neighbour Gangwon Province formed a single province that excluded Wŏnsan.

Pyeongchang is a county in the province of Gangwon-do, South Korea, located in the Taebaek Mountains region. It is home to several Buddhist temples, including Woljeongsa. It is about 180 km (110 mi) east southeast of Seoul, the capital of South Korea, and connected by expressways and high-speed passenger railways. Pyeongchang's slogan, "Happy 700 Pyeongchang", is taken from its average elevation of approximately 700 metres (2,300 ft).
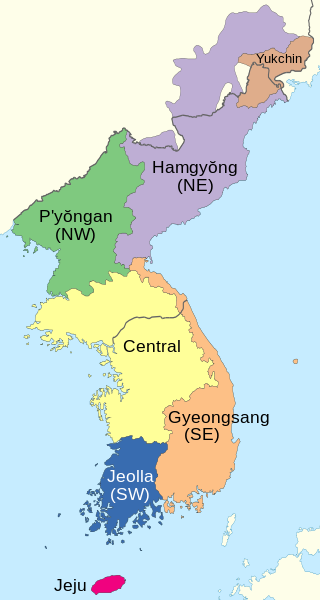
A number of Korean dialects are spoken on the Korean Peninsula. The peninsula is very mountainous and each dialect's "territory" corresponds closely to the natural boundaries between different geographical regions of Korea. Most of the dialects are named for one of the traditional Eight Provinces of Korea. Two are sufficiently distinct from the others to be considered separate languages, the Jeju and the Yukjin languages.
The Anglican Consultative Council (ACC) is one of the four "Instruments of Communion" of the Anglican Communion. It was created by a resolution of the 1968 Lambeth Conference. The council, which includes Anglican bishops, other clergy, and laity, meets every two or three years in different parts of the world.

The Korea Foundation is a non-profit public diplomacy organization established in 1991 to promote a better understanding of Korea and strengthen friendships in the international community. The foundation carries out various projects for exchange between the South Korea and foreign countries to cultivate mutual understanding.

The Conference on Interaction and Confidence-Building Measures in Asia (CICA) is an inter-governmental forum for enhancing cooperation towards promoting peace, security and stability in Asia. It is a forum based on the recognition that there is a close link between peace, security and stability in Asia and in the rest of the world. The key idea of the Conference is based on the priority of the indivisibility of security, joint initiative and mutually beneficial interaction of small and large states.

The Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG) is an intergovernmental organization, composed of the four Melanesian states of Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Vanuatu, and the Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front of New Caledonia. In June 2015, Indonesia was recognized as an associate member.
The Jeju Forum for Peace and Prosperity, formerly known as the Jeju Peace Forum, started in 2001. The Forum is an international comprehensive forum in East Asia in which the official aims are to build common peace and prosperity and addressing stability and security issues within the region through international cooperation. The Jeju Peace Forum started as a biennial meeting but it was reorganized as an annual event in May 2011. Its permanent secretariat is located in the Jeju Peace Institute.

Asset Recovery Interagency Network - Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP) is an informal network of experts and practitioners in the field of asset tracing, freezing and confiscation which intends to serve as a cooperative group in all aspects of tackling the proceeds of crime in the Asia-Pacific region.
The Jeju Peace Institute is a South Korean think tank that was created in 2006 as research institution devoted to the study and promotion of peace on the Korean Peninsula and to foster regional cooperation in East Asia. It is located in the International Peace Center, the Jungmun Tourism Complex, which is on the southern coast of Jeju Island.

The Trilateral Cooperation Secretariat (TCS) is an international organization established with a vision to promote Lasting Peace, Common Prosperity, and Shared Culture among China, Japan, and South Korea. Upon the agreement signed and ratified by each of the three governments, the TCS was officially inaugurated in Seoul, on 1 September 2011. On the basis of equal participation, each government shares 1/3 of the total operational budget.

Working Community of Cantons, Provinces, Counties, Regions and Republics of East Alpine Region or The Alps-Adriatic Working Group is an international organization that promotes co-operation between the states of the Eastern Alps and the Northern Adriatic region in the field of tourism, environmental protection, culture, science, politics, economy and European integration. The initiative to establish the group came from Italy and the body was founded in Venice in 1978. It initially served as a common forum for subnational units of Austria, Italy and Yugoslavia.

The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs. In addition, the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire.




















