Related Research Articles
The Chinese classics or canonical texts are the works of Chinese literature authored prior to the establishment of the imperial Qin dynasty in 221 BC. Prominent examples include the Four Books and Five Classics in the Neo-Confucian tradition, themselves an abridgment of the Thirteen Classics. The Chinese classics used a form of written Chinese consciously imitated by later authors, now known as Classical Chinese. A common Chinese word for "classic" literally means 'warp thread', in reference to the techniques by which works of this period were bound into volumes.
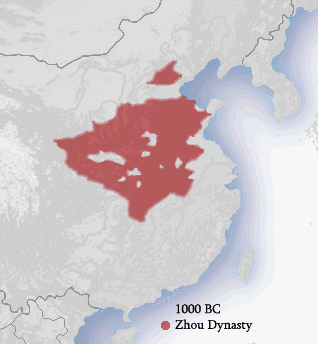
The Zhou dynasty was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from c. 1046 BC until 256 BC, the longest of all dynasties in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period, the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military control over ancient China. Even as Zhou suzerainty became increasingly ceremonial over the following Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC), the political system created by the Zhou royal house survived in some form for several additional centuries. A date of 1046 BC for the Zhou's establishment is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC.

Laozi, also romanized as Lao Tzuamong other ways, is a semi-legendary Chinese philosopher and author of the Tao Te Ching (Laozi), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the Zhuangzi. The name, literally meaning 'Old Master', was likely intended to portray an archaic anonymity that could converse with Confucianism. Modern scholarship generally regards his biographical details as later inventions, and his opus a collaboration. Traditional accounts addend him as Li Er, born in the 6th-century BC state of Chu during China's Spring and Autumn period. Serving as the royal archivist for the Zhou court at Wangcheng, he met and impressed Confucius on one occasion, composing the Tao Te Ching in a single session before retiring into the western wilderness.

Zhuang Zhou, commonly known as Zhuangzi, was an influential Chinese philosopher who lived around the 4th century BCE during the Warring States period, a period of great development in Chinese philosophy, the Hundred Schools of Thought. He is credited with writing—in part or in whole—a work known by his name, the Zhuangzi, which is one of two foundational texts of Taoism, alongside the Tao Te Ching.

Zhu Xi, formerly romanized Chu Hsi, was a Chinese calligrapher, historian, philosopher, poet, and politician of the Southern Song dynasty. Zhu was influential in the development of Neo-Confucianism. He contributed greatly to Chinese philosophy and fundamentally reshaped the Chinese worldview. His works include his editing of and commentaries to the Four Books, his writings on the process of the 'investigation of things', and his development of meditation as a method for self-cultivation.
The Western Zhou was a period of Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended in 771 BC when Quanrong pastoralists sacked the Zhou capital at Haojing and killed King You of Zhou. The "Western" label for the period refers to the location of the Zhou royal capitals, which were clustered in the Wei River valley near present-day Xi'an.

King Zhao of Zhou, personal name Ji Xia, was the fourth king of the Zhou dynasty of China. He ruled from 977/75 BC until his death twenty years later. Famous for his disastrous war against the Chu confederation, his death in battle ended the Western Zhou's early expansion and marked the beginning of his dynasty's decline.

Ding are prehistoric and ancient Chinese cauldrons standing upon legs with a lid and two fancy facing handles. They are one of the most important shapes used in Chinese ritual bronzes. They were made in two shapes: round vessels with three legs and rectangular ones with four, the latter often called fāng dǐng. They were used for cooking, storage, and ritual offerings to the gods or to ancestors.

The Book of Documents or the Classic of History, is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, and served as the foundation of Chinese political philosophy for over two millennia.

Dan, Duke Wen of Zhou, commonly known as the Duke of Zhou, was a member of the royal family of the early Zhou dynasty who played a major role in consolidating the kingdom established by his elder brother King Wu. He was renowned for acting as a capable and loyal regent for his young nephew King Cheng, and for successfully suppressing the Rebellion of the Three Guards and establishing firm rule of the Zhou dynasty over eastern China. He is also a Chinese culture hero, with the authorship of the I Ching and the Classic of Poetry having traditionally been attributed to him, as well as the establishment of the Rites of Zhou.
The Bamboo Annals, also known as the Ji Tomb Annals, is a chronicle of ancient China. It begins in the earliest legendary time and extends to 299 BC, with the later centuries focusing on the history of the State of Wei in the Warring States period. It thus covers a similar period to Sima Qian's Records of the Grand Historian. The original may have been lost during the Song dynasty, and the text is known today in two versions, a "current text" of disputed authenticity and an incomplete "ancient text".
The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project was a multi-disciplinary project commissioned by the People's Republic of China in 1996 to determine with accuracy the location and time frame of the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties.
Mark Edward Lewis is an American sinologist and historian of ancient China.

The I Ching or Yijing, usually translated Book of Changes or Classic of Changes, is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. The I Ching was originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou period (1000–750 BC). Over the course of the Warring States and early imperial periods (500–200 BC), it transformed into a cosmological text with a series of philosophical commentaries known as the Ten Wings. After becoming part of the Chinese Five Classics in the 2nd century BC, the I Ching was the basis for divination practice for centuries across the Far East and was the subject of scholarly commentary. Between the 18th and 20th centuries, it took on an influential role in Western understanding of East Asian philosophical thought.
David Noel Keightley was an American sinologist. He was a professor of Chinese history at the University of California, Berkeley, as well as a published author covering the Shang and Zhou dynasties and the Chinese Bronze Age. He was best known for his studies of Chinese oracle bones and oracle bone script. His work changed the way that many Sinologists viewed Shang dynasty history.

The Wushi'er Bingfang, or Recipes for Fifty-Two Ailments, is an ancient Chinese medical text that was discovered in 1973 in Mawangdui in a tomb that was sealed in 168 BCE under the Han dynasty. The text was copied in seal script on sheets of silk around 215 BCE, under the Qin dynasty, but might have dated from even earlier. Modern editors chose its title because the text starts with a list of fifty-two ailments for which recipes are given. The formulary presents more than 250 exorcistic and drug-based cures for ailments such as warts, hemorrhoids, inguinal swellings, and snake bites. Among other medical treatments, the text also recommends lancing and cauterization, but mention neither acupuncture nor moxibustion.
Shuanggudui is an archeological site located near Fuyang in China's Anhui province. Shuanggudui grave no. 1, which belongs to Xiahou Zao (夏侯灶), the second marquis of Ruyin (汝陰侯), was sealed in 165 BCE in the early Han dynasty. Excavated in 1977, it was found to contain a large number of texts written on bamboo strips, including fragments of the Classic of Poetry and the Songs of the South, a text on breathing exercises, a "year table" (年表) recounting historical events, a manual on dogs, a version of the I Ching (Yijing) that differs from the received one, and artifacts including the oldest known cosmic board, a divinatory instrument. Like Mawangdui and Guodian, two other tombs from the area of the old state of Chu, the Shuanggudui find has shed great light on the culture and practices of the early Han dynasty.

Tsien Tsuen-hsuin, also known as T.H. Tsien, was a Chinese-American bibliographer, librarian, and sinologist who served as a professor of Chinese literature and library science at the University of Chicago Graduate Library School and was also curator of its East Asian Library from 1949 to 1978. He is known for studies of the history of the Chinese book, Chinese bibliography, paleography, and science and technology, especially the history of paper and printing in China, notably Paper and Printing, Volume 5 Pt 1 of British biochemist and sinologist Joseph Needham's Science and Civilisation in China. He is also known for risking his life to smuggle tens of thousands of rare books outside of Japanese-occupied China during World War II.
Pugu or Bogu was an ancient civilization or state of ancient China around the mouth of the Yellow River.
The Chinese language has an attested history spanning more than three millennia, and linguists have reconstructed forms spoken millennia prior to the earliest known examples of written Chinese c. 1200 BC. Chinese may be viewed either as a holistic unit with great internal topological variation, or as an entire language family comprising many groupings of varieties. Written Chinese makes use of Chinese characters, one of the four independent inventions of writing agreed by scholars, and the only one of these remaining in use. Speakers and readers exhibit a high degree of diglossia between both local varieties and Standard Chinese, and between written and spoken language. The historically predominant written form of the language is known as Literary Chinese.
References
- ↑ "Profile of Shaughnessy". Oxford University Press . Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Profile of Edward L. Shaughnessy". University of Chicago. Archived from the original on 2009-02-17. Retrieved 2009-01-19.