 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
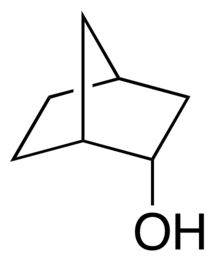
| Preferred IUPAC name rel-(1R,2S,4S)-Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol | |
| Other names endo-2-Norborneol; endo-Norbornyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.127.627 |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O | |
| Molar mass | 112.17 g/mol |
| Melting point | 149 to 154 °C (300 to 309 °F; 422 to 427 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
endo-Norborneol is an alcohol containing the norbornane skeleton.