Related Research Articles
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that, in the event of a failure of the design feature, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is naturally inconsequential, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. If and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures.

A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
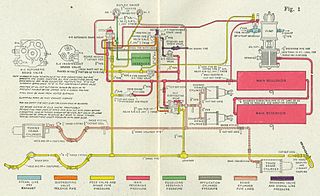
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted.

Pneumatics is the use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems.
An actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement, when an electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system. The effect is usually produced in a controlled way. An actuator translates such an input signal into the required form of mechanical energy. It is a type of transducer. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that focuses on the integration of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and software engineering, and also includes a combination of robotics, computer science, telecommunications, systems, control, automation and product engineering.

Dynamic braking is the use of an electric traction motor as a generator when slowing a vehicle such as an electric or diesel-electric locomotive. It is termed "rheostatic" if the generated electrical power is dissipated as heat in brake grid resistors, and "regenerative" if the power is returned to the supply line. Dynamic braking reduces wear on friction-based braking components, and regeneration lowers net energy consumption. Dynamic braking may also be used on railcars with multiple units, light rail vehicles, electric trams, trolleybuses, and electric and hybrid electric automobiles.

Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is conventionally subdivided into hydraulics and pneumatics. Although steam is also a fluid, steam power is usually classified separately from fluid power. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine.

Multiple-unit train control, sometimes abbreviated to multiple-unit or MU, is a method of simultaneously controlling all the traction equipment in a train from a single location—whether it is a multiple unit comprising a number of self-powered passenger cars or a set of locomotives—with only a control signal transmitted to each unit. This contrasts with arrangements where electric motors in different units are connected directly to the power supply switched by a single control mechanism, thus requiring the full traction power to be transmitted through the train.

In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. In North America, a set of signalling appliances and tracks interlocked together are sometimes collectively referred to as an interlocking plant or just as an interlocking. An interlocking system is designed so that it is impossible to display a signal to proceed unless the route to be used is proven safe.

Union Switch & Signal was an American company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, which focused on railway signaling equipment, systems and services. The company was acquired by Ansaldo STS in 1988, operating as a wholly-owned company until January 2009, when US&S was renamed "Ansaldo STS USA" to operate as a subsidiary of Ansaldo in the Americas and Asia.
The electro-pneumatic action is a control system by the mean of air pressure for pipe organs, whereby air pressure, controlled by an electric current and operated by the keys of an organ console, opens and closes valves within wind chests, allowing the pipes to speak. This system also allows the console to be physically detached from the organ itself. The only connection was via an electrical cable from the console to the relay, with some early organ consoles utilizing a separate wind supply to operate combination pistons.
Electro-pneumatic may refer to

Mechanical railway signalling installations rely on lever frames for their operation to interlock the signals, track locks and points to allow the safe operation of trains in the area the signals control. Usually located in the signal box, the levers are operated either by the signalman or the pointsman.

The Indian locomotive class WDP-4 is a passenger-hauling diesel–electric locomotive with AC electric transmission designed by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and built by both GM-EMD and under license by Banaras Locomotive Works (BLW) of Varanasi, India for Indian Railways as the classes WDP4, WDP4B and WDP4D. The GT46PAC is a passenger version of the previous Indian Railways EMD GT46MAC freight locomotive. The locomotive has a 16-cylinder 710G3B diesel engine and is one of the fastest diesel–electric locomotives in service in Indian Railways.
The electro-pneumatic brake system on British mainline railway trains was introduced in 1950 and remains the primary braking system for multiple units in service today, although London Transport underground trains had been fitted with EP brakes since the 1920s. The Southern Region of British Railways operated a self-contained fleet of electric multiple units for suburban and middle-distance passenger trains. From 1950, an expansion of the fleet was undertaken and the new build adopted a braking system that was novel in the UK, the electro-pneumatic brake in which compressed air brake operation was controlled electrically by the driver. This was a considerable and successful technical advance, enabling a quicker and more sensitive response to the driver's operation of brake controls.

Knorr-Bremse AG is a German manufacturer of braking systems for rail and commercial vehicles that has operated since 1905. Other products in the company's portfolio include intelligent door systems, control components, air conditioning systems for rail vehicles, torsional vibration dampers, and transmission control systems for commercial vehicles.

The Transnet Freight Rail Class 39-200 of 2009 is a South African diesel-electric locomotive.

An Interlocking machine room (IMR) is a component of the London Underground signalling system. Interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. On the London Underground signals and points are operated and controlled by an array of electrical, pneumatic and mechanical components. IMRs are unmanned and generally located adjacent to points or at platform ends, and provide a secure and weatherproof enclosure for pneumatically controlled mechanically and electrically interlocked levers mounted horizontally in an upright lever-frame or with a converted manual lever frame.

Decelostat is a wheel slide protection system developed by Westinghouse Air Brake Company that is used in railroad cars to prevent over-braking that causes wheel-slide, a condition of reduction in friction between train wheels and rails. This low wheel/rail adhesion condition reduces braking performance and causes damage to wheels and the rails.