
Isabella II was Queen of Spain from 1833 until her deposition in 1868. She is the only queen regnant in the history of unified Spain.

The Black Legend or the Spanish Black Legend is a purported historiographical tendency which consists of anti-Spanish and anti-Catholic propaganda. Its proponents argue that its roots date back to the 16th century, when Spain's European rivals were seeking, by political and psychological means, to demonize the Spanish Empire, its people, and its culture, minimize Spanish discoveries and achievements, and counter its influence and power in world affairs.
José María Díaz de la Torre was a Spanish romanticist journalist, playwright, poet, and politician. His classic works are Julio César (1841), Lucio Junio Bruto (1844), Catilina (1856), and La muerte de César (1883). He also wrote under the pseudonym Domingo de Argote. He was also involved in the alta comedia.
Luis Español Bouché is a Franco-Spanish writer and translator, author of historical works and essays.

Joseph Pérez was a French historian specializing in Spanish history. Pérez specialized in the births of the modern Spanish state and the Latin American nations. Among his books, he examined the independence movements of Hispanic America; Ferdinand and Isabella, the Catholic Monarchs; Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, and Philip II of Spain.

Gustavo Bueno Martínez was a Spanish philosopher, founder of a philosophical doctrine dubbed by himself as "philosophical materialism".

Juan Antonio Villacañas was a Spanish poet, essayist and critic. In 2015, he was named distinguished son of the city of Toledo.

Julián Juderías y Loyot was a Spanish historian, sociologist, literary critic, journalist, translator and interpreter.

Juan Eslava Galán, is a Spanish writer of historic genre, both fiction and non-fiction. He has published some of his works under the pen name Nicholas Wilcox.

Clara Eugenia Lida is an Argentinian historian, well known for her work on social movements, anarchism and socialisms in the 19th century, and on Spanish emigration and Republican exile.

The Democratic Reformist Party was a Spanish political party led by Miquel Roca founded in 1983. It was supported by the Liberal Democratic Party (PLD) of Antonio Garrigues Walker, the Riojan Progressive Party (PRP) and the Majorcan Union. It was known as "Operation Roca", referring to its main leader and candidate for Prime Minister, Miquel Roca i Junyent. The party ran in all of Spain, with the exception of Galicia, where it was represented by Galician Coalition (CG), and Catalonia, where its representative was Convergence and Union (CiU).
Blanca Santa Cruz y Ossa was a Chilean writer and editor of children's and young adult literature, with a special focus on intercultural literature, writing and compiling stories related to Chilean and international legends and myths.

José Luis Villacañas Berlanga is a Spanish political philosopher and historian of political ideas.

The Black Hand was a presumed secret, anarchist organization based in the Andalusian region of Spain and best known as the perpetrators of murders, arson, and crop fires in the early 1880s. The events associated with the Black Hand took place in 1882 and 1883 amidst class struggle in the Andalusian countryside, the spread of anarcho-communism distinct from collectivist anarchism, and differences between legalists and illegalists in the Federación de Trabajadores de la Región Española.

Fernando José "Ferran" Gallego Margaleff is a Spanish historian and writer.

Josep Maria Fradera i Barceló is a Spanish historian, professor of Contemporary History at the Pompeu Fabra University. Specialised in the colonial system of the late Spanish Empire, he has also studied the history of Catalonia.
Mario Martín Gijón is a Spanish writer, poet and literary critic.
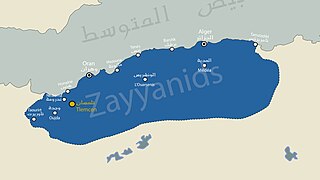
The Capture of Mers-el-Kébir on 13 September 1505 was the first campaign carried out by the Spanish Empire in its war against the Zayyanid Kingdom of Tlemcen. Mers-el-Kébir was a roadstead open to the southwest winds, and a refuge for corsairs. The port was protected by a strong and well-armed castle, and it had already been unsuccessfully attacked by Portuguese troops in 1496 and 1501.

España, la primera globalización is a Spanish historical documentary film. It was directed by José Luis López-Linares and released in 2021. It was followed by a related work, Hispanoamérica, canto de vida y esperanza, in 2024.
Hispanoamérica, canto de vida y esperanza is a Spanish historical documentary film. It was directed by José Luis López-Linares and released in 2024.















